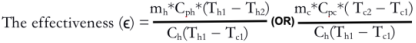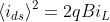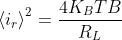Pressure vessel definition | what is pressure vessel | high pressure vessel | large pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a container that holds a lot of pressure.
It is a container that is designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure.
It is a closed vessel with the capacity to store high pressure liquids or gases at internal or external pressures, regardless of the pressure vessel’s size, shape, or dimensions.
The liquids/gases are contained in these leak-proof vessels. These containers are designed based on the application’s purpose.
Depending on the pressures, the operating temperatures of the containers change.
The vessel works on the internal preconditioning pressures that are lower or higher than the air pressure.

Pressure vessel stress | Hoop stress pressure vessel
Due to external tensile forces acting on the container’s internal surfaces, the container was able to resist the gas pressure. The thickness of a pressure vessel is proportional to the radius of the tank and inversely related to the maximum allowable normal stress of the material for the container’s internal surface.
The normal tensile stress is related to the vessel’s pressure and radius, but inversely proportional to the vessel’s thickness.
Pressure vessel fabrication | pressure vessel fabrication techniques | pressure vessel fabrication process:
Pressure vessel fabrication is an complicated process.
For the fabrication and assembling of the parts the steps required are follows:
Select the material for the fabrication.
cutting and burning of the material as per the requirement
machining of parts
cooling of weld and sand blasting
Assembling and welding of parts
Fabrication processes basic conditions:
Design conditions.
Procedures for welding to be used
Welding Specifications
Procedures for heat treatment will be used.
Requirements for non-destructive testing
Pressures should be tested.
Pressure vessel inspection | pressure vessel testing requirements | pressure vessel testing standards:
Construction of the container is tested to check the cracks, defects or any other existing failures.
Hydrostatic test:
Hydrostatic test use water for the test. This test is safer method as it releases small amount of energy whenever fracture occurs.
Pneumatic test:
Pneumatic test use air or gas for the test.
mass production often represent samples testing for the destruction in controlled environment.
Testing on pressure vessel is done to make sure the vessel is free from the defects, cracks or any other failures .
Visual Tests (VT):
Visual test is a type of test that provide information and overview regarding the pressure vessel by the observation of the internal and external substances of the tanks.
Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT) is a form of pressure vessel test that uses thin liquids as a penetrant on the pressure vessel’s surface. The fissures in the vessel’s surface are readily visible. Using a chemical and a penetrant, proper visualization can be observed under UV light.
Magnetic particle testing is performed in conjunction with magnetic current to detect flaws. Whenever there is a defect ,there will be disturbance in the magnetic current.
Radiographic Test (RT):
This type of test is tested using the X-rays to find out the defects on the external or internal surfaces of the vessel.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT):
Ultrasonic testing is the testing that detect the defects using the sound waves.
Whenever there are cracks on the external and internal surfaces of the vessel, the ultrasonic waves experience disturbances.
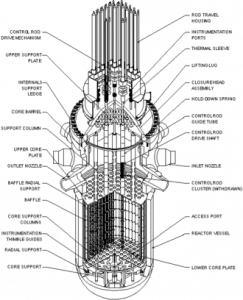
Reactor pressure vessel:
A reactor pressure vessel is a nuclear power plant that contains nuclear reactor coolant, a shroud, and the reactor core.
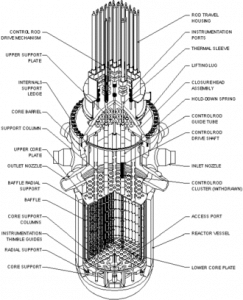
The classifications are as follows:
Reactor for light-water –
Reactor with graphite as a medium –
Thermal reactor cooled by gas –
Heavy-water pressurised reactor –
Reactor cooled by liquid metal –
Reactor for molten salt –
Components of the reactor vessel:
Body of the reactor vessel:
The large component containing the fuel assembly, coolant, and fittings to support coolant structures is the reactor body.
A reactor head is attached at the top of vessel.
Assembling the fuel:
The fuel assembly of nuclear fuel, which is typically composed of uranium or uranium–plutonium mixtures.
Typically, it is a rectangular block of gridded fuel rods.Reactor vessel body
Ammonia pressure vessel:
It is a Low pressure vessel.
In this container Ammonia is force fed for the storage by the circulation at low pressure in the vessel.
Pressure vessel material | High temperature pressure vessel material:
Carbon steel (low carbon)
Carbon manganese steel
Steel alloys
Non-ferrous materials
Use of pressure vessel | purpose of pressure vessel
Pressure vessels are primarily used to store gases and liquids at high pressures.
Pressure vessel applications are based on the requirements:
Industry of Oil and Gas: A container is used as a receiver at high temperatures and pressures.
Chemical Industry: It is a pressure vessel in which a process (chemical reaction) needs to take place, culminating in a fundamental change in the container’s content.
Energy (Power Generation) Industry: The energy (power generation) industry emits polluted gases.Therefore pressure vessels are used to store such gases. nuclear power plant uses reactor pressure vessels.
Pressure vessel head types | different types of pressure vessel heads:
There are different types of tank heads and they vary according to the shape according to the advantage to the application:
Ellipsoidal Head:
Most economical.
H=1/4D (Height =H, Diameter =D) has a radius ratio of 2:1 on the major and minor axes, allowing it to withstand greater pressure.
Head with a Hemispherical Shape
This is a more spherical head, with a radius equal to the tank’s cylindrical section.
It aids in the even distribution of pressure across its surface.
The dish and cylinder share a toroidal-shaped transition known as the knuckle.
type 4 pressure vessel:
Type 4 pressure vessel is all carbon fibre pressure vessel containing polyamide or polyethylene plastic.It has low weight and high strength.carbon fibre gives more strength to the vessel that it can sustain high loads.It also increases the corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance of pressure vessels. This type of vessel has maximum volume , Hence it has capacity to store hydrogen at high pressure.
type V pressure vessel:
high-volume pressure container of type v Type V approaches depend on advancements in three major technological fields: materials, design, and tooling.
It uses single material to manufacture a laminate system that gives structural strength at high pressures. It also form barrier layers to persist fluids and gases substances.
Conical head pressure vessel:
Conical Head:
It is also called as tapered tank head. It is used for vessel bottom or cover plates.
It has concentric cone shape.
The conical shaped head contain large and small end cone.
Applications:
Depending on the thickness of the material it can be equipped with around 8000 mm dia. and wall thickness of 20mm.
The conical head forced on the bottom of the pressure vessel to accomodate internal materials and connect two stage vessels of different diameters.
Difference between boiler and pressure vessel:
A pressure vessel is a container which contains the fluids ,gases or combination at high pressures. whereas a boiler is a container that contains the liquid that is water such that it can be boiled by the heat source at higher temperatures.
Pressure vessel dished ends dimensions | pressure vessel end caps:
Dished ends are the caps that are attached to the end of the main body by welding process.
They are manufacured using diffrenet methods so as to reach the application requirements taht depends on the type of dished end.
The type of each dish end gives the characteristics of the end caps.
For plate thicknesses of 25 mm / 1.0 inch or greater.
Plates with a thickness of less than 25 mm / 1.0 inch.
For plate thicknesses of 25 mm / 1.0 inch or greater.
Pressure vessel plumbing:
The pressure vessel is the container having switches that control the opening and closing of the container.
It requires minimal amount of pressure when the tap is opened and it slacks when the tap is closed.
When it reaches to the lowest pressure, the pump stops and the pressure also starts dropping.
The pressure then drop in the pipes to the on switch pump and pump starts again.
Pressure vessel failure modes include ductile rupture, brittle fracture, and abrasion.
abnormal deformation,
insecurity (buckling),
ratcheting (progressive deformation),
fracture due to fatigue,
rupture due to creep,
ratcheting creep,
interaction between creep and fatigue,
buckling creep,
and the impact of the environment on cracking.
Heating pressure vessel | central heating pressure vessel:
An heating pressure vessel is the expansion tank. It is a small tank and protects closed water heating which are not open to ambient temperature.
systems and hot water systems from high pressures.
The container contains air having compressibility cushion shocks caused by hammering and absorbing excessive water pressure caused due to the thermal expansion.
Domestic applications
Automotive applications
Hot water expansion vessel pressure setting | expansion vessel pressure setting:
water pressure should be -60 Psi.
Thermal expansion container contains an pressurized compressed air. It expands and contracts in response to the expanded water from the water heater.
Check the expansion tank’s air pressure.
Pressure vessel with lug support:
Vertical vessels with a height-to-diameter ratio of 2-3 are typically equipped with bracket supports. These are made of plates and attached to the vessel with the shortest possible weld length.
- It is less expensive.
- Can be easily attached to the vessel with a short weld.
- It is simple to level.
- If a sliding arrangement is provided, it can absorb diametrical expansions.
- Because of their ability to absorb bending stresses eccentrically of loads, thick wall vessels are best suited for them.
In order to measure the liquid level in a pressure vessel, the gaseous pressure in the vessel’s head must be measured with a second transducer. To obtain the hydrostatic pressure due only to the column of liquid, subtract the head pressure from the overall pressure.
Pressure vessel operation | pressure vessel operation principle:
These vessels operate by reaching a specific level of pressure to meet the application’s requirements. The design is specification of the vessel is the application purpose such as storing ,containing , heat exchange and chemical reaction processing of the products.
Valves, release gauges or heat transfer are used to proper delivery in the vessel.
The pressure level of the the normal atmospheric pressure is approximately 15 psi and it cam increase up to 15000 psi.
Replacement pressure vessels:
Repair of the pressure vessels is done to maintain its operating conditions.
The replacement should be in order to maintain the safe operations and to maintain trouble free service.
The vessel condition repair contains following considerations:
mechanical problems,
Rules for construction of pressure vessels:
The pressure vessel construction requires specific prohibition and non mandatory guidance for the material slections , design of the vessel, design of the components , inspection and testing of the vessel and the parts ,markings and the reports , high pressure protection and certifications of the vessels .
The pressure applied on the internal and external surfaces of the container should be between 10-10000psi ,it may go up to 70000 psi that is the maximum limit.
pressure vessels can be fired or unfired.
The pressure applied can be from external sources or the application of heat transfer.
Vertical pressure vessel:
Vertical vessel is the orientation of the vessel which represents the container in the vertical direction(upright).
It has different supports than the horizontal pressure vessel. It fits with different types of supports foe example skirt and lug that is able to hold the weight of the vessel.
They can perfectly fit into the small spaces.
Water pressure vessel design | hydrostatic pressure vessels | hydrostatic test procedure for pressure vessel:
Hydrostatic testing uses water for the test.
It includes components such as piping systems, gas cylinders, boilers, and pressure vessels.
Theses components are tested to check the strength and any kind of leakage from the system.
Hydro tests are quite required for the repair and replacements pf the equipment that will operate under the desired conditions.
Hydrostatic test is the type of pressure test that can work by using the water and filling water in the components that removes the air contained within the system. and it pressurizes system with up to 1.5 times the design pressure.
What is unfired pressure vessel:
This is type of the vessel that gains the heat from the source either directly or indirectly.
To avoid overheating such containers should observe the caution measurement while handling the system.
Industries that utilize unfired pressure vessel:
petrochemical
power generation
oil and gas
Types:
Thermal oil heaters
Boilers.
Proof testing pressure vessels:
Proof pressure testing is the testing used to verify whether a component can sustain the pressure above the operating pressure without any permanent damage to the system. It is a form of stress that can demonstrate the fitness of the expansion joint under the high pressure conditions.
The test can also prove whether the component can sustain the high pressures. It is a non-destructive testing procedure, as opposed to other methods.
Different types of nozzles in pressure vessels:
Radial Nozzle
Non-Radial Nozzle
Hill Side Nozzle
Tangential Nozzles
Angular Nozzles.
Pressure vessel closures:
The pressure vessel closures provide closure guidance.
These are commonly employed in medium to large pressure containers.
It also has locking mechanisms and attachments for secure use.
Pressure Vessel Closures Have Arrived.
Products are available.
Closures for Pressure Vessels
Aluminum pressure vessel:
Aluminum is being investigated as a replacement for stainless steel, with the major draw being its lower density and the expectation of a significantly lower tare weight.
Pressure vessel with cladding:
A cost-effective solution is to apply a layer of corrosion-resistant material of appropriate thickness to the equipment’s contact surfaces, made of a cost-effective and structurally strong material such as carbon steel.
The technique of integrating two layers of different materials is known as cladding or lining.
While the word Lining is broad and can refer to a variety of materials, the term Cladding is used when the corrosion-resistant layer given is metallic and well-bonded to the surface. As a result, the word Cladding is frequently used to refer to steel-fabricated equipment such as pressure tanks and shell and tube heat exchangers.
Column pressure vessel:
Pressure vessels operate at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure, whereas columns operate at atmospheric pressure.
Furthermore, pressure vessels are subjected to pressure on all sides of their internal surfaces.
This is in contrast to columns, which only experience pressure in one direction.
Pressure vessels are built to hold liquids and gases at high pressures.
A column’s principal function, on the other hand, is to separate gases from liquids using trays.
In summary, you can select high performance pressure tanks using the information in this guide.
Ultrasonic testing of pressure vessels:
Ultrasonic testing is the testing that detect the defects using the sound waves.
Refers to the thickness of the material’s plate. Whenever there are cracks on the external and internal surfaces of the vessel, the ultrasonic waves experience disturbances.
Difference between pressure vessel and storage tank:
The primary distinction between a pressure vessel and a storage tank is that pressure vessels contain liquids or gases at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure.
Storage tanks, on the other hand, contain liquids or gases under normal air pressure.
Because pressure vessels can be highly catastrophic, they have more stringent safety requirements.
Storage tank safety design requirements are not as stringent as those of their counterparts.
Different types of pressure vessels:
Pressure vessel types depends on the design of the vessels for the functionality of the applications in the industries. Mainly pressure vessels can be divided into the types according to their purpose for the applications. According to above factors mainly pressure vessels have three types:
Storage vessels:
These tanks are mainly useful for the industrial applications. These typically used in horizontal or vertical manner. It can be available in any size ranges. It is available in variable shapes like cylindrical or spherical for their vertical or horizontal manners. The material used in for the manufacture of the the type of product is carbon steel considering the external environment.
Such vessels need careful construction as the internal substances can be damaged without proper maintenance.
Process vessels:
Process vessels are designed as per the requirements of the application while construction to reach the required specifications. Various processes can be performed in pressure vessels.
Pressure vessels can be used combined with other products as per the application requirements.
So the manufacturing material required for such vessel components can be of unique material or multiple different materials.
Other types include:
High-Pressure Vessels: Autoclaves
- Tanks for Expansion,
- Exchangers of heat,
- Tanks for high-pressure water,
- Tanks for Vacuuming,
- Pressure Vessels ASME,
- Pressure Vessels with thin Walls,
- Boilers are closed pressure vessels that heat fluids, most commonly water.
Jacketed pressure vessel | Pressure vessel jacket | Design of a jacketed pressure vessel:
A jcketed vessel is a container designed to control the temperature of its contents by encircling the vessel with a cooling or heating “jacket” through which a cooling or heating fluid is circulated.
A jacket is an exterior chamber that facilitates consistent heat exchange between the fluid moving in it and the vessel’s walls.
Liner less composite pressure vessels (CPVs) have the highest pressure vessel efficiency (burst pressure x volume/weight) of any composite pressure vessel. They are also known as type 5 (type V) tanks in some sectors.
Pressure vessel for liquid nitrogen:
Cryogenic liquid cylinders are vacuum-jacketed, insulated pressure containers. To prevent the cylinders from pressure buildup, they are outfitted with safety release valves and rupture discs. These containers can withstand pressures of up to 350 psig and hold 80 to 450 litres of liquid.
Pressure vessel cleaning | Pressure vessel cleaning procedure:
Internal polishing.
Internal cleaning and drying is automated.
Cleaning with oxygen.
Flushing with de-ionized water.
Cleaning with steam.
Shotblasting on both the inside and outside of the building.
Rinses with solvents
Baking in the oven to remove contaminants.
Coating both internally and externally
NVR (non-volatile residue) analysis
Particulate matter counts
Surface finish is measured using a profilometer gauge (Ra)
Measurements of coating thickness
Dimensions of the anchor profile
Pressure vessel relief valve:
Pressure vessel relief valve is the device that protect the container by the release of high pressures.
The operation is automatic
Valve can be opened and closed. the valve is opened at certain level and and it closes when the level return back to normal position.
Pressure vessel safety checklist:
External inspection. Cracks, overheating, deformation, leakage.
Structural inspection
Geometric dimension inspection
Surface defect inspection
Wall thickness measurement
Material
Pressure vessel with the coating layer
Welding seam hidden defects inspection
Pressure vessel shear stress:
Cylindrical pressure vessel:
Maximum in-plane shear stress ( τmax(in plane)) =(pgr)/(4t)
Maximum out-plane shear stress (τmax(out plane)) =(pgr)/(2t)
Spherical pressure vessel:
Maximum in-plane shear stress (τmax(in plane))=0
Maximum out-plane shear stress (τmax(out plane))=(pgr)/(4t)
Pressure vessel welding requirements | pressure vessel welding ticket | pressure vessels welding process:
Pressure vessel welding is the joining process that is used to connect the metal plates of vessel using the heat or the pressure. It should be good quality that should sustain loading conditions.
Pressure vessel are used to store the liquids and gases at higher pressure rather than at atmospheric pressure. Welding of the container should be high quality structures and high strength materials as it should sustain the loading conditions.
If the good surface is used, then welding will be easy. There might be occurrence of the errors during the welding process.so it is required to apply some testing test to detect the errors.
Porosity is one of the major factor that can occur during the welding. porosity occurs mostly in any component during the welding process.It creates gas bubbles that look like voids during the testing.To avoid such defects it is advisable to use proper welding methods.
Another important factor is the nitride which is highly adherent contaminant. That can cause edges brittle and create porosity in welding processes.
Inclusions can be mixed with the weld pool and get stuck in the component during the solidification. This can be eliminated by using brush before the solidification.
Thin walled pressure | Thin walled pressure definition | Thin pressure vessel:
Thin walled pressure is the type of vessel that has wall thickness smaller than overall size of vessel.
t wall<r(vessel)
The internal pressure is higher than external pressure.
Thick walled pressure | Definition of Thick Walled Pressure:
This is a vessel with the a wall thickness that is 1/10 or 1/20 more than its radius. The wall encounters more circumferential stress on the interior surface and lessens as it approaches the exterior diameter.
Advantages of composite pressure vessels:
Better performance results.
Fibers carry the load on the composite.
The load on the fibers is distributed by the resin matrix.
The filament winding procedure is used to create a composite pressure vessel.
Air pressure vessel | Air receiver pressure vessel | Air pressure vessel testing:
Air pressure vessels are used to store the fluids, vapors and gases at high pressure.
It is also called as air pressure tanks, tanks storage and containment units.
Pressure testing is used to maintain the integrity of the vessels at high pressure levels.
Non-destructive test.
FAQ/Short Notes
How do you test a pressure vessel:
Testing on pressure vessel is done to make sure the vessel is free from the defects, cracks or any other failures .
Visual Tests (VT):
Visual test is a type of test that provide information and overview regarding the pressure vessel by the observation of the internal and external substances of the tanks.
Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT):
This is a technique of test in which transparent liquids are used as penetrants on the surface of a pressure vessel.
It shows clearly the cracks on the vessel surface. Under the U.V. light, proper visualization can be observed using fluorescent chemical with the penetrant.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT):
Magnetic particle testing detects defects by using a magnetic current.
whenever there is a defect ,there will be disturbance in the magnetic current.
Radiographic Test (RT):
This type of test is tested using the X-rays to find out the defects on the external or internal surfaces of the vessel.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT):
Ultrasonic testing is the testing that detect the defects using the sound waves.
Whenever there are cracks on the external and internal surfaces of the vessel, the ultrasonic waves experience disturbances.
What is the distinction between a pressure vessel and a storage tank?
The difference between pressure vessels and storage tank is that the pressure vessels works at higher pressures and storage tanks works at normal atmospheric pressures.
Storage tanks store the fluids.
Pressure vessel hold the fluids at high pressures.
Whenever a vessel reaches a certain pressure, it becomes a pressure vessel.
When pressures reach 15 Mpa or greater.
What is the frequency with which a pressure vessel should be tested:
At least once in every five years.
What are the uses of pressure vessels:
To hold fluids at high pressures.
High reactive chemicals , petroleum products can be stored at high pressures in pressure vessels.
For the heat exchange and removal of excess heat.
For the chemical reactions at certain pressures and temperatures.
Which material is used in manufacturing a pressure vessel:
steel made of carbon
Steels with low alloy content
Steels with a high alloy content
Carbon steel, manganese steel, and so forth.
Why are semispherical end caps used on cylindrical pressure vessels rather than flat ones:
Cylinders are used as they are less expensive than spheres but the spheres are more stronger at the corners. So the spherical or rounded ends are fitted at end caps rather than flat ones .
The following are some of the advantages of a spherical pressure vessel over a cylindrical pressure vessel:
Spherical pressure vessel has smaller surface area per unit than any other pressure vessel shapes. As there is lesser surface area, the amount of the heat transfer from the high temp area will be less than other shapes. So the spherical pressure vessel is more efficient than any other pressure vessels.
Figure 1: Spherical pressure vessel
Figure 2: Cylindrical pressure vessel


For more post on Mechanical related topics, please follow our page.