Zn2+ derived from atom zinc has an atomic number of 30 with a molecular mass of 65 g/mol Let see what is zn2+ and how it is formed as given below.
Zn2+ is an inorganic ion which carries a 2+ charge on it. Zn2+ has come from its principal atom ie. the zinc atom. Zinc when loses its 2 electrons and then converted into zn2+ ion. Like zn, zn2+ shared all the physical characteristics of the zinc atom.
Let us learn how to draw the lewis structure for zn2+ and calculate the formal charge, shape and other important aspects of the zn2+ ion.
How to draw zn2+ lewis structure?
Zn2+ is a monovalent inorganic ion. Let us draw the lewis structure for zn2+by following the below given rules.
Mark the charges on Zn2+
Zn2+ is not a neutral molecule but instead a charged molecule. The +2 charge on the zinc atom indicates that it has lost two electrons. Hence +2 is the charge carried by the zinc atom.
Count the valence count for Zn2+
Zinc has electronic configuration of [Ar] 3d¹⁰4s² whereas for zn2+ , electronic configuration corresponds to [Ar] 3d¹⁰4s0. Hence valence electron count for zn2+ is 10.
Drawing of Zn2+ lewis structure
Zn2+ lewis structure is the same as its structural formula ie. Zn2+. This is due to the reason that valence electrons present in the outer d orbitals of Zn2+ are completely fulfilled and do not participate in bonding. Hence there is no need for the lewis dot for the Zn2+ lewis structure.

Zn2+ lewis structure resonance
Generally, resonating structures add more stability due to the movement of electrons within the molecule. The possible resonating structures for the zn2+ is given below.
Zn2+ does not show resonance because of filled d orbitals. The whole system is already at a stable position and hence no electrons are available for delocalization. However, Zn2+ does have a vacant 4s orbital which can accept electrons from the outer molecule.
Zn2+ lewis structure shape
The shape is an important aspect of any existing molecule as it does affect the spectral properties of that molecule. Let us go through the shape of the zn2+ lewis structure.
Zn2+ as an ion, does not have a definite shape inside the solution. However, inside the solution where the solvent is water. A hypothetical layer is formed around the zn2+ ion as shown in the given figure.
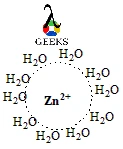
Zn2+ lewis structure formal charge
The overall charge carried out by the zn2+ ion will be called its formal charge. Let us see the formal charge of zn2+.
The formal charge on zn2+ is +2. In the case of ions like zn2+, the charge present on them is equivalent to their formal charge. Unlike in the case of neutral molecules where we have to consider lone pairs and bond pairs.
Zn2+ lewis structure angle
Angle is found when a bond is formed between the central atom with its next atom present within the molecule. Let us figure out the angle for zn2+.
In zn2+, there is no angle formed between the zn2+ and another atom. This is because zn2+ is a monovalent ion and exists inside the solution only. However, within the solution, it is surrounded by a firm layer of water only with no bond established between them.
Zn2+ can not exist inside the solution only. Many salts of zinc like zncl2, znbr2 and zni2, all exist as zn2+ ions inside the solution.
Zn2+ lewis structure octet rule
The statement of the octet rule says that all the involved atoms in the bonding should have 8 electrons or a stable electronic configuration. Let us see the octet rule of zn2+.
Zn2+ has followed the expanded octet rule as 10 electrons are present in the last shell after the loss of two electrons. The filled d orbitals indicate the stable electronic configuration. Zn2+ belongs to the 4th period and hence has a d orbital in its valence shells.
Zn2+ lewis structure lone pairs
Every atom is associated with two type of electrons pairs. one is valence electron pairs and the other one is lone pairs. Let us explore below for zn2+.
In the zn2+ lewis structure, no lone pair is present. This is because all the electron pairs are already engaged in bonding with no lone pair. Therefore, no lone pair is presented in the lewis structure of zn2+.
Zn2+ valence electrons
To know the number of valence electrons available for zn2+, Let us go through its valence electronic configuration.
The zn2+ has 10 valence electrons. The zinc atom belongs to the 3d series of the periodic table with the electronic configuration of [Ar] 3d¹⁰4s². For the zn2+, it becomes [Ar] 3d¹⁰4s0 and indicates that only 10 electrons in its last subshell.
In zn2+ ion, [Ar] is representing 18 electrons. However, these are so closely associated with the nucleus that cannot be available for bonding. Hence we do not consider them in valence electrons.
Zn2+ hybridization
The term hybridization is used whenever there is the formation of any molecule. The phenomenon of hybridization for zn2+ is given below.
The hybridization of zn2+ depends upon the fact what kind of ligand is attached to it. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is used for determining hybridization in the case of inorganic ions. Some common hybridization types of zn2+ salts are enlisted in the given table.
| Zinc salts (containing zn2+ ions) | Hybridization |
| ZnCl2 | Sp |
| ZnBr2 | Sp |
| ZnC₄H₆O₄ | Sp3 |
| ZnO | Sp3 |
Is zn2+ soluble in water?
The solubility parameter of any chemical molecule is always checked with water first as water is a universal solvent. Let us see if zn2+ is soluble in water molecules or not.
Zn2+ is soluble in the water molecule. This happens because a water-soluble compound is formed when zn2+ and water is mixed together.
How and why zn2+ is soluble in water?
Let us find out the reason behind the solubility of the zn2+ in water.
Zn2+ is soluble because of the formation of Zn(OH)2 entity as shown in the reaction: Zn2+ +OH– = Zn(OH)2. The water loving product Zn(OH)2 is responsible for the solubility.
Is zn2+ a strong electrolyte?
A strong electrolyte is a chemical species which dissociates completely. Let us explore for zn2+ as given below.
Zn2+ is a strong electrolyte. This is because zncl2 salt in which zn2+ existed completely dissociates in ions. Hence comes under the category of a strong electrolyte.
Is zn2+ acidic or basic?
Depending on the nature of the intended ion and the availability of the valence electrons. These two factors decide basic or acidic nature. Let us look for zn2+.
Zn2+ is both acidic and basic. This is because zn2+ can accept electrons as well as donate electrons. zn2+ also known as amphoteric ion as it act as both.
Why and how zn2+ is both acidic and basic?
Let us find out why zn2+ is both acidic as well as basic.
Zn2+ is act as an acid by giving up H+ while it acts as a base by giving OH– ion in the solution as shown in the given below reactions of Zn(OH)2.
- Zn(OH)2(s)+2H+(aq) →Zn2+(aq)+2H2O(l)
- Zn(OH)2(s)+2OH−(aq) →[Zn(OH)4]2−(aq)]
Is zn2+ polar or nonpolar?
Polarity and non-polarity are decided by the electronic geometry of the molecule. Let us see that zn2+ belongs to which one.
Zn2+ is non-polar in nature. This is due to the reason that most of the zinc salts such as zncl2, and znBr2 have a linear electronic arrangement. As a result net magnetic moment is zero.
Is zn2+ a lewis acid or base?
The entity which accepts electron pairs refers to lewis acid and if donates then consider a lewis base. Description for lewis acid or base nature of zn2+ is given below.
- Zn2+ can acts as base as given below– Zn(OH)2 + HCL(acid) → ZnCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- Zn2+ act as acid when react with base– Zn(OH)2 + 2KOH(Base) → K2Zn(OH)4 + H2O(l)
In the first reaction zn2+ acts as a base, it donates lone pair to HCl and behaves as an acid in the second reaction as it accepts electron pair from the KOH
Is zn2+ linear?
A molecule is said to be linear when there is a formation of an angle of 1800 between the central atom and the neighboring atoms. Let us identify for zn2+.
Zn2+ does exist in a linear shape only in those salts which consist of monodentate ligand only. For example zncl2 and znbr2. This means the linear structure of zn2+ is dependent upon the fact which ligand will attach it.
Is zn2+ magnetic?
Magnetism arises due to the spinning of the electrons on its axis. The detail about the magnetic nature of zn2+ is given below.
Zn2+ is non-magnetic in nature. This is because, in zn2+ compounds, no free electrons are not available to generate the magnetic field.
Why and how zn2+ is non-magnetic?
Non-magnetism is attributed to the non-availability of free electrons.
Zn2+ is non-magnetic as its d orbitals are fully-filled and hence stable. A large amount of energy is needed to break the stability of the system so that electrons can shift to the 4S orbital. This breakage of energy is not practical.
Is zn2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
Paramagnetic compounds are those which are capable of showing a magnetic field while diamagnetic ones are incapable of doing the same. Let us explore for zn2+.
Zn2+ is diamagnetic. It has no free spinning electrons to generate the magnetic lines around itself.
Why and how zn2+ is diamagnetic in nature?
Diamagnetism arises when the intended ion does not cooperate with the external magnetic field. The reason behind the diamagnetic attribute of zn2+ is given below.
Zn2+ is diamagnetic because the magnetic moment of the electrons present in the d subshells are filled and hence they cancel out each other magnetic lines. Therefore, when the external magnetic field is applied, zn2+ does not provide any response to it. Hence, accountable for diamagnetism.
Is zn2+ a conductor?
A conductor is a substance or any entity which generates electricity or current when exposed to any external source. Let us observe for zn2+.
Zn2+ is not a conductor. This is because the conduction property is directly associated with magnetism and zn2+ is diamagnetic.
Why and how zn2+ is a non-conductor?
Let us discuss the reason behind the non-conduction of zn2+ ions.
Zn2+ does not generate electricity it is a non-conductor. This is because there is no movement of electrons possible as all the electrons are engaged and no unpaired electron which can generate electricity.
Is zn2+ metallic or non-metallic?
The reason behind an element is called metal or not metal solely depends upon its natural existing characteristics only. Let us find for zn2+.
Zn2+ is metallic in nature as it fulfilled the characteristics of the metal element. Moreover, the zn2+ ion comes from the zinc element which is a transition metal and marked as a metal in the periodic table.
Is zn2+ a mixture?
Ions do not exist as such as they need a counter ion or they combine with another entity to attain stability. Let us discuss for zn2+ as given below.
Zn2+ is a mixture. This is due to the reason zn2+ existence is not possible according to chemistry laws. Therefore, to form zn2+, it is mixed with water sometimes or any other suitable chemical.
Is zn2+ brittle?
The word brittle means anything which can be easily broken. The detail about the brittle nature of zn2+ is given below.
Zn2+ is not brittle because it comes under the metal category and metal is generally non-brittle. However, zn2+ is exist in the solution. Therefore, its elasticity increases which are accountable for its hardness.
Is zn2+ crystalline or amorphous?
If a substance has a well-defined shape it is known as crystalline otherwise consider it amorphous with a disordered arrangement. Let us find out for zn2+.
Zn2+ is crystalline as all the electrons are engaged in a definite manner and adding stability to the system.
Is zn2+ hard?
The hardness of any ion depends upon the electronegativity and the size of the ion. See if the zn2+ is hard or soft.
Zn2+ is a soft acid ion as it has a low electronegative value and a bigger size.
Is zn2+ lighter than steel?
Zn2+ is an ion whereas steel is an alloy composed of carbon, silicon and manganese etc. Let us discuss for zn2+ in the following paragraph.
Zn2+ is not lighter than steel as it belongs to the heavy transition metal series with atomic number 30. Therefore it is considered a heavy metal.
Is zn2+ malleable?
Malleable is a property of any element to attain any shape without breaking and losing its elasticity. The following paragraph discuss the same for zn2+.
Zn2+ is not malleable because zn2+ belongs to the zinc atom and it is ductile in nature in its pure form. Therefore its ion ie. zn2+ is ductile, not malleable.
Is zn2+ radioactive?
A compound is called to be radioactive only when it emits radioactive rays. Let us check whether the zn2+ is radioactive or not.
Zn2+ is not radioactive as it has a stable electronic configuration and a stable nucleus which does not disintegrate naturally.
Conclusion
Zn2+ is a stable ion which can adopt any geometry and hybridization depending upon the fact with which molecule it will be bonded. In addition, it comes under an amphoteric ion and is also a soft acid.
Read more about following Lewis structure
Also Read:
- Nco lewis structure
- N2f4 lewis structure
- Of2 lewis structure
- Caco3 lewis structure
- Socl2 lewis structure
- Hcooh lewis structure
- Br3 lewis structure
- Sbr4 lewis structure
- Coh2 lewis structure
- Co lewis structure

Hello…Myself is Pomila Sharma. I have done my master’s in Chemistry with a specialization in synthetic organic chemistry. I have published 4 research articles. I am very passionate about the chemistry world. I believe it’s all about chemistry so let’s explore it together.