In this article, we get to know about the Do Proteins Contain Carbon; carbon based proteins, their structure and interaction in protein synthesis.
One of the fundamental components of living organisms is protein. Peptide bonds connect the longer amino acid residues that constitute polypeptides. There are around 20 amino acids, with carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur being the most common elements in each.
What proteins contain carbon?
Since most of the proteins are structural, a large number of them are regulatory proteins known as enzymes. Like carbohydrates and lipids, they are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, but they also include nitrogen, sulphur, and phosphorus quite frequently.
Do all proteins contain carbon?
Along with carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms, all proteins also contain atoms of nitrogen and sulphur. Many proteins also contain phosphorus atoms and minute amounts of other elements. In living organisms, proteins have a number of activities, and these biological functions are frequently used to categorise proteins.
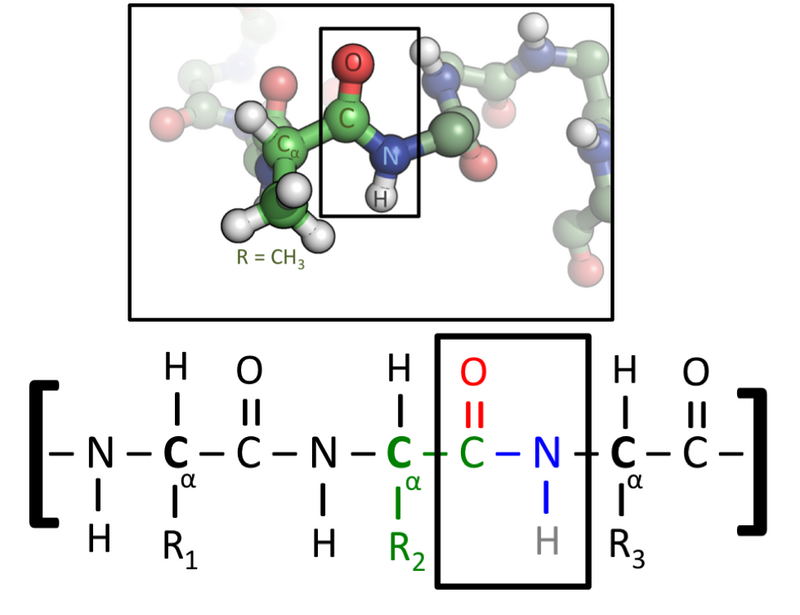
Why does protein have carbon?
Carbon is the only atom contributes towards force. Proteins prefer to have 31.44% of carbon. A protein’s structure and function are determined by its particular amino acid sequence.
Is there any protein without carbon?
Each amino acid contains a carboxylic acid end and an amino end. Hence there is no protein without carbon atom exists in the nature. There could be no free rotations around the carbon-nitrogen bond because it is partially a double bond.
How much of carbon is there in protein?
It is observed that proteins prefer to have 31.44% of carbon. The core always contains more than this proportion since hydrophobic groups have a propensity to bury within it. Research is done on the carbon content of proteins from various species. Between 25 to 40 percent of the carbon is present.
Do proteins need carbon?
Carbon serves as the macromolecules’ primary building block. Because of its special abilities to establish covalent interactions with up to four different atoms, the carbon atom is ideally suited to function as the fundamental structural element or “backbone,” of the macromolecules.
Ex: Between amino acids, peptide bonds—also referred to as covalent bonds—are created. Interactions are formed by the combination of an amino group from one amino acid and a carboxyl group from another amino acid. Chains of amino acids called polypeptides are joined together by peptide bonds.
Use of carbon in proteins?
Structural integrity and stability to the proteins. Every molecule contains a core carbon (C) atom known as the α-carbon, whereby an amino (NH3) group and a carboxylic (-COO) group are both attached. The final two bonds of the α-carbon atom are normally filled by a hydrogen (H) atom and an R group.
Ex: 12 of the amino acids are synthesised by human body; the remaining amino acids are obtained from the foods that we eat, including meat, beans and nuts.
Do proteins contain carbon bases?
Of all the carbon-based compounds in creatures, proteins are the most diverse. The majority of the elements that constitute living organisms are built on carbon atoms. Carbon atom is the core element in the basic structure of proteins.
Do nucleic acids contain carbon?
A group of virtually similar building components called nucleotides make up the long, chain-like molecules known as nucleic acids. A pentose (5-carbon) sugar is attached to a phosphate group that is subsequently joined with an aromatic base by a nitrogen bond in each nucleotide.
How many carbon bases are there in protein?
Proteins include four amino acids, each with four carbon atoms; they are aspartic acid, asparagine, threonine, and methionine. Animals are capable of synthesising the prevalent aspartic acid and asparagine.
a. How many carbon bases are there in protein structure?
The main carbon atom is connected to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a side chain or R group and a hydrogen atom. Proteins contain the four amino acids aspartic acid, asparagine, threonine, and methionine, each of which has four carbon atoms.
Ex: Structure: A protein is a polymer synthesized from amino acid monomers. Molecules called amino acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur on sometimes. 20 distinct amino acids are used by organisms to synthesize proteins.
b. How many carbon bases are there in protein synthesis?
The genetic info. needed to make proteins is carried by DNA. The genetic code is made up of the four nucleotides A, T, C, and G. The amino acid sequence in a protein is determined by the base sequence. Totally four carbon bases are present in protein synthesis.
c. How many carbon bases are there in protein molecules?
As a result, the ratio of the acidic carboxyl groups of aspartic and glutamic acids to those of the amino acids having basic side chains is probably identical. Proteins comprise three of these fundamental amino acids, each of which has six carbon atoms.
Conclusion:
In this article, we studied about the carbon role in protein structure and their interactions with other groups and importance of carbon in macromolecules.
Also Read:
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Transplanting plants examples
- Chromosome structure
- Plant cell parts and functions
- Monera examples
- Generalist species examples
- Nonvascular plants examples
- Is cytosine a pyrimidine
- Is bromelain an enzyme
- Foliose lichen
Hi….I am Ganeshprasad DN, completed my Ph.D. in Biochemistry from Mangalore University, I intend to use my knowledge and technical skills to further pursue research in my chosen field.


