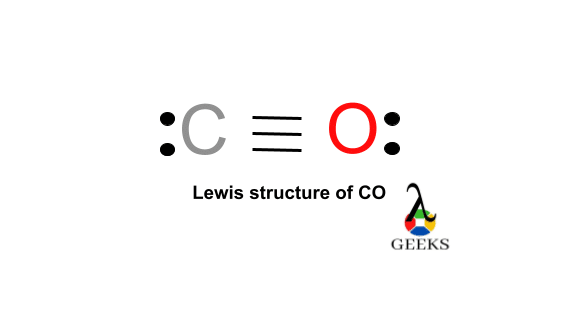Phosgene (CCl2O) consists of a central carbon (C) atom with 4 valence electrons, bonded to two chlorine (Cl) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom. Each Cl contributes 7 valence electrons, and O contributes 6, totaling 24 electrons. The Lewis structure displays a double bond between C and O, and two single bonds between C and each Cl atom. The molecule adopts a trigonal planar geometry around the carbon atom, with bond angles approximately 120°, characteristic of sp² hybridization. The C=O bond is highly polar due to the electronegativity difference (C: 2.55, O: 3.44), influencing CCl2O’s reactivity and toxicity as a chemical weapon and industrial compound.
Ccl2o structure is also known as phosgene. This is neutral molecule, having formal charge zero. The shape of the Ccl2o Lewis structure is trigonal planner with angle of 120. Hybridization of Ccl2o is sp2. This is can not be ionic but in acidic form. This is a polar molecule.
In this article we study about CCl2O Lewis structure, shape , geometry and many more in details.
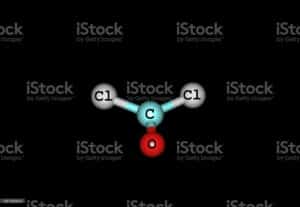
Ccl2o Lewis structure :
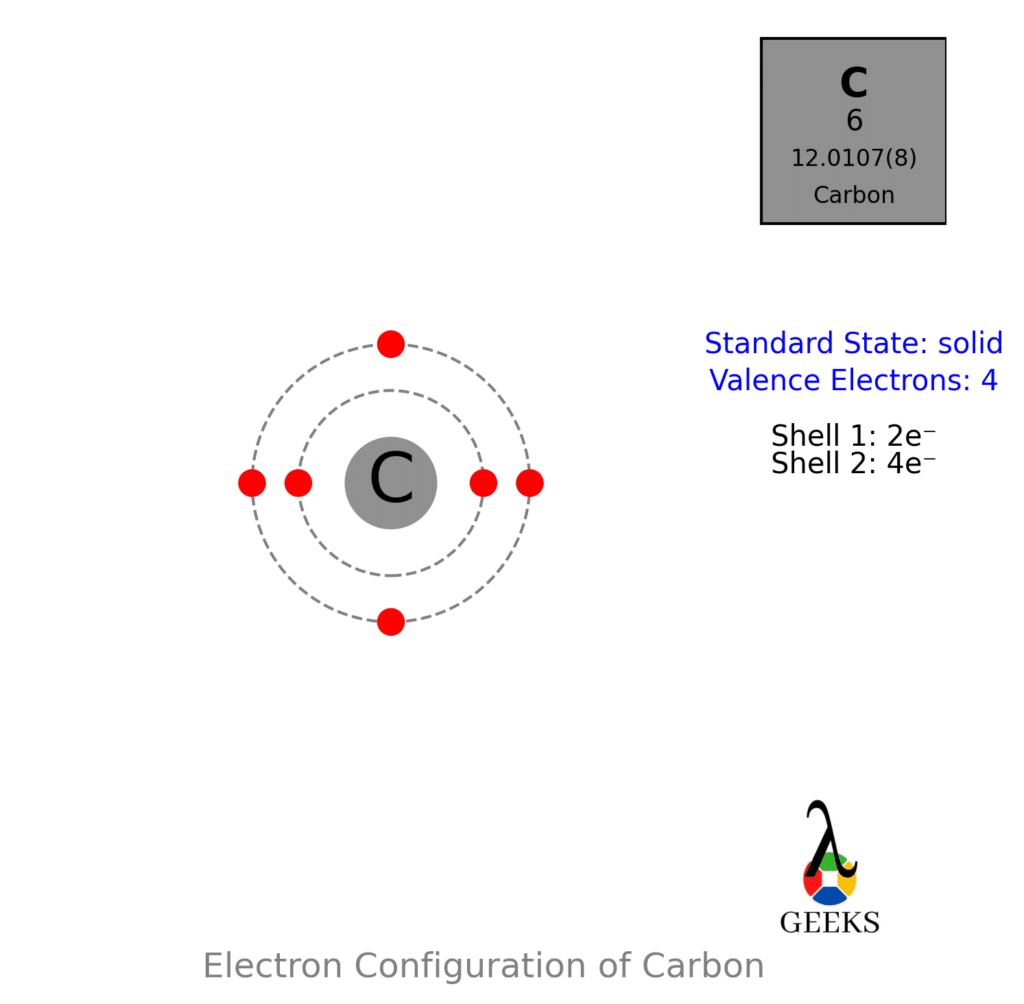
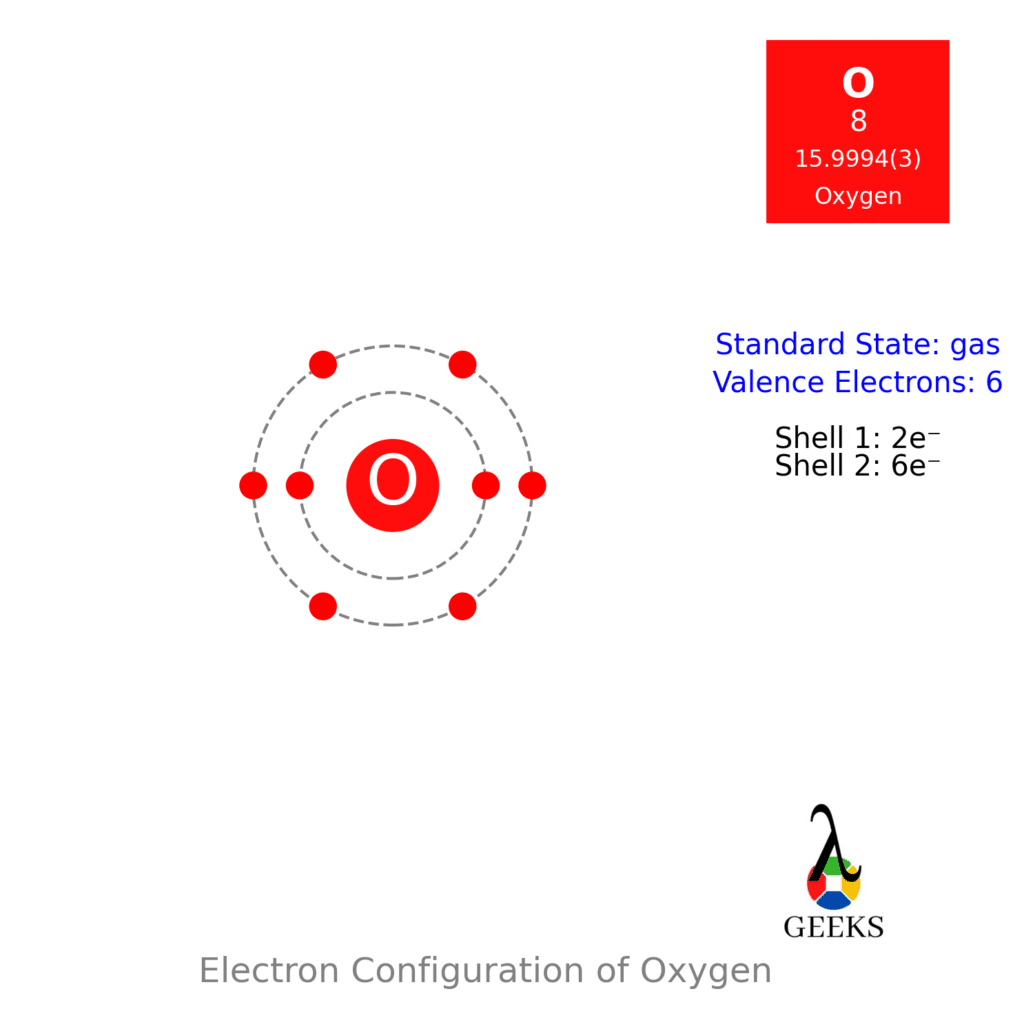
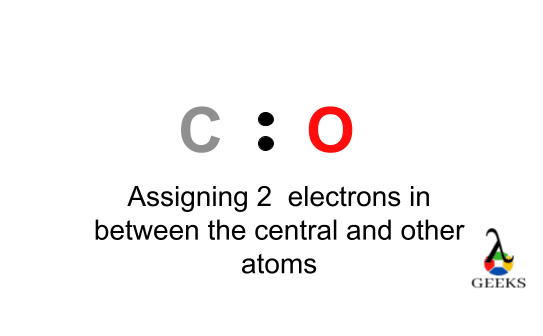
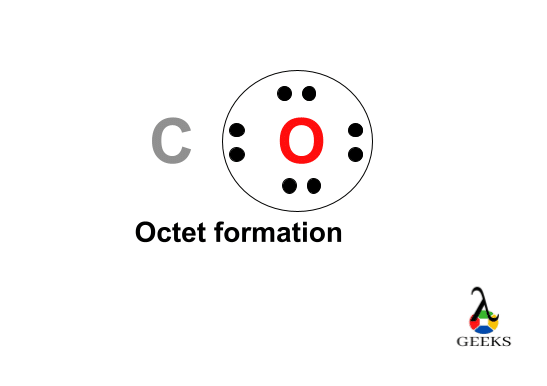
For arrangements of electron the diagrammatic represent will require to make for Ccl2o Lewis structure. One C, one O, and two Cl atom will require to form the Lewis structure for Ccl2o. The total number of valence electrons here= 4 + 6 + 7*2 = 10 + 14 = 24.
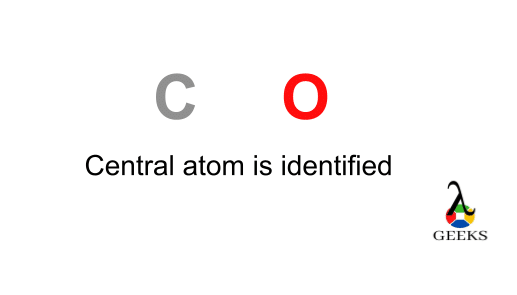
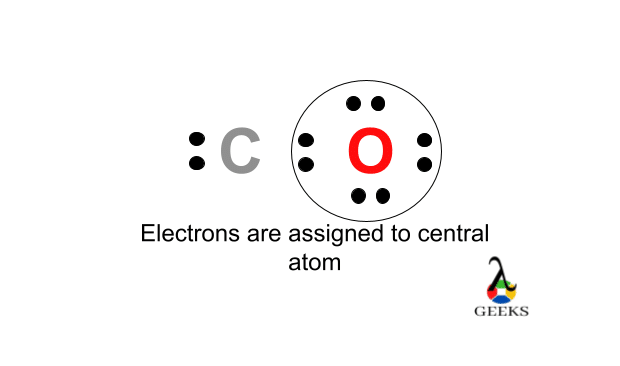
Here the carbon is the least electronegative element . We will place carbon in the central for more stability of molecule. The chlorine , oxygen atoms obey the octet rule here. The best Lewis structure also found for it , having formal charges will zero.
The values we found for all the elements are having the least possible formal charges within the Ccl2o lewis structure. Therefore, this is the possible Lewis structure representation of Ccl2o.
Ccl2o lewis structure resonance :
The best resonance structure is , where all the atoms in Ccl2o show zero formal charge. So the carbon in middle and the atoms are besides with obeying octet rule.

Ccl2o lewis structure shape :
The central carbon atom in Ccl2o Lewis structure has two bonding and three nonbonding lone pairs of electrons. The electron pairs three groups are arranged in a planer but in trigonal. Trigonal planner is the shape of the Ccl2o Lewis structure.
Ccl2o lewis structure angle:
The bond angle of Cocl2 Lewis structure is 120. The arrangement is AX2. On central atom there is 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pairs. The electron pairs which are present here are staying in plane. So, the molecular shape is trigonal planner in Ccl2o Lewis structure.
Ccl2o lewis structure formal charge :
By determination of the formal charge of a molecule Ccl2o Lewis structure. For each of the atom ,the valence electrons we already know. Total amount of valence electrons is 24 in case of Ccl2o structure.
Formal charge on carbon atom = 4-(0-4)=0. Formal charge on chlorine atom = 7 – [ 6 + 1] = 7 – 7 = 0. Formal charge on oxygen atom = 6 – [ 4 + 2 ]= 6 – 6 = 0 . Formal charge is zero in all. so this is a neutral molecule.
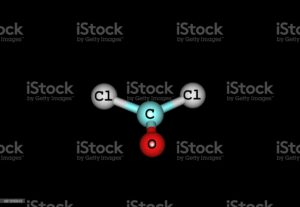
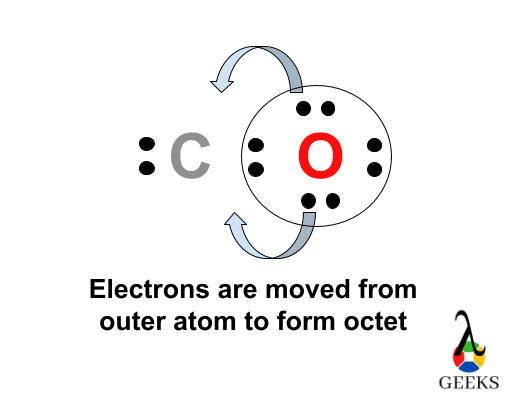
Ccl2o lewis structure octet rule :
When the eight electrons in outermost shell than we know the atoms in a molecule is stable. Octet rule obey the rules.
The chloride atoms share single bonds with the carbon atom here. One double bond found in between oxygen and carbon. The octet rule here satisfied for all the atom in Ccl2o Lewis structure. Eight valence electrons of Ccl2o lewis structure allowing for molecular stability.
Ccl2o lewis structure lone pairs :
There are two bonding and two lone pair regions in Ccl2o Lewis structure. The electronic geometry of Ccl2o lewis structure is tetrahedral.
After ignoring the two lone pairs here the molecular geometry is showing bent . Thus, for Ccl2o Lewis structure the shape of the molecule is trigonal planner. The Bond angle is 120. The arrangements of the Ccl2o Lewis structure is AX2.
Ccl2o valence electrons:
Need to know the number of valence electrons for each atom in Ccl2o lewis structure. For CoCl2 or we can other wise called (Phosgene gas): C = 4; O = 6; Cl = 7. We conclude that, the total amount of valence electrons in case of phosgene is 4 + 6 + (7×2) = 24.
Ccl2o hybridization:
There are two sigma bonds present , those are C-Cl bonds. So two sp2 hybrid orbitals of Carbon bond with 3p orbital of Chlorine. From the sp2 hybrid orbital of Carbon we sure that , C=O bond consists of one ???? bond.
So, 2p orbital of O and one π bond overlapping with carbon here .This conclude sp2 hybridization will found in case of Ccl2o.This maintained at 120 degree in the mixture of s and p. This form trigonal symmetry.
Ccl2o solubility:
Ccl2o reacts slowly with water. It form carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid by reacting with H2O. With caustic solution , Ccl2o is readily reacts. In case of ammonia and ammonia water this even more readily proceeds.
In most liquid hydrocarbons, benzene, toluene and glacial acetic acid ,this is more soluble. Phosgene or Ccl2o is sparingly soluble in H2O. Hydrochloric acid and carbon dioxide found by decomposition.
Is Ccl2o ionic ?
Ccl2o Lewis structure is not ionic, this means not ionized. This is in neutral form. Ccl2o is an covalently bonded with each other. Ccl2o is a nonflammable gas . This is colorless. It present in small amounts but chemically manufactured. It occurs naturally from the breakdown of chlorinated compounds.
By proper arrangement of atoms the pure structure of the molecule can be found. Holding the atoms together tightly due to chemical bonds. The Ccl2o molecule contains 3 bonds in total.
Is Ccl2o acidic or basic ?
Ccl2o is acidic. This is possibly neutralized by calcium oxide, sodium bicarbonate, calcium hydroxide and ammonia. It best possibly mixed with the H2O as solution. This can be used in safe way to neutralize phosgene.
The outcomes we found are generally non-toxic or harmful. Cocl2 is the organic chemical compound which can be called as phosgene. This is a colorless gas.
Is Ccl2o polar or nonpolar ?
Ccl2o is a polar molecule. The shape of Ccl2o is trigonal planner. Three areas of electron repulsion found around the carbon atom, which is present in middle. Both C-Cl bonds are polar in nature because the d electronegativity of C and Cl is difference.
The molecule is Asymmetric molecule due to presence of the Oxygen atom. The dipoles here are doesn’t cancel out each other in the Ccl2o Lewis structure. This is happens because the E.N of the C-Cl and C-O is different.
Conclusion :
Ccl2o structure is also known as phosgene. This is neutral molecule, having formal charge zero. The shape of the Ccl2o Lewis structure is trigonal planner with angle of 120. Hybridization of Ccl2o is sp2. This is can not be ionic but in acidic form. This is a polar molecule.
Also Read: