Tosca Tutorial – Table of Content
We have broken the entire Tosca tutorial into the below list of articles. Now we are going to understand about the concepts of Tosca Test Case Design and Test Data management through out this tutorial. We have wrote this article with simple words and keep the write up shorts which help the new comer to understand the concept easily with lesser time.
- Tosca Tutorial #1: Tosca Overview
- Tosca Tutorial #2: Tricentis Tosca Setup – Install, Uninstall and License Configuration
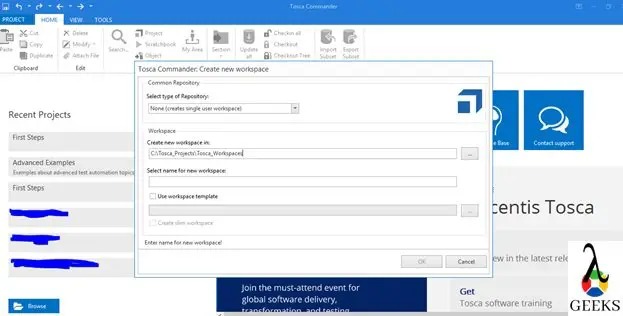
- Tosca Tutorial #3: Tosca Workspace Creation
- Tosca Tutorial #4: Understanding of TOSCA Commander and Tosca User Management
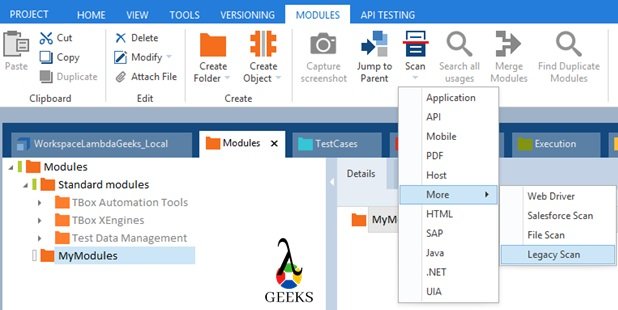
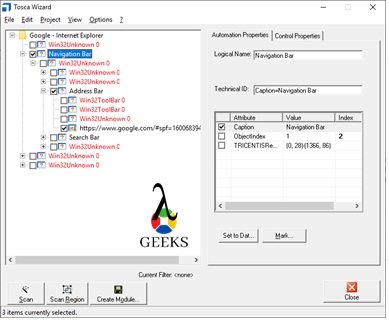
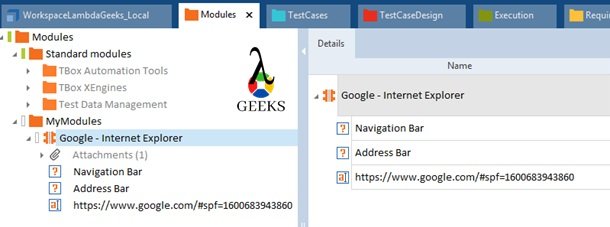
- Tosca Tutorial #5: Tosca Scanning – An Introduction to Modules
- Tosca Tutorial #6: Tosca Test Case Creation
- Tosca Tutorial #7: Tosca Parameters and Library– Buffer, Business Parameter, TCP
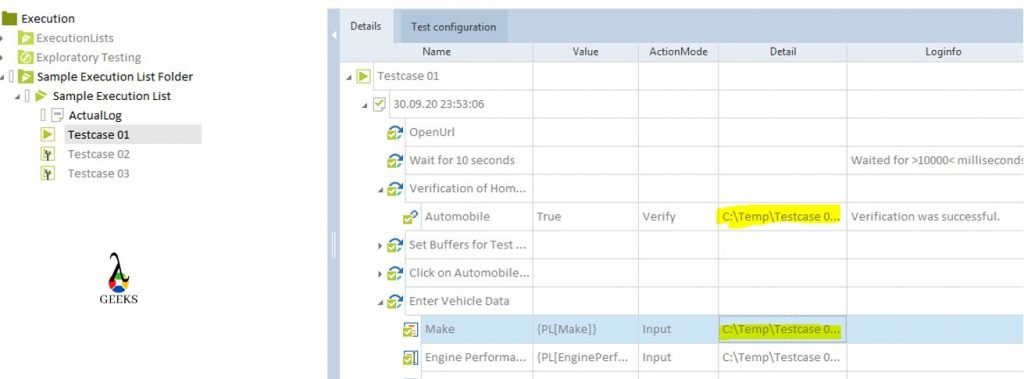
- Tosca Tutorial #8:Tosca Test Execution, Reports, and Bug management
- Tosca Tutorial #9: Test Case Design – An approach to test data management
- Tosca Tutorial #10: Tosca Test Data Management.
- Tosca Tutorial #11: API Testing in Tosca
- Tosca Tutorial #12: Tosca Interview Questions and Answers
In this Tosca Test Case Design and Test data Management article, we will learn about the step by step implementation approach of Tosca Test Case Design and overview of Test Data Management. If you want to prepare for TOSCA Interview Questions, please click here.
Tosca Test Case Design (TCD)
This is an approach to isolate the test data from the technical sections of test cases. So, the data and test cases are kept separately. The Tosca Test Case Design section has the capability to break our test cases into a logical structure. It is also help us to plan and design the testcases in a efficient and structured way to reduce the development and maintenance efforts.
Use the Tosca Test Case Design section is performing the below activities –
- Create the testsheets, which is a combination of all possible test cases for any particular scenario or template. Basically, testsheets are holding the data for different combinations.
- The concept of class in test case design approach, helps to reuse the common data across the test cases which reduce the efforts of data management.
- With the help of instances, we can create the specific data for TestSheets, TCD Attributes, or TCD classes.
- Create TestCase Templates and assign the Testsheets.
- We need to instantiate or re-instantiate Templates to generate the instance test cases as per the testsheets.
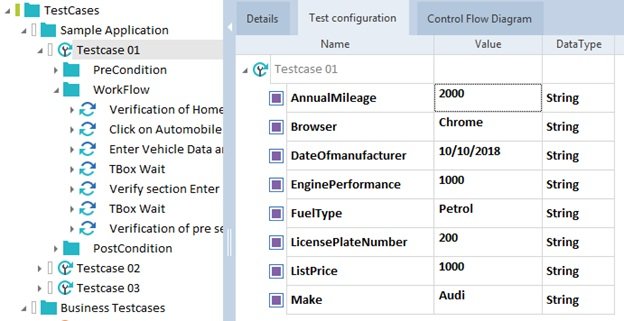
- Manage test data in testsheets and execute the instance test cases
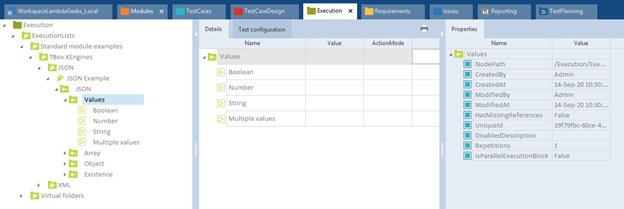
Test Case Design objects:
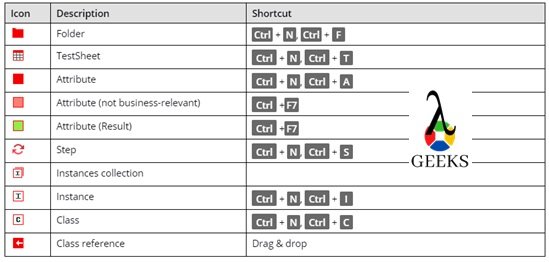
The table below lists all components available in the Test Case Design section, and keyboard shortcuts where applicable.

- Folder – The test case design folder is used to group the test sheets or classes in a logical way.
- TestSheet – TestSheet is a list of data for all possible combinations of Tosca test cases. Each data set represents one unique test case.
- Attribute – It’s referred to as the different data parameters corresponding to each application field.
- Attribute(not business-relevant) – It’s used for comment or description purposes.
- Attribute(result) – It’s used for result purposes.
- Instances Collection – It holds the Instances i.e., all possible values available for particular attribute.
- Instances – This is the value of each attribute/parameter. It can be created TestSheets, Attributes, or Class level. Instances of Testsheets are basically a test case name.
- Class – This is similar to testsheets, but it’s used for the reusable purpose. All the common data are stored here, which can be reused in multiple testsheets.
- Class reference – It’s acting as a link of Classes from Testsheets. We can create it with the drag-drop method.
Object hierarchies in Test Case Design:
- A TestSheet may have Attributes, Instances, TestSteps, and class references.
- A class may be the combinations of class Attributes and Instances.
- Again, an Attribute can keeps further Attributes and Instances.
- A Step can keeps more Steps and Attributes.
Step-by-step process to implement Test Case Design:
- Step1: Create the Class if there is some common sections are available for multiple test cases. For example, Login is a common section in most of the application. So, we need to create a class as per the below diagram –
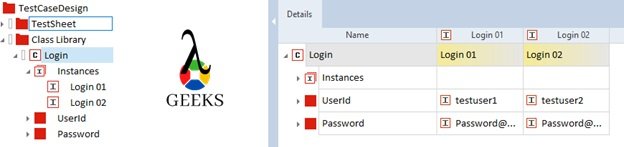
- Step2: Create testsheets as per the below structure and link the classes. Testsheets are used for the unique individual scenario. Based on the different data combinations, different test cases will be generated as per the instances of testsheets.

- Step3: Create template test cases. We can convert any existing technical test case into a template test case by selecting “the Convert to Template Testcase” option after right-clicking on it.
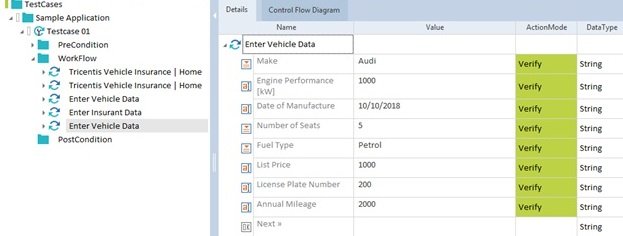
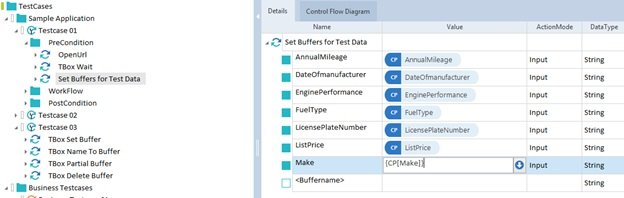
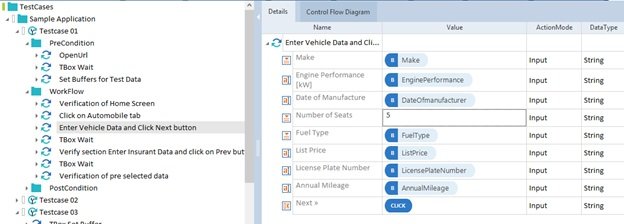
- Step4: Assign the testsheet into the template test case by drag and dropping the testsheet into the template test case. Only one testsheet can be assigned to one template. After this, we can assign the Test Case Design data Attributes/ parameters into the test steps by drag-drop method or typing. Syntax for linking the parameters – {XL[parameter_name]}. The template test case can not be executed.

- Step5: After assigning the data parameters, we need to generate the instance test cases. It can be done by opting the option Instantiate or Re-instantiate by right-clicking on template test cases. After the, all the possible test cases will be generated based on the data combinations of test sheets.

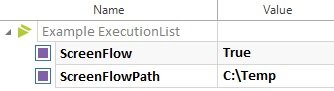
- Step6: Now, we can create an execution list to execute the instance test cases.
Advantages to TCD:
- · Dynamic handling of objects/data is easy
- · Reusability of test cases
- · No scripting involved
- · Data and technical components are kept separately. In the case of data change, no need to modify the test cases.
Disadvantages of TCD:
- · Test case design section is very complicated
- · A little expensive
- · The UI takes time to understand
Reference Link – https://documentation.tricentis.com/tosca/1300/en/content/testcase_design/testcase_design_intro.htm
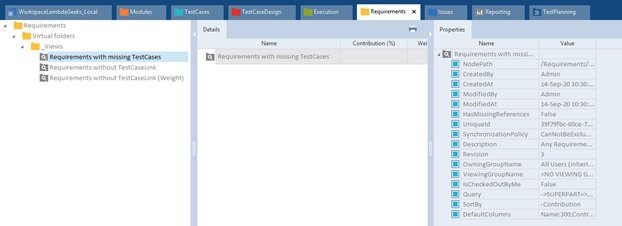
Tosca Test Data Management (TDM)
Test Data Management is an approach to manage the required test data for test execution. It will help us to use the data which are stored externally.

- Test data management is an another important component for data management which is available along with the standard installation of Tricentis Tosca Test suite.
- DB2, MS SQL Server and Oracle repositories – Tosca test data management (TDM) component uses the same database which is used to create the common repository of the workspace.
- SQLite repositories – For SQLite, TDM uses the separate repository to store the data.
- After creation of a new workspace, by default Tosca is getting connected with the repository.
- If required, Tosca is able to connect different database as TDM repository instead of default database.
Connecting to a TDM repository: Create Configuration parameter as TDMConnection in the root level and assign connection string in below format -<Databasetype>(<ConnectionString>)[dynamicmode=<on or off>,schema=<Schemaname>]
Standard module to handle TDM:
The standard module path – “Standard modules->Test Data Management->Test Data Management – Legacy.”
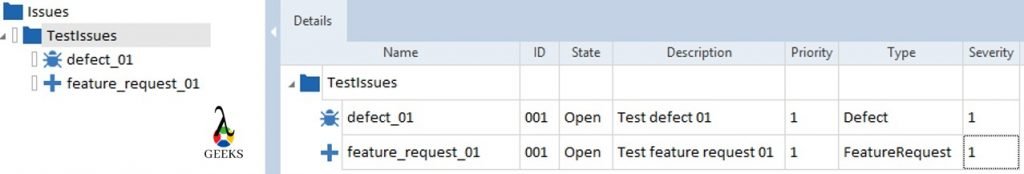
- TDM Create Object – The TDM Create Object module helps to create a fresh TDM object for a specific object type. Initially, the new TDM object can be created with empty value.
- TDM Find Single Object – It is used to search for a TDM object within the TDM repository.
- TDM Set Attribute – Set Attribute module is able to set the values for any existing TDM object.
- TDM Set State – This module is able to set the values of state for any existing TDM object.
- TDM Add Association – This module is used to define an association between two TDM objects. This association receives an individual role name which allows the mapping.
- TDM Remove Association – This module is used to remove the association between TDM objects.
- TDM Delete Object – This module is used to delete the TDM Objects from the TDM repositories.
- TDM Save – This Module saves the TDM object in the TDM repository.
Click here to learn more on Test Data Management.
Conclusion:
In this Tosca Test Case Design and Test data Management article, we have learned about Test Case Design and Test Data Management. Click here to understand more from the Tricentis Support portal on this topic.
Please click to read the most important topic of TOSCA Tutorial – Understanding of Tosca Case Creation.