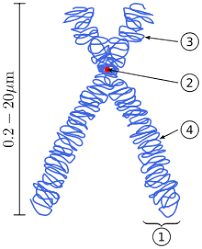
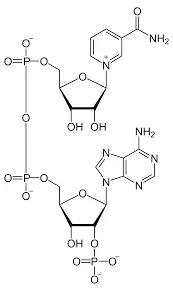
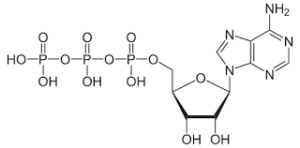
Mutation is said to be an alternation in any of the DNA sequence. It can be a result of the mistakes for DNA copying at cell division.
With regards to the question for is independent assortment mutation, the combination number that shall result in 23 of the maternal and the paternal homologues which shall result from the independent assortment is said to be 2^23. Thus, it is a cause of mutation.
Any change in the sequence of the nucleotides of the organism genome or the extrachromosomal DNA is said to be mutation. Thus, is independent assortment mutation shall be classifying in this. The genomes that are viral seem to have either the genome of RNA or DNA. Mutation are the outcome of the error at the time of viral or DNA replication, meiosis or mitosis or any other type of the DNA damage.
Mutation can also be a result of the deletion or insertion of the DNA segments of the DNA at the time of mobile genetic elements. It might as well give some changes that shall be noticeable which is mostly phenotype. This, is independent assortment mutation type of mutation can be a part of the abnormal and the normal process of biology that shall include cancer, evolution and also the developing stages of immune system that contains junctional diversity.
They are said to be the ultimate mutation source for the entire variation in genetics that shall help in having a raw material on which the evolutionary forces shall act upon like that is what is called to be natural selection. This can lead to have several type of outcome with the genes getting mutated having no effect with getting to alter the gene product and percent gene from getting to work good or in complete manner.
So in human genetics, for instance, when you look at a condition like Huntington’s disease, and you see that it follows this pattern where an affected person who passes that to a child, the child has a 50 percent chance of being infected. That’s dominant Mendelian inheritance. Mendelian inheritance describes the determination of traits by means of dominant and recessive alleles of a particular gene whereas non Mendelian inheritance describes the inheritance of traits which does not follow Mendelian laws.
What is independent assortment?
On context to, is independent assortment mutation, this method gives rise to new alleles combination with having a cross over
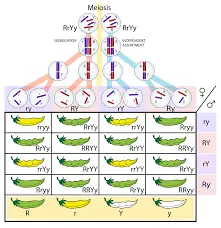
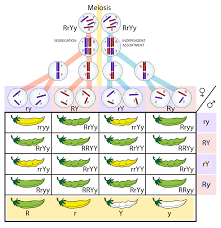
The law for independent assortment tells that “Separate genes for the other trait is passed on independently from one and another from the parents to the offspring”. Along with a fertilization that is random there are many possibilities for the variation in genes that shall exist between any of the two people.
There is a crossing over at the prophase and then independent assortment takes place at the anaphase when the chromosome sets with the new alleles of combination. The genetic variation shall be introduced by having random fertilization of the genes that shall be made by meiosis. At the time when the cell divides at meiosis, the homologous pair of chromosome shall get distributed to the daughter cell.
After having itself distributed to the daughter cells and then at the separate chromosome shall have itself segregated independently of each of them. This is said to be independent assortment. Along with the query of is independent assortment mutation, it outcomes to have many unique and specific gene combination for the chromosomes. The cause for the variation on genetic cam be mutation. Gregor Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity and laid the mathematical foundation of the science of genetics.
The inheritance patterns seen in Mendel’s monohybrid and dihybrid crosses depend on three sets of assumptions: Each trait is determined by a single gene locus. Each gene had two alleles, one provided by each parent. Independent assortment in meiosis takes place in eukaryotes during metaphase I of meiotic division. It produces a gamete carrying mixed chromosomes. Gametes contain half the number of regular chromosomes in a diploid somatic cell.
The general base for the law of independent assortment stays in in the stage of meiosis 1 of the gamete making when the homologous pairs are lined up in not so obvious orientation at the middle of cell as they prepare themselves to part. Meiosis can lead to having of variation in genetics for random fertilization, mutation, crossing over between the chromatids of the chromosomes that are homologous at meiosis and ultimately for random mating done in organism.
Causes of Independent Assortment
It was W Bateson that did explain the lack of independent assortment in the sweet pea and the link was given in Drosophila by TH Morgan.
The statement for is independent assortment mutation relates to one of its causes. This law is one of the result for the independent division of the chromosomes in several other gametes. The crossing over takes place in the genes of each of the chromosome and are then rearranged.
After this there is the crossing over that takes place on each of the chromosome. This helps in discussing of the random inheritance of genes from bot of the parents. The genes when are close placed and link up together in the group and are made to travel as a single unit is called to be linkage. This helps in stopping the method of independent assortment. This all happen in meiosis 1.
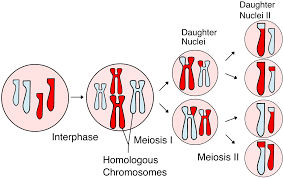
The chromosome here shall be moving in in random motion to have the poles separated at the time of meiosis. The gamete shall end up in 23 of the chromosomes after meiosis but then this process means that each of the gamete shall have 1 of the other combination that is different of the other chromosomes. The homologous chromosome is seemed to be distributed in random basis to the daughter cells and then segregate with each other.
The rest of the two laws are the Law of Dominance and Law of segregation. With on considering is independent assortment mutation, Mendel noted that it shall not look same like the parental genes. And thus, the allele that comes first cannot be influenced by the second allele on any terms. The other reasons for this method getting distributed with each other and also to the parents is linked to its theory of coming from seating of 10,000 pea plants.
- The first generation shall be seen with seeds being round and yellow only.
- The second generation shall have a labelled ratio of the phenotypic ones and shall be scattered and inherited on each basis.
- The second generation has a ratio labelled of the phenotypic one of which was scattered and inherited individually with the F2 ones having seeds that are self-pollinated. Self-pollination means that the pollination is done between same flower or same plants that are genetically same.
- At last there are 4 of the results seen- round yellow, round green, wrinkled green and wrinkled yellow.
- The ratio for the 2nd generation was 9:3:3:1 with it being phenotype and based on individual division.
Independent assortment example
This law defines any random inheritance of the genes from the paternal and maternal source.
For the part of example and to consider is independent assortment mutation, we can consider a virtual situation if the rabbits that can have two of the traits visible being the eye color and the fur color.
The fur color shall be available in two being white and black taking either of the two color. The eye color shall be either red or green. The dominance in the fur area shall be the black fur (B) being dominant over white(b), while the allele of green eye (G) being dominant to red(g). This is a complete hypothetical example to know the law and understand if is independent assortment mutation.
Here, both the rabbits are mixed up. This means that both of the rabbits that look black and have green eyes yet are true to being a heterozygous genotype. Both the rabbits fused have the genotype of BbGg. In this survival of the two rabbits, all of them on each basis have the same mix of traits. Before having to breed, each of the rabbit shall have to make gametes. It implies that despite the parent phenotype of having green eyes and black fur, the baby can inherit any other combination of the trait.

For example, any one baby might receive the genotype of bbgg, giving it a red eye and white fur look. On the alternate, a rabbit born can also gave the genotype of Bbgg that shall have a black fur and the red eyes. This is called to be independent assortment and thus for the line of is independent assortment mutation is true. The example of Mendel has peas of two traits used up to explain this.
This is the result of the process called as meiosis. It takes at this time. Meiosis is same as mitosis but the final product here is the making of gamete cells. The gamete cells have its DNA half being regular diploid but are said to be haploid. This is vital for sexual reproduction that allows the cells of two gametes to fuse and then make the diploid zygote that shall have the DNA needed to have a new organism.
How is independent assortment mutation?
This law states to give new genes combination as its result on each of the chromosome. This takes places at meiosis.
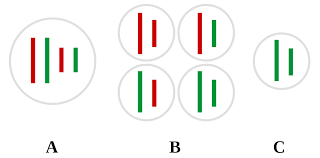
When the cells divide at the time of meiosis, the homologous pair of chromosome are distributed in random basis to the daughter cells and then other chromosomes are separated out being independent of each other.
The chromosome here must move at random in order for the poles to be separated during meiosis. After meiosis, the gamete will end up in 23 of the chromosomes, but this process means that each gamete will have 1 of the other combinations that are different of the other chromosomes. The homologous chromosome appears to be distributed to daughter cells at random and then segregates with each other.
There is a cross called as the dihybrid cross that simplifies the independent assortment. It is a cross between the two parents that breed true and then express the other trait for the two character. The laws are not clear for the events that take place at this point. It is at the metaphase 1 that the alignment of the pairs that are homologous occur. The alleles trait different to the gametes that are made describing it the best.
Crossing over occurs during the prophase, followed by independent assortment during the anaphase, when the chromosome settles with the new alleles of combination. The genetic variation will be introduced through random fertilisation of the genes produced by meiosis. When the cell divides during meiosis, the homologous pair of chromosomes is distributed to the daughter cell. All their offspring are heterozygotes (genotype RW), displaying both white and red fur. Codominance is an example of Non-Mendelian inheritance.
The general basis for the law of independent assortment remains in the stage of meiosis 1 of gamete formation, when homologous pairs are lined up in a not-so-obvious orientation at the center of the cell as they prepare to part. Meiosis can result in genetic variation for random fertilisation, mutation, crossing over between the chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, and ultimately for random mating in organisms.
Independent assortment in meiosis takes place in eukaryotes during metaphase I of meiotic division. It produces a gamete carrying mixed chromosomes. Gametes contain half the number of regular chromosomes in a diploid somatic cell. With is independent assortment mutation, Activation of proto-oncogenes also called as activating mutations can occur either by large-scale alterations, such as gain/amplification, insertion, or chromosome translocation, or by small-scale mutations, such as point mutation.
Is independent assortment Mendelian?
Although Mendel’s principle of independent assortment states that alleles of different genes will segregate independently into gametes, in reality, this is not always the case.
Mendel’s law of independent assortment states that the alleles of two or more different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene.
The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop. Independent assortment of genes and their corresponding traits was first observed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 during his studies of genetics in pea plants. With is independent assortment mutation, formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of each diploid pair of homologous chromosomes into each gamete independently of each other pair is so.
When cells divide during meiosis, homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed to daughter cells, and different chromosomes segregate independently of each other. This called is called independent assortment. It results in gametes that have unique combinations of chromosomes. Independent assortment states that the inheritance of various genes occurs independently of each other. In the law of independent assortment, the combination of genes and their probability is calculated and assumed by multiplying the probabilities of each gene.
Non-Mendelian traits are traits that are not passed down with dominant and recessive alleles from one gene. Polygenic traits are considered non-Mendelian because their alleles are located on more than one gene which allows for more alleles and phenotypes. Examples of polygenic traits are hair color and height. Non-Mendelian inheritance includes extranuclear inheritance, gene conversion, infectious heredity, genomic imprinting, mosaicism, and trinucleotide repeat disorders.
Also Read: