In this article Radioactive decay examples are derived. Radioactive process is actually a continuous breakdown process of a matter’s atomic nucleus. In this process energy is emitted from any matter’s nucleus.
16+ radioactive decay examples are given in section of below,
- Medical equipment
- Glass
- Ceramics
- Clocks and watches
- Smoke detector
- Fertilizers
- Gas Lantern Mantles
- Food
- Glowing items
- Recycled metal
- Irradiated Gemstones
- X ray imaging
- Security
- Measurement
- Space exploration
- Human body
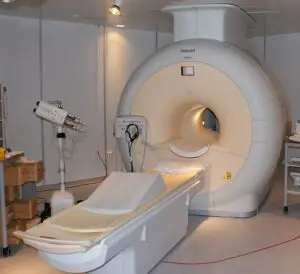
Medical equipment:
In various machines in the medical field radioactive element is widely used. From where radioactive decay is emitted these types of material are used in the medical field for treating health of a patient. Nuclear Regulatory Commission department regulate the use of radioactive decay in medical field.
Near about one third patients are admitted for acted a rare and fatal liver disease using radioactive or radiation materials. The radioactive or radiation materials are called radio pharmaceuticals. To reduce the tissue of the cancerous, reduce and shrink a tumor this radioactive object is used.

Image Credit – Wikipedia Commons
Glass:
In the industry of glassware the radioactive decay is used. Thorium – 232 and potassium – 40 radioactive type objects is used inside the glassware factory. Some glass made product also contain uranium this type of glass is called Vaseline glass.
Glass is transparent amorphous solid and it is non crystalline. In the glass others chemical are also present like silica.

Image Credit – Wikimedia Commons
Ceramics:
Thorium, uranium, potassium radioactive type objects is used inside the ceramics. Ceramics can be divided in two categories as non metallic material and inorganic material. In the field of production engineering the examiner are tried to new type products of ceramics that general people can use in their everyday lifestyle.
In almost everywhere ceramics are present. In bricks, glass, plates even in toilet the ceramic made of products are present. In automobile, clock and watches, snow skies, airplanes, appliances, space shuttles the ceramics products are available. Even in some superconductors ceramics presence can be observe.
In the ceramics the objects which are present they are powders, water, earthen elements, mixture of clay and mixing all together the desired object is made.

Image Credit – Wikimedia Commons
Clocks and watches:
In our daily the most common and useful radioactive example is clocks and watches. Promethium – 147 radioactive type objects is used inside the clocks and watches. Another type radioactive type objects is used inside the clocks and watches is Hydrogen – 3.
For this reason luminous type dials actually a compromising. For this reason in dark area we easily can see the time without any hassle. Now a day where this modern type watches is used. In older watches and clocks Radium – 226 is used.

Image Credit – Wikipedia
Smoke detector:
The term for the smoke detector is smoke alarm. The radioactive example which is use in our regular life this is the smoke detector. Mainly alpha decay is used in the smoke alarm. Americium – 241 this radioactive object is used inside the smoke detector.
The Americium – 241 radioactive elements is actually particularly placed in the middle portion of the charged plates. From Americium – 241 element release alpha decay to the environments.
Two plates which are charged are used to construct the design of smoke detector. Others things which are used in the design of the smoke detector they are, a battery, a mechanism of alarming, a detector battery. The terminals are attached to the equipment of the smoke detector in a very interesting way. One terminal of the smoke detector is attached with the detector of current and another one terminal is attached with the positive side plate of the smoke detector.

Image Credit – Wikimedia Commons
Others some facts which are we to concern about is listed below,
- At least in every 9 – 10 years the smoke detector should be definitely replaced.
- The connection of the smoke detector always interconnected.
- Large buildings should contain more smoke detector.
- Monthly checking and maintenance is needed.
Fertilizers:
Fertilizer is an element which is mainly used in agriculture field for improve the productivity and growth of the plants. Fertilizer actually a element which is enhance the fertility naturally of the soil or elements which carry the chemicals alternatively use as soil by prior crops.
In the fertilizer the radioactive elements are used they are uranium and thorium. The other chemical element which are contain by the fertilizer is hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, calcium, sulfur, sodium, silicon, aluminium and many more.

Image Credit – Wikimedia Commons
Gas Lantern Mantles:
Thorium – 232 radioactive elements is used in the gas lantern mantles. This gas lantern mantles actually incandescent lights. When fuel is burn like kerosene, propane and white gas heat is produce and as a result mantles is made from which light is comes.
The gas lantern mantles components made of ceramics other elements present in this is cerium oxide, thorium oxide and magnesium oxide. The construction of the gas lantern mantles is very simple.

Image Credit – Wikipedia
Food:
There is lots of food is present in nature from their radioactive decay is always emitted. The food items are,
Brazil nut – From the Brazil nut near about 12000 picocurie per kilogram radiation decay is emitted.
Butter beans – From the butter beans near about 4600 picocurie per kilogram radiation decay is emitted.
Bananas – From the bananas near about 3500 picocurie per kilogram radiation decay is emitted.
Avocados – From the Avocado near about 2500 picocurie per kilogram radiation decay is emitted.
Water – From the water near about 100 picocurie per kilogram radiation decay is emitted.
Red meat – From the red meat near about 3000 picocurie per kilogram radiation decay is emitted.
Peanut butter – From the peanut butter near about 120 picocurie per kilogram radiation decay is emitted.
Glowing items:
In lots of glowing item which we are used in our daily life radioactive element is present. Mainly in the glowing item thorium and uranium are used. These items can glow in dark places without battery or electricity.
In the glowing items mainly very low level radiation of beta is emitted. The emission of the beta radiation easily can be stopped with help of cloth or sheet of paper.
Recycled metal:
We are known the process of the recycle is very convenient for us and also for our surrounding. But some time the process of recycle can causes some unwanted bad situation. The metals which are used again and again for recycling causes emitting of radiation decay. We always should some take some care of it,
- Taking a distance
- Time limitation
- Checking shielding
Irradiated Gemstones:
In lots of gemstones which we are used in our daily life radioactive element is present. Mainly in the irradiated gemstone item gamma radiation is continuously emitted. The irradiation is a term which meaning is very board. In irradiated gemstones full range of radiation of electromagnetic present and also visible light, X rays, ultraviolet rays, infrared radiation is present.
X ray imaging:
X ray imaging is a very process which is done without any pain and it is very speedy process. From this x ray imaging the radiation is emitted. Mainly by the help of x ray a picture is taken for any particular place of our body.
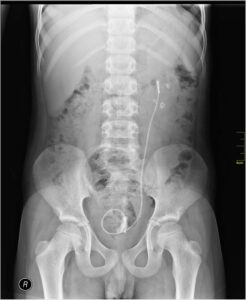
Image Credit – Wikipedia Commons
Beam of the ray is going through of our body and after that absorbed different amount of radiation which is depend upon the material density.
But excess amount of doing x ray imaging is not good for our body.
Mainly the images are taking by the help of x ray process is,
- Arthritis
- Bone cancer
- Osteoporosis
- Dental decay
- Fracture
- Blocked blood vessels
- Breast cancer
- Swallowed items
Security:
In our modern society the most and effective security process is done for security is radiation decay. When a man is pass through the radiation decay test an image is clearly comes to the examiner that what object he is carrying. Mainly this process x ray is done. Alpha radiation is emitted in this process.
Measurement:
In the special measuring instruments like gauges and devices the radiation of radioactive elements are used thus we can get appropriate measurement and accuracy. Not only in measuring devices is the radiation radioactive also used in checking instrument. For checking the fluid levels, defects present in the welds, very small measure in physical this process is followed.
Read more about Gauge pressure : It’s Important Properties with 30 FAQs
Space exploration:
In space exploration the radiation of radioactive is uses. Actually interstellar space is very dark for this reason the surrounding temperature became very low. The temperature reaches about zero degrees centigrade. For overcome this problem radioactive element are use so that the equipment of the aircraft can move and don’t freeze neither the equipment could not open up.
The radiation of the radioactive elements gives heat to the equipment of the aircraft.

Image Credit – Wikipedia Commons
Human body:
From our body very little amount of radiation of radioactive is emitted. From our body mainly carbon – 14 radioactive element is present. For this reason the archaeologists easily can determine the range of age for skeleton. The main source of the radioactive in our body is when we took breathe from environment little amount is absorbed.
Frequent Asked Question:-
Question: Write disadvantages of radioactive decay examples.
Solution: Some disadvantages of radioactive decay examples is given below,
- Irritation in skin
- Hair loss
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Bladder infection
- Sore throat
- Dry mouth