HOF is the chemical formula for hypofluorous acid. Here we are discussing about HOF lewis structure, characteristics and some facts about it.
HOF (hypofluorous acid) can also be written as FHO. HOF has some synonyms like fluoranol, fluoroalcohol, hydroxyl fluoride and fluoridohydridooxygen. HOF (hypofluoro acid) or fluoranol is an fluorine oxyacid which is a conjugate acid of hypofluorite. HOF has molecular weight of 36.006. HOF consists of three elements mainly hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine.
How to draw HOF lewis structure?
The lewis structure of HOF can be drawn by considering the following steps:
- Predict the group positions of hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine atoms on periodic table
- Count overall valence electrons available on HOF lewis structure.
- Selection of central atom which is most electronegative from all the atoms and the rest of the atoms are being bonding atoms.
- Make bonding within all H, O and F atoms of HOF lewis structure.
- Remaining valence electrons are put on the bonding atoms which are being non – bonding electrons.
- Then count the lone pair electrons on HOF lewis structure.
- Check whether the H, O and F atoms have complete or incomplete octet in HOF lewis structure.
- Finally predict the shape, hybridization and bond angle of HOF lewis structure.
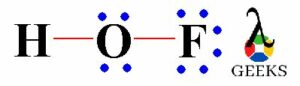
HOF valence electrons
The HOF lewis structure composed of three elements i.e. hydrogen atom, oxygen atom and fluorine. Thus, the hydrogen atom belongs to 1st periodic table group, oxygen atom belongs to 16th periodic table group and the fluorine atom belongs to 17th (7A) periodic table group. Therefore, the H, O and F atoms contain one, six and seven valence electrons respectively, in their valence shell outer orbital.
The total valence electrons available on hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine atoms of HOF lewis structure is calculated as follows:
Hydrogen atom of HOF lewis structure has valence electrons is = 01
Oxygen atom of HOF lewis structure has valence electrons is = 06
Fluorine atom of HOF lewis structure has valence electrons is = 07
Hence, total valence electrons on HOF lewis structure is = 1 (H) + 6 (O) + 7 (F) = 14.
Therefore, the valence electrons on HOF lewis structure are fourteen.
If we see the total electrons pairs on HOF lewis structure, the HOF valence electrons get divided by two.
Thus, total electron pairs on HOF lewi structure = 14 / 2 = 7
Therefore, there are seven electron pairs in MOF lewis structure.

HOF lewis structure lone pairs
The HOF lewis structure has total 14 valence electrons, out of which four electrons are the bond pair electrons which forms two single sigma covalent bonds with hydrogen and oxygen (H-O) atom and oxygen and fluorine (O-F) atom. Hence, the remaining 10 valence electrons go to O and F atoms.
Thus, the oxygen atom has four non – bonding electrons and fluorine atom has six non – bonding electrons on HOF lewis structure. These 10 non-bonding electrons of HOF are being the five lone electron pairs. Hence, the HOF lewis structure has total five lone electron pairs available on it two on O atom and three on F atom.
HOF lewis structure octet rule
There is two lone pair electrons are on oxygen atom and three lone pair electrons are on fluorine atom of HOF lewis structure. Hence, the hydrogen atom of HOF lewis structure has two bonding electrons satisfied it’s valency as per it capacity. The O atom contains 4 bond pair electrons (creates H-O and O-F bonds) and 4 non-bonding electrons.
Hence O atom of HOF lewis structure has eight electrons and have complete octet. The fluorine atom of HOF lewis structure has two bonding electrons forming O-F bond and also it has six non – bonding electrons. Thus, F atom of HOF lewis structure has total eight electrons and its octet is also complete. So, in HOF lewis structure the O and F atoms has eighit electrons which shows complete octet.
HOF lewis structure formal charge
The presence of formal charge on any lewis structure makes it more stable structure. Evaluation of formal charge on any molecules is done with the help of below given formula:
Formal charge = (valence electrons – non-bonding electrons – ½ bonding electrons)
The HOF lewis structure formal charge evaluation is done with the help of using above given formula. Here, first we have to evaluate the formal charge present on each hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine atoms of HOF lewis structure.
Hydrogen atom: Valence electrons on hydrogen atom of HOF = 01
Non- bonding electrons on hydrogen atom of HOF = 00
Bonding electrons on hydrogen atom of HOF = 02 (2e = one bond)
Thus, Formal charge on hydrogen atom of HOF lewis structure is = (01 – 00 – 2/2) = 00
So, the Hydrogen atom of HOF lewis structure contains zero formal charge.
Oxygen atom: Valence electrons on Oxygen atom of HOF = 06
Non – bonding electrons on Oxygen atom of HOF = 04
Bonding electrons on oxygen atom of HOF = 04 (2e = one bond)
Thus, Formal charge present on oxygen atom of HOF lewis structure is = (6 – 4 – 4/2) = 00
So, the oxygen atom of HOF lewis structure contains zero formal charge.
Fluorine atom: Fluorine atom has Valence electrons on HOF = 07
Fluorine atom has Non- bonding electrons on HOF = 06
Fluorine atom has Bonding electrons on HOF = 2 (2e = one bond)
Thus, Formal charge present on fluorine atom of HOF lewis structure is = (07 – 06 – 02/2) = 00
So, the fluorine atom of HOF lewis structure contains zero formal charge on it.
Therefore, the HOF lewis structure has overall zero formal charge present on it.
HOF lewis structure resonance
In HOF lewis structure, there is no multiple bonds are present and also even there is no positive or negative formal charge is present on it. Thus, there is even no movement of electrons as all the atoms of HOF lewis structure already has complete octet. Hence, HOF lewis structure cannot show any resonance structure.
HOF lewis structure shape
HOF acid follows AX2E2 generic formula of VSEPR theory. Here, A is central atom, X is bonded atoms with central atom and X is lone electron pairs on central atom. According to which the HOF acid has bent molecular shape and tetrahedral electron geometry.
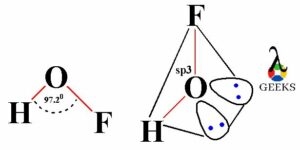
HOF lewis structure angle
The HOF acid has the bent molecular shape and tetrahedral electrons geometry as the central O atom has two bonding atoms and two lone electron pairs. Therefore, as per the VSEPR theory the HOF acid should have 109.5 degree bond angle. But in HOF the H-O bond angle is less than O-F bond angle, thus the bond angle of HOF get decreases and have 97.2 degree bond angle.
HOF hybridization
With accord to VSEPR theory module HOF lewis structure belongs to AX2E2 generic formula, so HOF shows bent shape and tetrahedral geometry. Also it has H-O-F bond angle of 109.5 degree. Thus, HOF (hyprflorous acid) acid has sp3 hybridization.
Why HOF has sp3 hybridization?
In HOF molecule, the central O atom has two bonds with H and F atoms and also it has two lone electron pairs. Thus as per VSEPR theory HOF molecule has tetrahedral electron geometry and sp3 hybridization.
HOF solubility
HOF is an explosive substance and mostly insoluble in most of the organic solutions. Thus when HOF get added to water it behaves as an intermediate substance for oxidation of water by fluorine. Also it get decomposes as O2 and HF molecules. Hence, HOF is insoluble in nature and also unstable.
Is HOF soluble in water?
Yes, HOF is soluble in water. When HOF gets added to water it shows rapid explosive nature of reaction and thus HOF acts as an intermediate substance for water oxidation by fluorine molecule. Also the decomposition of HOF acid gets occurs and it get dissociates into HF and O2 in alkaline condition. Also on reaction with water of HOF it can produce peroxide and hydrogen fluoride in acidic medium.
Is HOF a monobasic acid?
No, HOF is not a monobasic acid it gets ionizes as fluorine and oxygen when added to water. Thus it cannot act as monobasic acid.
Why HOF is not a monobasic acid?
Monobasic acids are those acids which can have only one detachable hydrogen atom (H+ ion) per molecule in water. All the halogen atoms can produce monobasic oxyacids except the case of HOF. HOF is also an oxyacid but it is not monobasic in nature.
HOF is an oxyacid but it is exists in unstable form. As on dissolving in water it shows explosive behaviour and thus decomposed as fluorine (HF) and oxygen (O2). Hence, HOF does not act as a monobasic acid in nature.
Is HOF polar or non- polar?
HOF is a polar acid in nature as it has asymmetrical arrangement of all atoms and the dipole creates get cancel each other.
Why HOF is polar?
In HOF molecule, there is more electronegativity difference between hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine atoms. The electronegativity difference between H and O atoms are 1.24 and electronegativity difference between F and O atom is 0.54.
Thus it creates a dipole within the molecule and developed the partial negative charge on central O atoms and partial positive charge on bonding H and F atoms. There is no electron density present on H atom. But the F atom has more electron density which pulls the electron cloud towards itself and hence cancels the dipoles in HOF molecule. Hence, HOF is a polar molecule.
Is HOF stronger than HOCl?
Yes, HOF acid is stronger than HOCl acid. The fluorine atom is more electronegative in nature than chlorine and thus HOF can be stronger than chlorine.
Why HOF is stronger than HOCl?
In oxyacids, the weaker the O-H bond the stronger is the acid as the H+ ions can readily dissociates. In HOF the O-F bond is quite stronger as compared to O-Cl bond in HOCl.
The atomic size of F atom is less than Cl atom and also F is more electronegative than Cl. In HOF the O-F bond is stronger due to which the O-H bond becomes weaker and hence HOF is stronger than HOCl.
Is HOF ionic or covalent?
HOF is not ionic because it is an unstable covalent compound having two H-O and O-F covalent bonds within HOF molecule.
Why HOF is covalent?
HOF acid is strong acid and has single sigma covalent bonds within H and O atoms (H-O) and O and F atoms (O-F). The covalent bond is a strong bond which does not breaks easily. Hence, the HOF cannot ionize easily and so it is a covalent acid.
Is HOF ionic hydride?
No, HOF is not ionic hydride because it is an oxyacid. Oxyacids formed when the halogen reacts with water.
Why HOF is not ionic hydride?
When halogen like fluorine reacts with water gives the production of unstable oxyacid like HOF (hypoflurous acid). HOF is an intermediated of oxidation of water and fluorine.
F2 + H2O → HOF + HF
Thus, HOF is being an oxyacid, so it is not ionic hydride.
Is HOF isoelectronic?
No, HOF is not isoelectronic in nature. HOF is only one oxyacid of fluorine atom. Isoelectronic compounds are those two or more compounds which has similar structure and similar atoms position and bonding with same electronic configuration but different in properties. HOF does not have any similar molecule and hence it is not isoelectronic.
Is HOF ionic or molecular?
HOF is molecular because it cannot form ions. HOF is a triatomic molecule consisting of three atoms i.e. hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine atoms. Also it is only the oxyacid of fluorine and on decomposition it forms molecules like HF and O2. Hence, it is a molecular and not ionic.
Is HOF ion dipole?
Yes, HOF has a net dipole moment of 2.23. In HOF molecule fluorine atom is more electronegative than O and H atoms and hence the net dipole pulls towards the F atom. Thus HOF acid has dipoles.
Conclusion:
HOF is only one oxyacid of fluorine. HOF lewis structure has 14 valence electrons and has 7 electrons pairs from them two are bond pair electrons and five lone pair electrons. There is no formal charge on HOF molecule and has covalent bonds within H-O and O-F. The HOF lewis structure has bent shape and tetrahedral geometry also it has bond angle of 97.2 degree. Hof is a polar acid.
Also Read:
- N2h2 lewis structure
- Nh2cl lewis structure
- Ccl2f2 lewis structure
- Hcooh lewis structure
- Scl4 lewis structure
- Cas lewis structure
- Hocl lewis structure
- Scl6 lewis structure
- Cai2 lewis structure
- Ch3cooh lewis structure

Hello everyone, I am Dr. Shruti M Ramteke, I did my Ph.D. in chemistry. I am passionate about writing and like to share my knowledge with others . Feel free to contact me on linkedin