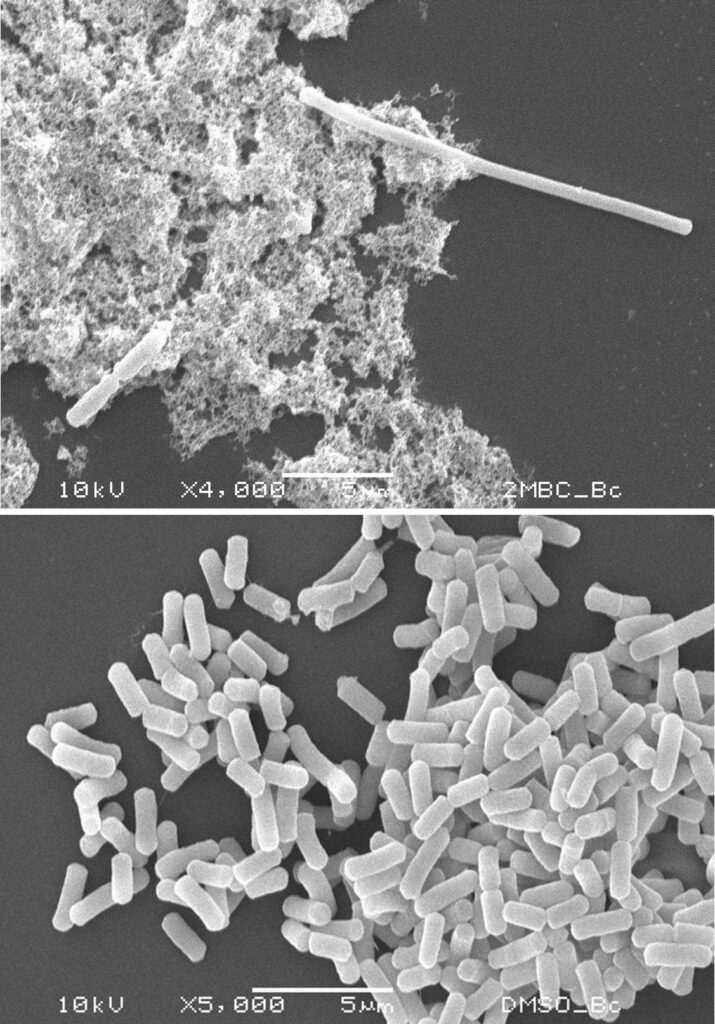
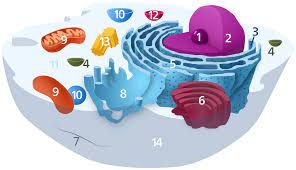
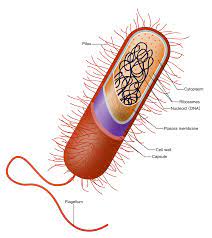
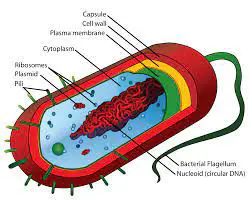
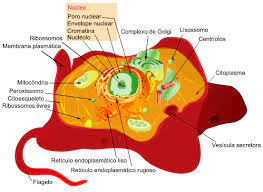
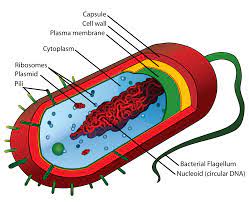
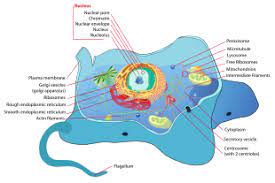
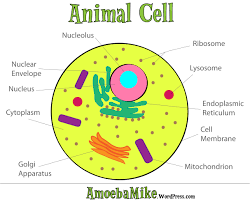
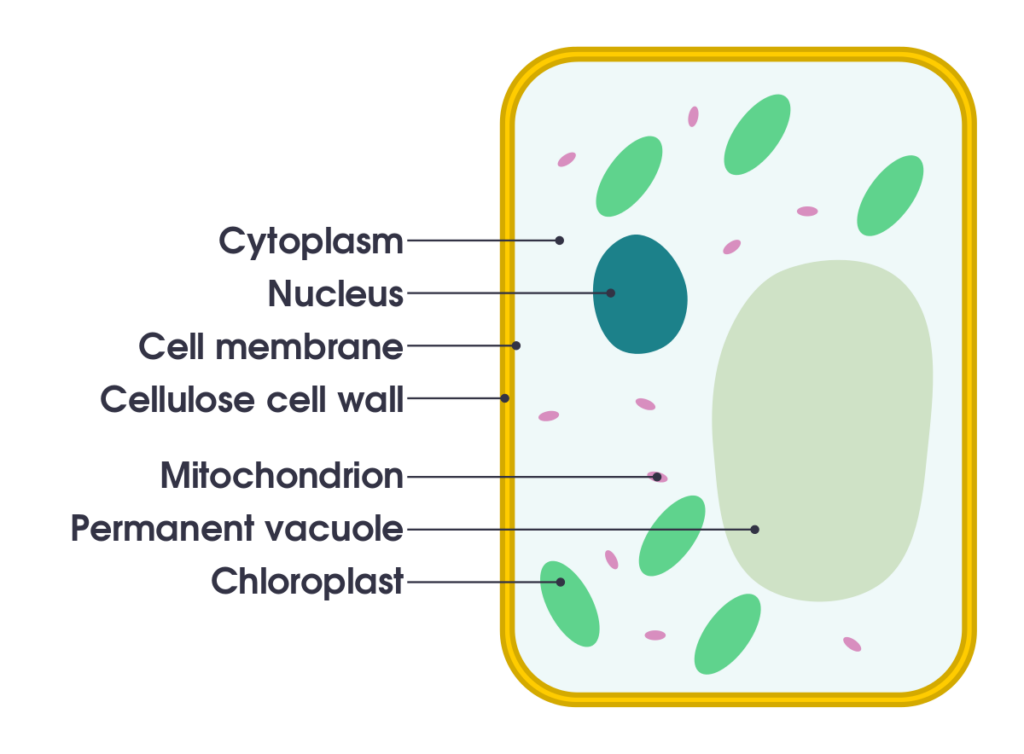
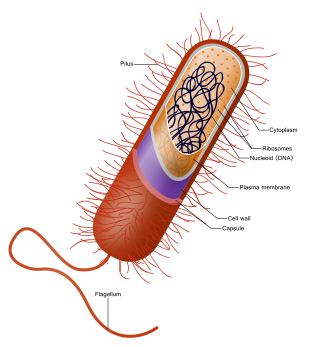
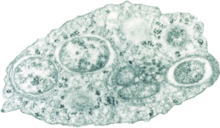
Cytoplasm is any solution with thick consistency filled up in each of the cell and is thus enclosed within the cell membrane.
In concerned with the question for do bacteria have cytoplasm, the answer is yes. They are just like the cells of eukaryotes having a cytoplasm which is one among the organelle in the eukaryotes.
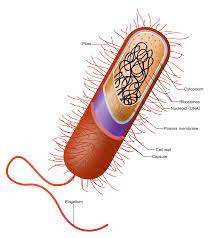
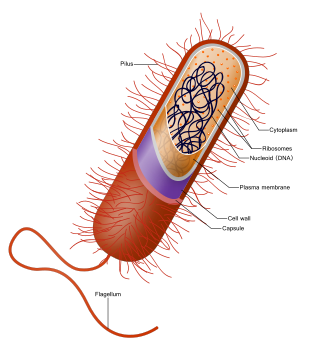
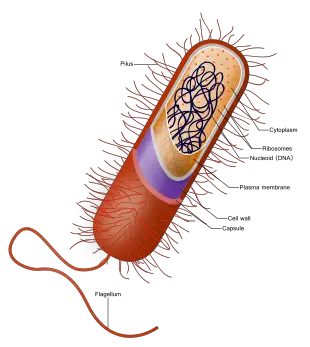
There are other organelles in the bacteria which include the plasma membrane the ribosomes and the cytoplasm. There are a lot characters that separate the eukaryotic cell from the circular DNA that is in the nucleoid, it also lacks few membrane surrounded organelle.
Cytoplasm is also called protoplasm of the bacterial cell is like a gel just like matrix made of 80% of the water enzymes, gases, the waste, inorganic ions and have compounds that have less molecular weight and have structures of cell like that of the chromosomes, ribosomes and the plasmids.
In some of the cells which also include the bacterial cell, also have a cell wall. In the bacteria, the cytoplasmic membrane involves the cytoplasm and is situated having in the cell wall of the bacteria. The membrane of the cytoplasm is also called plasma membrane and is simply the cell membrane.
Do all bacteria have cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is also found in the cells of eukaryotes and comprises of many of the wastes and the ions needed for the cell.
This is not typical of all the bacteria but some of the microorganism does have the intracellular membranes along with many of the extensions like the cytoplasmic membranes.
The cell of the bacteria does lack a nucleus that has a membrane. The hereditary products of the bacteria are naked and are inside the cytoplasm. The only type of organelle that the bacteria have is the Ribosomes.
There is a part called the nucleoid that indicates the place of the cytoplasm where the DNA is kept and is actually single and the chromosome are of circular type. The bacteria are also found in colonies and unless till then they do have single cells.
The bacteria are called to be the cells of ancestry and reproduce by the process of binary fission that gets in process with duplicating the genetic substance and then making it sure to split to make two daughter cells that are identical to that of the parent.

Why bacteria have cytoplasm?
The interior of bacteria is made up of proteins and phospholipids they helps cell regulation throughout.
The part for do bacteria have cytoplasm is yes and the protoplasm or the cytoplasm inside them helps in for the metabolism, the growth of cell and getting the process of replication maintained.
It is a matrix structure looking like a gel and is made of the wastes, the gas, nutrients, the water and the enzymes which also have the structures for plasmids, the ribosomes and the chromosome present in them. The cytoplasm is enclosed within the cell envelope.
The cell envelopes entrap all the components of the cytoplasm and also it. Unlike all the true cells the bacteria have no confined membrane nucleus with a chromosome DNA stand which is localized but is not contained in the area of the cell known as nucleoid.
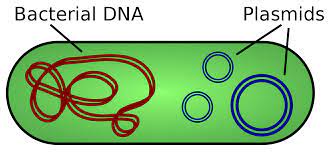
All the components of the cell are scattered in the entire part of the cytoplasm. Just like the chromosomes; the plastics are composed if the DNA material that is circular. They are not a part for reproduction. The plasmids do get to replicate on it and is not concerned for survival.
The membrane of the cytoplasm is a trait for the bacteria structure and also shares it with the other cells that are living and also acts as a barrier that gets them to allow having a selective communication with the surrounding. The membrane is quote organized and are not symmetric from both ends with have separate functions.
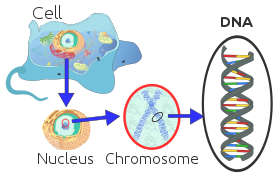
How bacteria have cytoplasm?
The boss of the cell that directs the functions inside is the nucleus with water being the major part of the cell.
The cytoplasm is mostly of a gel like material inside the cell that is composed up of the organelles except the nucleus and the semi fluid which is the cytosol. The cytoplasm has a lot going on.
The cytosol is regarded to be the crowded part where many of the actions do take place. The cell is kept alive for many of the organelles like that of the endoplasmic reticulum, the mitochondria, the Golgi apparatus with having special functions as well.
There are few molecules that keep on shuffling between the organelles and the proteins that are made to synthesis. ATP is the storage for energy which is made and the waste is discarded. The cytoplasm also has cytoskeleton made of the protein fibers.
There are many ions that help in for osmosis and is mostly for keeping the cell from getting swelled up with water and the leaves so that the cell does not get to dry up or malfunctions. Glycolysis also does take up in here and there is also the provision for chemical signal transmission.
Do bacteria have cytoplasmic membrane?
There is a presence of 70s ribosome in the cytoplasm of the bacteria and is also much packed up with also many granules.
The answer for do bacteria have cytoplasm is yes along with it also having a cytoplasmic membrane which is made up of the phospholipids. The composition of the cytoplasmic is the proteins and lipids.
The basic components that make the lipid layer of the cytoplasmic membrane is the phospholipids that vary within the length of acyl chain, getting them saturated and making a branch that shall carry the main groups and may vary in the charges present along with the size.
The cells can be made of many materials and one of the most general is the cell membrane that gets to separate the materials of the cell from the surrounding of cell. All of the cells have the cell membrane and they come with slight variations with some cells having cell wall.
Most of all the metabolic process takes place in the cytoplasm of the bacteria and also have inclusions like the ribosomes, the cytoplasmic granules, the plasmids. The ribosomes are actually made up of 30% of the ribosomal proteins and are if 70% ribosomal RNA. The association of these needs the help and involvement of magnesium.
Where is the cytoplasm in a bacterial cell?
Cytoplasm of bacteria includes the reserves like the cyanophycin, granules, carboxysomes, glycogen and the polyphosphate granules giving buoyancy to cell.
Within the cells of the bacteria, the cytoplasmic membrane gets to cover the cytoplasm and is situated within the cell wall of the bacteria. The cytoplasmic membrane is also called the plasma membrane or even is refereed as cell membrane.
The cytoplasm of the bacteria has 70s ribosomes within one single subunit having a molecule of 16s ribosomal RNA and one large unit having double molecules of 23 and 55 ribosomal RNA. The ribosomes are related to get the genetic material translated from molecular level. the number of ribosomes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ.
Ribosomal convert the language of nucleic acid to the building block of proteins which is the amino acids. Proteins are the ones that are used to serve all the functions within a cell and a living being. They have gas vesicle that is hollow and is spindle like and is composed of proteins and planktonic bacteria.
The cytoplasm has a lot of organelles which have membrane and also includes many of the membrane that have less inorganic and the organic stuffs and is called the inclusion bodies. Inclusion body is the place where the membrane differs from the unit membrane being typical.
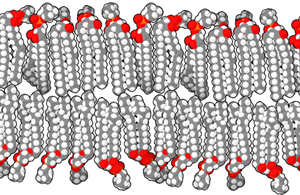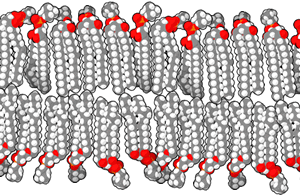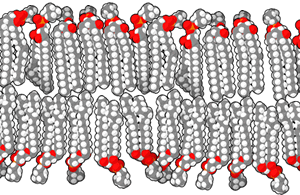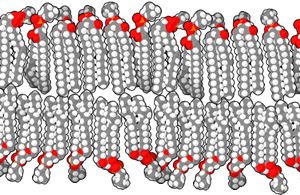
What is cytoplasm of bacteria made of?
The cytoplasm is also referred to as the protoplasm and the cell of the bacteria has it in form of a gel matrix which is made up of 80% water.
The cytoplasmic membrane or the plasma layer of the bacteria is made up of the phospholipid bilayer and is set for all the basic functions if the cell membrane likes being a permeable membrane for many molecules.
They serve as the direction to many of the molecules that get to transport in the cell. Along with this usage, the membranes of the prokaryotes also serve as the site for energy storage where it is the site where the force for proton motive is made.
Unlike the eukaryotes the membrane of the bacteria with some of the exceptions in methanotrophs and mycoplasma on a basic level do not have sterols. There are many small organisms that do have compounds that do relate structurally and are called hopanoids.
In the bacteria having the cytoplasm there can be seen traces of few fatty acids inside the membranes. On addition with all the unsaturated and saturated fatty acids that are typical the cytoplasm of bacteria also has fatty acids with add on to methyl the cyclic ones that are even and hydroxyl.
Also Read: