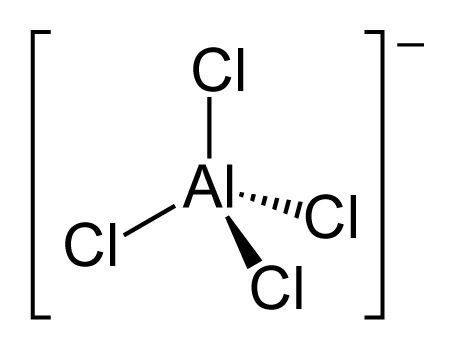
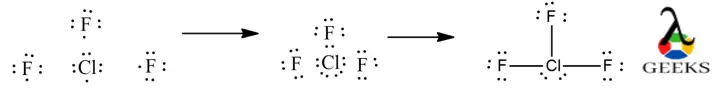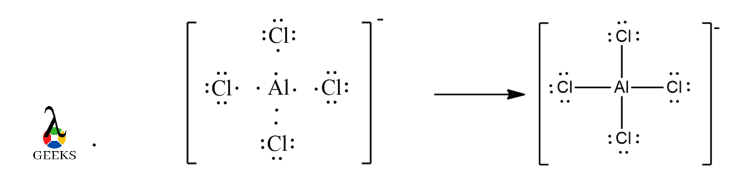Here, we shall learn how to draw ClF3 lewis dot structure, to count valence electrons, octet rule, its solubility and other such important characteristics.
ClF3 lewis structure is an inter-halogen compound that plays a very important role as solvent, in nuclear chemistry, therefore knowing ClF3 lewis structure, its bonding and connectivity with atoms is very crucial.
ClF3 lewis structure is a simple electronic representation of the skeletal structure of the molecule, about how the electrons are arranged around the atoms.
How to draw ClF3 lewis structure ?
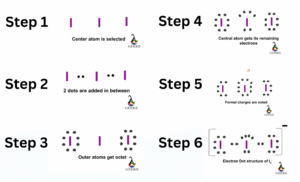
- ClF3 lewis structure can be drawn by first by counting the total valence electrons of all the atoms combined. Cl has electronic configuration : [Ne]3s23p5 and F electronic configuration : [He]2s22p5. Therefore, it has a total of 28 valence electrons available.
- The central atom is chosen based on their electronegativity and a skeletal structure is drawn. Electronegativity of Cl = 3.16 and F =3.98, thereby choosing Cl has the central atom.
- Each atom tries to fulfil its octet by accommodating 8 electrons around it to follow octet rule. A single bond is drawn from each atom with the valence electrons to the nearby atoms.
- The Cl is surrounded by a total of 10 electrons in the Lewis dot structure, thereby, violating octet rule.It can accommodate extra electrons apart from the 8 electrons already assigned through bond and lone pairs is, because it has expanded empty 3d shells.
- The remaining electrons not forming covalent bond will stay as lone pair of electrons.
Note: Elements having expanded valence shells like 3d elements, it can exceed the octet rule like SF6 , PF5 or elements with fewer valence electrons can have incomplete octet like H2 .
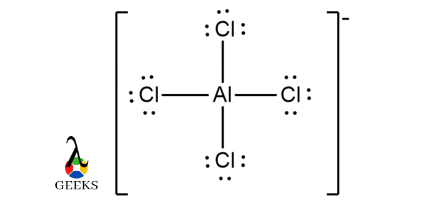
Construction of ClF3 Lewis Structure step by step :
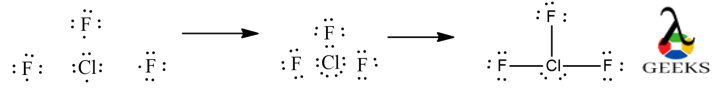
ClF3 lewis structure formal charge :
ClF3 lewis structure formal charge briefs about the electronic charge of each atom in a molecule based on the Lewis dot structure.
Generally, formal charge can be calculated mathematically by the formula :
Formal charge = (Number of valence electrons in a free atom of the element) – (Number of unshared electrons on the atom) – (Number of bonds to the atom)
In addition, Charge on the molecule= sum of all the formal charges.
Formal Charge of Fa , Fb , Fc = 7-6-1 = 0 (All the F atoms are equivalent)
Formal Charge of Cl = 7- 4- 3 = 0

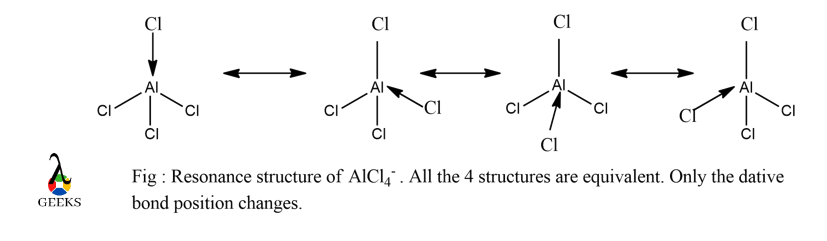
ClF3 lewis structure resonance :
In ClF3 lewis structure, all the F atoms are equivalent and they cannot form double bonds as their octet gets completed with a stable noble configuration when single bond formation with the central atom takes place.

ClF3 lewis structure octet rule :
Octet rule states that an atom tries to bond in a manner that allows them to take 8 electrons in their valence shell to fulfil their octet. However, many molecules with atoms that has expanded subshells can take up more than 8 electrons, thereby, violating octet rule.
Here, Cl has expanded subshell 3d orbital that is empty. It takes up 2 lone pairs of electrons and 3 bond pairs giving a total of 10 electrons in their outermost shell. Thus, it violates octet rule.
The F atoms take up 8 electrons as per octet rule as they do not have expanded subshells.
ClF3 valence electrons :
Cl electronic configuration : [Ne]3s23p5
F electronic configuration : [He]2s22p5.
Each F atom has 7 outermost electrons, there are 3 F atoms making a total of 21 valence elctcrons. Cl atom has 7 valence electrons.
Therefore, it has a total of 28 valence electons available.
ClF3 lewis structure lone pairs :
From the Lewis dot structure, it is evident that Cl has 2 lone pairs of electrons. Each F atom has 3 lone pairs of electrons.
The total lone pairs of electrons are 11 .
ClF3 hybridisation :
A simple method to calculate number of orbitals taking part in bond formation using VSEPR model is thorugh a mathematical formula given below :
Hybridisation of a molecule = ( Valence electrons of the central atom + Number of monovalent atoms attached to the central atom + Negative charge on the molecule – Positive charge on the molecule )/2
ClF3 Hybridisation = ( 7 + 3 – 0 – 0 )/2 = 5 = sp3d
The central atom is Chlorine. Its electronic configuration in ground state : [Ne]3s23p5 and the excited electronic configuration : [Ne]3s23p43d1 . There are two lone pairs of electrons, one in 3s and the other in one of the 3p subshells occupying the two of the 5 hybrid orbitals. The remaining 3 unpaired electrons, two in 3p subshells and one in 3d subshells will form bonds with the 3 F atoms.
It can be either Trigonal bipyramidal or Square pyramidal geometry.
It adopts a trigonal bipyramidal geometry (Fig: a) as the lone pairs are at 1200 to each other which prevents from steric repulsion of the lone pairs as well as the bond pairs.

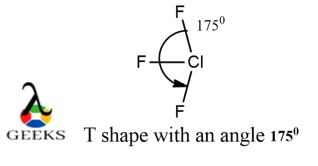
ClF3 lewis structure shape :
When we talk about shape of a molecule, we do not consider their lone pairs hybridization. Therefore, the shape is about how the bond pairs are oriented in spatial dimension which gives ClF3 a T-shaped structure.
The F atoms in axial position are not exactly at 900 but somewhat at 880 due to lone pair- bond pair repulsion.

ClF3 lewis structure angle :
The angle is not exactly 1800 but less than it as there is lone pair- bond pair repulsion which exceeds the bond pair-bond pair repulsions. It has approximately an angle of 1750 . Also the F atoms in axial position are not exactly at 900 but somewhat at 880 due to lone pair- bond pair repulsion.
Is ClF3 acidic or basic ?
It is surprising to know this interhalogen compound can act as both Lewis acid and Lewis base.
In other words, this can be termed as amphoteric. As a result, they are mainly used for establishing a solvent system.
The reaction below shows how ClF3 acts as a base and an acid in different conditions :
AsF3 + ClF3 à [ClF2]+ [AsF4]– Here, [ClF2]+ , a cationic species is formed, therefore, it acts as an acid.
ClF3 + NOF à [NO]+ [ClF4]– Here, [ClF4] , an anionic species is formed, therefore, it acts as a base.
Is ClF3 ionic ?
No, it is not an ionic compound.
This AX3 form of interhalogen compounds do not have great electronegativity difference.
It is a covalent liquid with ionic percentage less than 40% as per Fajan’s rule. Cl has electronegativity of = 3.16 and F = 3.98 whose difference is not appreciable enough to consider it as an ionic compound.

Is ClF3 polar or nonpolar ?
It is a polar interhalogen compound. This can be justified by considering the dipole vectors.
The compound is not perfectly T shaped so the F atoms in axial positions do not cancel each other. Furthermore, the dipoles’ vectors adds up to the axial vectors which gives a resultant vector of greater magnitude than the vector in the opposite direction.
Thus, some magnitude of dipole moment is left which makes the compound a polar one.

ClF3 solubility :
ClF3 is a very reactive gas so its solubility in different solvents have to be checked properly before dissolving it in it. Few solvents in which it is soluble are listed below :
- Benzene
- Toluene
- Acetic acid
- Hexane
It is soluble in these solvents retaining its stability but at lower concentration. It explodes at higher concentration.
Is ClF3 tetrahedral ?
No, ClF3 cannot be tetrahedral. According to VSEPR model of hybridization, its geometry is trigonal bipyramidal as it is most stable in that form with less steric repulsion.
Is ClF3 linear ?
No, ClF3 is not a linear molecule.
The molecule is considered to be planar as the orientation of the central atom Cl and the surrounding atoms F forming bonds with Cl are arranged in a T-shaped manner but it is not a linear molecule. Its shape is strictly limited to T-shaped which is not linear in real sense.
Conclusion :
ClF3 is an interhalogen compound with trigonal bipyramidal geometry , sp3d hybridisation and planar T-shaped which is mainly used in solvent system.
Also Read: