The drag coefficient is a dimensionless physical quantity influenced by the various parameters that can be affected by the motion in the fluid medium.
In the study of fluid mechanics, the drag coefficient plays a vital role as it resists the motion of the solid object in the fluid medium. This drag coefficient depends on velocity, the object’s cross-sectional area, and density. Is the drag coefficient constant if the parameter mentioned above varies?
We are trying to answer the above equation in this post. Let us discuss how and when is drag coefficient constant and the facts related to the constant drag coefficient below section.
The drag coefficient is directly influenced by the velocity of the flow of the object in the fluid. If the velocity is kept constant over a period, there may be a change in the drag, but the drag coefficient is constant as it is the dimensionless quantity.
CD=2FD/ρv2A
From the above formula, if we consider the object motion in the fluid, the terms FD, ρ, and A are constant for the same object; thus, only possible changes in the velocity we can write the above equation as
CD=Constant/v2
Thus the change in velocity inversely corresponds to the drag coefficient.

How does drag coefficient vary?
Some factors like air resistance, shape and geometry of the object affect the drag coefficient. But the variation of the drag coefficient completely depends on the velocity of the object in the fluid.
The square of the velocity of the object is proportional to the drag coefficient of the object in fluid surroundings. The drag coefficient varies with the square of the relative velocity of the object.
Consider the aerodynamic drag; if the velocity of the object increases to its square value, the drag coefficient falls down at the same value. Thus at a higher velocity, the drag coefficient is less, giving the better performance. So it is clear that increase in velocity, the drag coefficient decreases.

When does drag coefficient vary?
In most cases, the drag coefficient varies with velocity inversely. But other than the velocity, there are several factors responsible for the variation of the drag coefficient. Some of them are listed below:
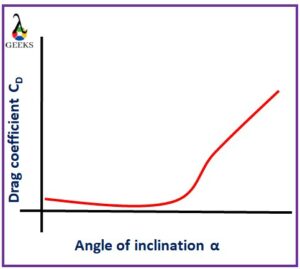
- The angle of object – The factors angle of inclination of the object in the fluid surface is one reason for the variation of the drag coefficient. When the angle of attack is smaller, the drag coefficient is lower.
- The density of the medium – If the object is low from one medium to another medium of different densities, the drag coefficient varies for the same object. Consider that object is moving from air to water; the density of the air and water is different from one another. Thus the drag force offered to the object changes, thus varying the drag coefficient.
- Another necessary consequence of vary in drag coefficient is the type of flow. When the airflow or hydraulic flow is turbulent at a higher velocity, variation in the drag coefficient will occur.
- Cross-sectional area –The reference area of the object’s cross-section influences the drag force. If the area of the object is doubled, the drag force is also doubled. Thus varying the drag force causes the proportionate change in the drag coefficient.
D=Aref×constant; where Aref is the area of reference.
When is drag coefficient constant?
In most cases, the constant drag coefficient is referred to as the constant velocity –that means if the velocity of the object on the fluid medium is kept constant, the drag coefficient would also remain constant.
However, the constant drag coefficient depends on the Reynolds number too. As long as the Reynolds number is constant for the object flow, the drag coefficient remains constant.
One fact we need to observe here is the Reynolds number of the object motion in the fluid medium is also depends on the entities like speed, density and viscosity of the medium. Thus constant drag coefficient is associated with the terms involved to describe the motion of the body in the fluid environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens when an object possesses a high drag coefficient?
The low or high value of the drag coefficient directly impacts the motion of the object in the fluid.
If an object possesses a higher drag coefficient, the object might be a flat plate whose ability to move in the fluid surface is relatively slow. The object with a high drag coefficient exhibits significant resistance to the motion.
What is meant by Reynolds number?
In fluid mechanics, the Reynolds number describes the flow pattern of the object in different fluids.
Reynolds number can be defined as the dimensionless number given by the ratio of inertial force over the viscous force of the fluid. The Reynolds number helps to categorize the flow of the fluid system as the turbulent, streamlined, or laminar flow.
Can the drag coefficient of a body be greater than 1?
The value of the drag coefficient depends on the nature of the flow such as streamline or turbulent flow.
If two objects of the same area of cross-section move with the same velocity may have different drag coefficients. The drag coefficient for a streamlined body is always less than 1, whereas, for un-streamlined bodies, the drag coefficient value can be 1 or more than 1.
Does the size of the object affect the drag coefficient?
The drag coefficient and the size of the object correlated to one another. Objects of different sizes possess different viscous and inertial forces responsible for the drag force.
The different viscous and inertial force refers to the different Reynolds number; this means that the size of the object refers to a change in the Reynolds number. So it is clear that the size of the object influences the drag coefficient to several extent.
Does the drag coefficient depend on the altitude?
Drag coefficient is independent of the height. The increase or decrease in the altitude does not make any impact on the drag coefficient.
In some cases, as the altitude increases, the Reynolds number may change; thus, there will be a change in the drag coefficient. But if the Reynolds number remain unchanged even if the altitude changes, the drag coefficient is unaffected by the altitude.
Also Read: