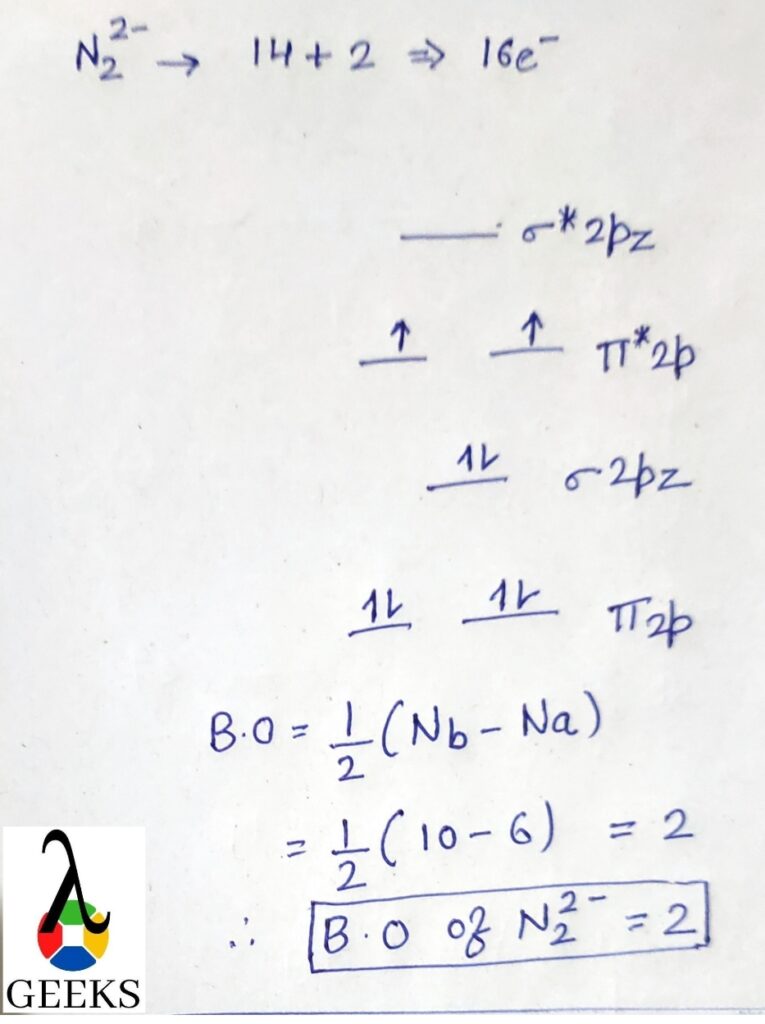This article is regarding Brf5 lewis Structure, characteristics, and properties of Brf5.
Bromine pentafluoride, commonly known as Brf5, is a chemical used in the uranium processing industry and as a propellant for rockets. There is a liquid associated with this that is corrosive.
It becomes highly toxic and combustible when it reacts with organic matter. Brf5 lewis structure is an interhalogen compound with properties of Fluorinating.
How to draw Brf5 lewis structure?
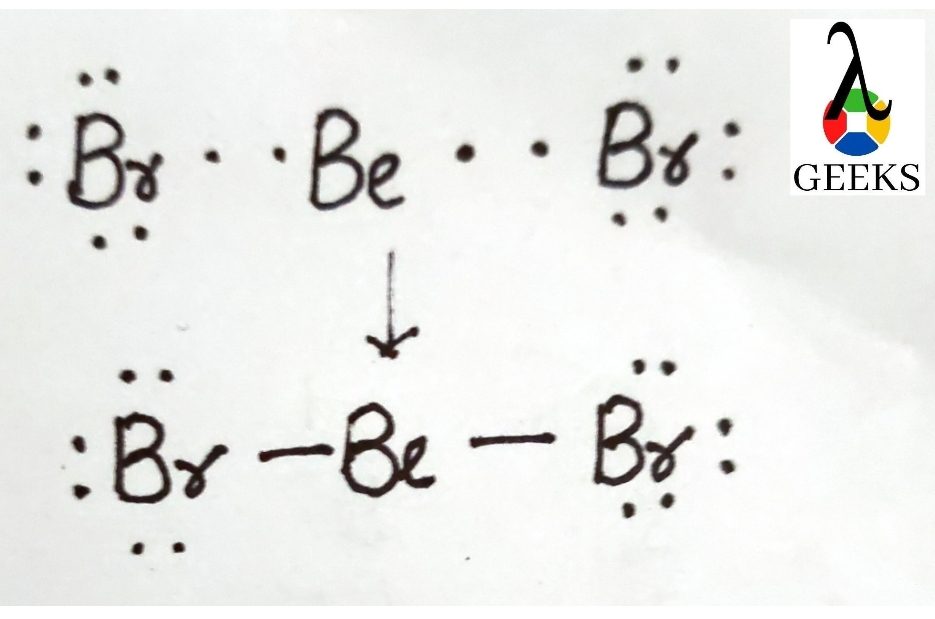
In its outermost shell, bromine has seven valence electrons, which makes it a member of the halogen family. The halogen family also includes fluorine, which has 7 electrons in its outermost shell. So Bromine shares 5 electrons with fluorine and forms covalent bonds.
Bromine valence electrons = 7
Fluorine valence electrons =7*5 =35
Total valence electrons = 42
Thus total electron pairs for bonding = 21, and participate in bond formation.
and remaining 1 pair as a lone pair.
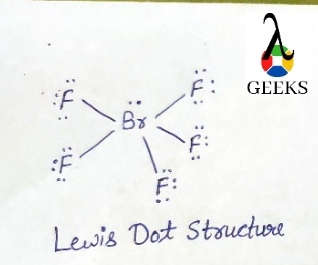
Bromine act as a central atom due to less electronegativity than fluorine. A Lewis dot structure consists of five Br-F bonds in Brf5.
Brf5 lewis structure resonance
In Lewis structure of Brf5 is composed of 42 valence electrons. We can distribute the valence shell around the nucleus to fill the outermost layers of each atom once we know how many there are in Brf5. There is no resonance observed in Brf5 and no isomers exist in Brf5.
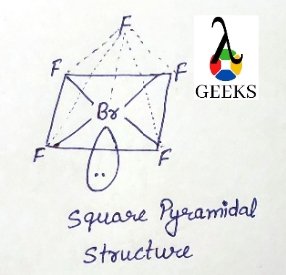
The bromine (Br) atom makes up one of the five fluorine atoms in Brf5. While the bromine (Br) atom is in the center, the fluorine (F) atoms are scattered around it.
Brf5 lewis structure shape
Brf5 has a pyramidal square shape. It indicates that the basic atom has a single pair of electrons.
The square pyramidal effect of BrF5 molecular structures is due to the individual electron pairs on the core bromine atom.
Brf5 lewis structure formal charge
The formal charge is found as (valence electrons- nonbonding electrons-½ bonding electrons).
Formal charge on Br = 7-5-2 =0
Formal charge on F = 7-6-1 =0
The Brf5 Lewis structure has a zero formal charge.
Brf5 lewis structure angle
Brf5 has an octahedral shape with a 90-degree angle.
There is repulsion between each atom which should be explained by VSEPR Theory.
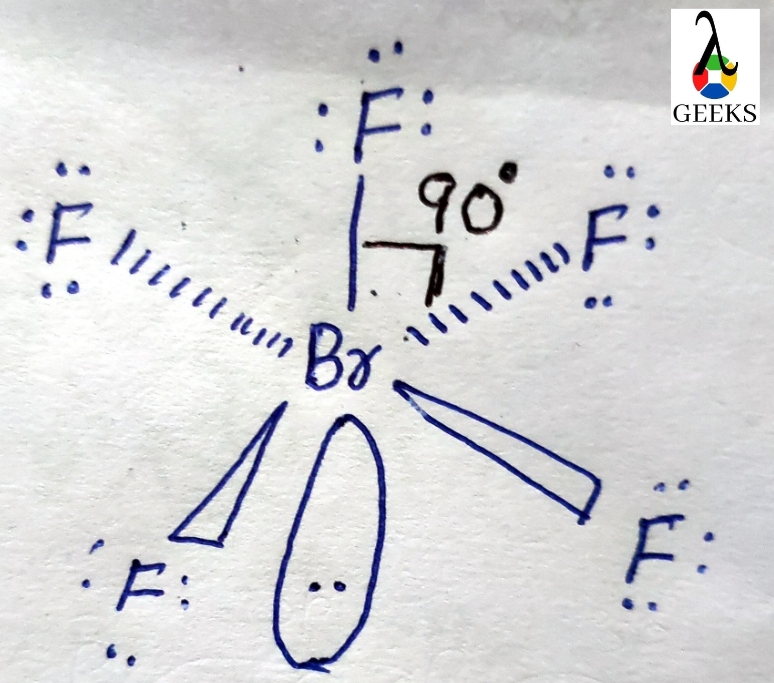
Brf5 lewis structure octet rule
A molecule needs eight electrons to complete its octet, which means they need 8 electrons in the outermost shell. This is known as the octet rule and is used to work out how close an atom is to a specific other atom or molecule.
In the Brf5 lewis structure, bromine (Br) belongs to period four, which means it has a valence electron capacity greater than eight. Once knowing that, how many electrons are present in Brf5, the distribution of electrons around the central atom is done. Thus Center atom Bromine in Brf5 lewis structure has expanded its octet.
Brf5 lewis structure lone pairs
Valence electron of Br = 7 and there are five sigma bonds present between bromine and fluorine atoms.
Hence, there is only one lone pair present in Bromine(Br) hybrid orbitals. These lone pairs of electrons are also called non-bonding electrons
Brf5 valence electrons
There are seven valence electrons present on the bromine(Br) atoms and seven valence electrons on fluorine(F) atoms. They both belong to the halogen family.
In total Brf5 consist of 42 valence electrons and is calculated as,
Bromine valence electrons = 7
Fluorine valence electrons =7*5 =35
Total valence electrons = 42
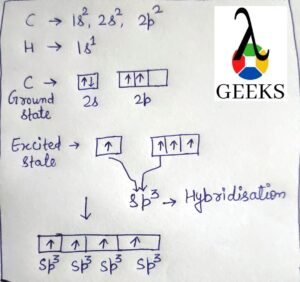
Brf5 hybridization
Bromine atom Electronic configuration: 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p63d104s24p5.
Or
Br = [Ar]4s2 3d104p5
Some electrons are shifted to 4d-orbitals to obtain a pentavalency. There are two p-orbital that are unpaired. Bromine atoms at this point are excited and their will occurrence of hybridization takes place.
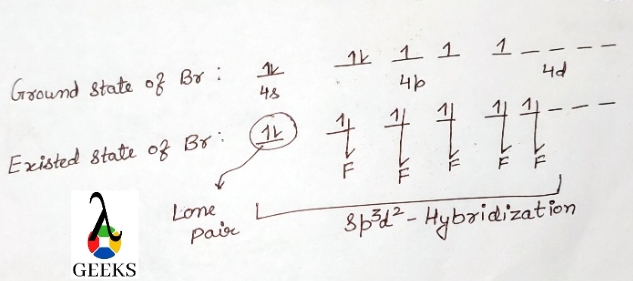
Four of the orbitals are 4s, three 4p, and two 4d, while the six steric nodes are involved in hybridization. So the Hybridization of Brf5 molecules is sp3d2. There is a five sigma bond formation that occurs between five fluorine atoms and five valence electrons of bromine.
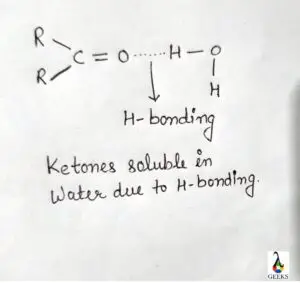
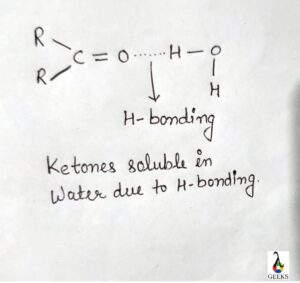
Brf5 solubility
Brf5 is soluble in water, it reacts with water violently and produces explosive and some toxic that is hazardous to human.
It is the fluorinating agent.
BrF5 + H2O —-> HBrO3 + HF
Bromine Boric
Pentafluoride acid
Is Brf5 ionic?
For a molecule should be ionic its electronegativity difference should be more and one atom consist of a partial positive and another atom should possess a partial negative charge. So in the case of Bef5 Bromine(Br) and Fluorine (F) have an electronegativity difference of less than 1.02, so they are not ionic.
Since all halogens are non-metals, this electronegativity difference can only exist between metals and non-metals, Brf5 is not ionic.
Is Brf5 acidic or basic?
Brf5 lewis structure is highly reacting with water and forms boric acids.
As a result of highly electronegative halogens in this molecular structure, the molecule reacts with a variety of organic substances, including water (H2O) also. Thus Brf5 lewis structure is having some basic properties because it acts as a metal fluoride and converts into [Brf4]+ and [Brf6]–.
Is Brf5 polar or nonpolar?
The molecules are polar when the electrons are not evenly shared between the atoms in their covalent bonds.
It is a polar molecule with a square pyramidal molecular geometry and an asymmetric charge density centered on the nucleus.
The molecule is composed of five fluorides surrounded by a central bromine atom and a lone pair of electrons.
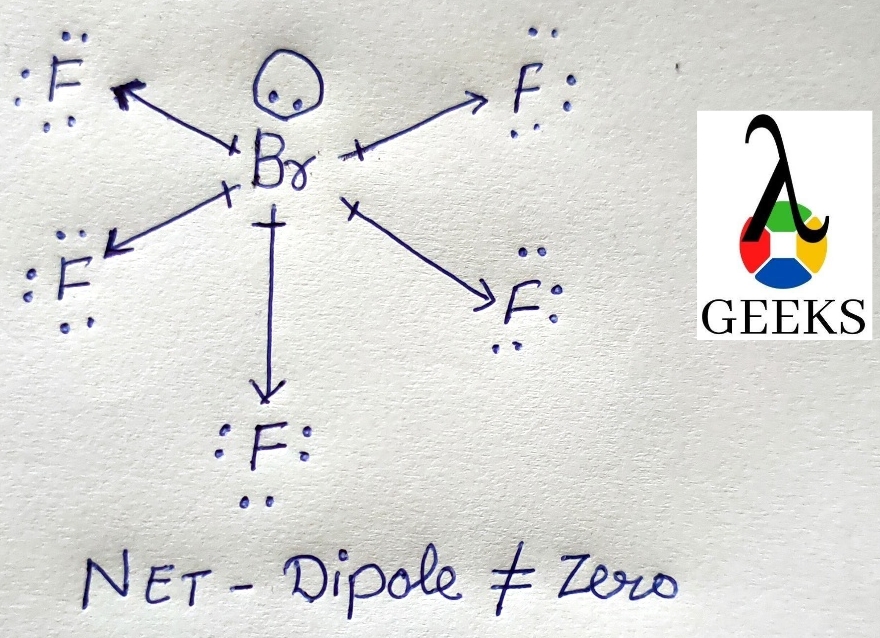
It is therefore polar. Thus Brf5 lewis structure gives information about the polarity of molecules and its reactivity is also explained through it.
In terms of structure, Brf5, or bromine pentafluoride, is similar to PCl5, which has a bipyramidal trigonal structure. As the Brf5 Lewis structure is completely symmetric around the central phosphorus atom, there is no net dipole moment.
Conclusion
It has been established above via various illustrations and facts that Brf5 is a polar molecule. However, it is mostly used in aeronautical rocket propulsion. It consists of 42 valence electrons in total, due to the asymmetrical distribution of electrons it shows square pyramidal geometry. BF5 is a powerful fluorinating agent.
Also Read: