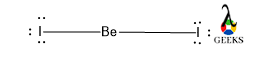In this article we will discuss about Dibromine,Br2 its lewis structure, properties and other facts.
Dibromine, Br2 consists of two bromine atoms joined through a single bond. Bromine is one of the lightest element in halogen family. Dibromine is a reddish brown liquid with a pungent smell which is very toxic for inhalation.
How to draw Br2 lewis structures ?
Lewis structure of a molecule is mainly drawn to understand how the bond formation takes place when two atoms or more got united. The lewis structure of a compound is drawn by considering only the valence electrons present in the outermost shell. It uses dots and lines to depict electrons and bonds respectively.
So the structures drawn by this concept are called lewis dot structures.
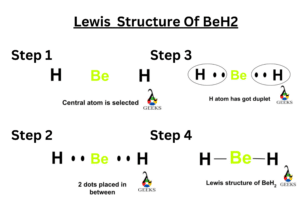
Lewis dot structures can be drawn for both covalently bonded and ionic bonded compounds. Dibromine,Br2 is chemical compound with two bromine atoms combined together. Let’s see how to draw the lewis structure of Br2.
- Calculate the total number of valence electrons. Bromine is a group 7 element having seven electrons in its valence shell. Since dibromine has two bromine atoms the total number of valence electrons present in Br2 is 7×2 = 14 electrons.
- In this step we draw the symbols for two bromine atoms surrounding with their seven valence electrons.

- In the next step the two bromine atoms shares their one electron each other to form a single bond. Now both the bromine atoms are combined together and they attained stability by satisfying octet rule.

Br2 resonance
Resonance can be defined as the movement or the delocalistion of electrons present in an atom of any compound. Resonance can only seen in compounds with double bonds and the electrons involved with these bonds are easy to move across the bonds.
While drawing the resonance structure the actual properties like the number of electrons present around the atom shouldn’t change. Even though there is double bond in dibromine it is not allowed to move across, because if they do so the molecular structure not exist. So there is no resonance structure for dibromine.
Br2 Shape
Dibromine is a linear shaped molecule with one bromine – bromine sigma bonds. Br2 is symmetrical in its structure.

Br2 Formal charge
Formal charge is a charge assigned to an atom when it is get combined with other atoms to form a stable compound. The formal charge assigned to an atom can be easily found out by the below equation
Formal charge of an atom = ( Valence electrons – No. of lone pairs – No. of bonds formed)
Valence electrons present in bromine is 7. In which 6 were lone pairs and one electron is shared to make bond with another bromine atom
Formal charge of bromine is = 7-6-1
= 0
So the formal charge of bromine in Dibromine, Br2 is 0.
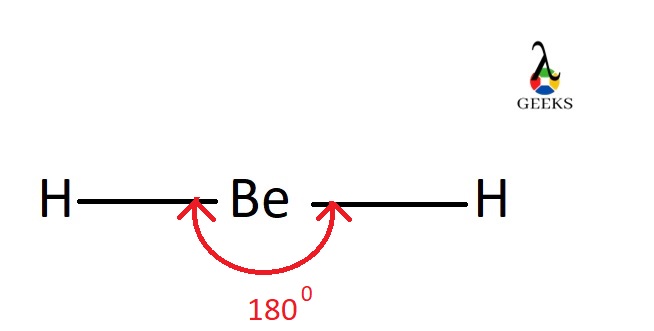
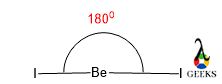
Br2 Bond angle
Bond angle is the angle made between three atoms when they combine together to form a stable compound. Dibromine is a linear or symmetrical molecule with one Br- Br sigma bonds. The bond angle made by a linear molecule is 1800. So the bond angle of Br2 is 1800.

Br2 Octet rule
According to octet rule, when atoms combine together to form compounds they are found to be more stable when their outermost shell are filled with eight electrons. Atoms lose or gain electrons to obey the octet rule. In the case of dibromine there is two bromine atoms.
Each bromine has seven electrons in its valence shell. It need one more electron to attain stability. When these two atoms combines together both of them shares their electrons to each other. Hence their valence shell is filled with eight electrons and they are stable now. Since both of the bromine atom has eight electrons in its valence shell Dibromine obeys octet rule.
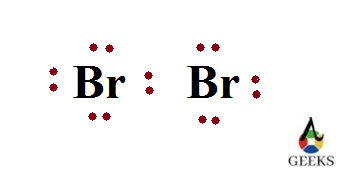
Br2 Lone pair of electrons
Lone pair of electron or non bonding electrons are the electrons present in the valence shell of an atom which doesn’t took participation in bond formation. Since they doesn’t form bonds they can be called as non bonding electrons.
The lone pair of electrons in one bromine is 3. So the total number of lone pair of electrons present in two bromine atoms of dibromine 6.

Br2 valence electrons
The electrons present in the valence shell or the outermost shell of an atom is called as its valence electrons.
Total number of valence electrons present in dibromine is 14.
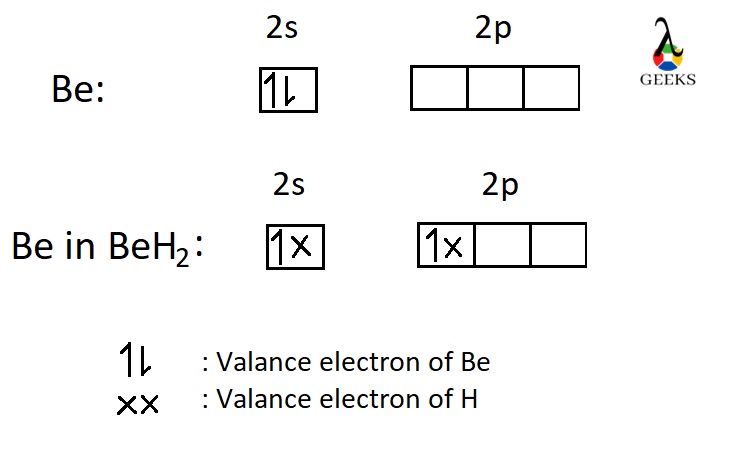
Br2 Hybridisation
According to the concept of hybridisation, the atomic orbitals with slightly different energies unites together to form atomic orbitals with same energy and shape. The new orbitals formed are stable and named as hybrid orbitals. The number of hybrid orbitals is equal to that of the orbitals got united.
There is different types of hybridisation called
- sp3
- sp2
- sp
- sp3d
- sp3d2
- sp3d3
Hybridisation of a molecule can be found through a formula, which is
Hybridisation of a molecule = No. of sigma bonds + No. of lone pairs
If the count is 4 then sp3 hybridisation ,3 then sp2 and if 2 then sp.
In dibromine there is one sigma bond and three lone pair of electrons.
Hybridisation of Br2 = 1+3 = 4
So the hybridisation in dibromine is sp3. Its structure is linear.
Br2 Solubility
Solubility can be defined as the ability of a substance or solute to get dissolved in a solvent to form a solution. The most commonly used solvents in field of chemistry is water, ethanol, acetone, ether, benzene, chloroform etc.
Dibromine is slightly soluble in water because it is not a polar molecule like water. But dibromine is found to be soluble in most of the organic solvents like benzene, gasoline, chloroform, ether, methanol, ethanol, carbon disulphide, carbon tetra chloride,CCl4.
Is Br2 Ionic or not ?
A covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between the combining atoms but ionic bond formation takes place through the electrostatic force of attraction between a positive and negative ion. The positive and negative ions are cation and anion respectively.
Dibromine is formed by the mutual sharing electrons between two bromine atoms. So Br2 is a covalent compound not an ionic compound.
Is Br2 Polar or not ?
There are only two bromine atoms are attached together through a single bond in dibromine. So it is non polar in nature.
Is Br2 Acidic or Basic ?
Dibromine is a lewis acid. A lewis acid is a substance which can accepts electrons.
Summary
Dibromine is a chemical compound which exists as liquid and gas in room temperature. This article summarise the following key points
- Dibromine is a covalent compound with non polar character.
- Dibromine shows acidic behaviour.
- Br2 follows sp3 hybridisation.
- It is soluble in organic solvents and sparingly soluble in water.
- Its lewis structure drawing pattern.
Also Read: