Displacement reaction examples take place when a reactant is replaced by other reactant. This research is going to represent detailed explanations of the examples of Displacement reaction.
There are some effective Displacement reactions examples are listed below:
Example 1: Single displacement reaction
In this single displace reactions only one of the reactants release the ion and replaces the other reactant with the formation of a new compound.
The reaction between Iron and Copper sulphate is a perfect and simplest example of single displacement reaction. Here copper sulphate releases the sulphate ion and it gets added to Iron metal and gives out ferrous sulphate and Cu metal.
Equation:
Fe + CuSO4 = FeSO4 + Cu
Besides, when Zinc metal reacts with Hydrochloric acid a single displacement reaction can be noticed to be happened. In this reaction Zinc Chloride forms as chloride ion adds on with the zinc metal. Bubbles forms in the reaction which indicates the formation of hydrogen gas.
Equation:
Zn + 2HCl = ZnCl2 + H2
Another effective example of single displacement reaction could be explained that is the reaction between ferric oxide and Coke. Coke is replaces with Carbon Dioxide and free Fe metal has been obtained as product.
Equation:
2Fe2O3 +3C = 4Fe + 3CO2
Read more about Displacement reaction
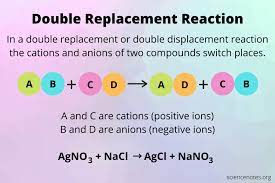
Example 2: Double displacement reaction
When two salts reacts with each other and both the reactants are replaced by each other such as the positive and negative ions are exchanged by each other, that type of replacement reaction is called Double displacement reaction.
The reaction between sodium sulphide and hydrochloric acid gives out Sodium chloride and hydrogen sulphide. Here sodium sulphide trades its sulphide ion to HCl and HCl trades its Chloride ion to Sodium sulphide.
Equation:
Na2S + 2HCl = 2NaCl + H2S
Besides, when silver nitrate reacts with sodium chloride they exchange their anions and give out silver chloride and sodium nitrate. It is an example of precipitation reaction as well. AgCl has been identified to be precipitated here.
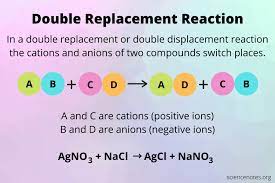
The reaction between Barium chloride and Sodium sulphate gives out barium sulphate precipitate and sodium chloride.
Equation:
BaCl2 + 2NaSO4 = Ba(SO4)2 + 2NaCl
Example 3: Displacement reaction examples based on reactivity of elements
Displacement reaction happens by depending on the reactivity of the metals. More reactive metals easily replace the less reactive metals from the compounds. This is the main reason behind the displacement reaction.
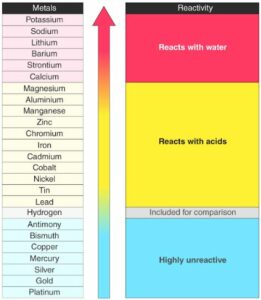
When lead is made to react with copper chloride it gives out lead chloride and free copper metal. As lead is more reactive than copper it easily breaks the bond between copper and chloride ion.
Equation:
Pb + CuCl2 = PbCl2 + Cu
Another example can be described by mentioning the reaction between Zinc and Copper sulphate. It reactive zinc becomes successful in extracting sulphate ion from Copper sulphate mad gives out Zinc sulphate.
Equation:
Zn + CuSO4 = ZnSO4 + Cu
Example 4: Acid-base reactions
The Neutralization reactions between Acid and Bases are considered to be great displacement reaction examples. When an acid neutralizes a base, the replacement of ions among acids and bases takes place and support the principle of displacements reaction. Double displacement reaction takes place here anyway.
For an example, when hydrochloric acid reacts with potassium hydroxide, it neutralises the base and reaches out to a certain neutral kevel of pH, the replacement of hydrochloric acid trades its chloride ion to potassium and gives out the natural salt potassium chloride.
Equation;
Table salt formation follows the same principle as the above one. NaCl is called table salt generally. When strong Hydrochloric acid reacts with strong base sodium hydroxide it produces table salt and water.
Equation:
HCl + NaOH = NaCl + H2O
This is an example of Strong Acid-base Neutralization reaction.
Read more about Neutralization reaction
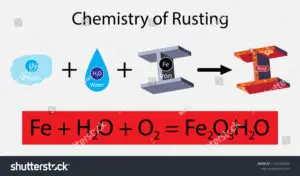
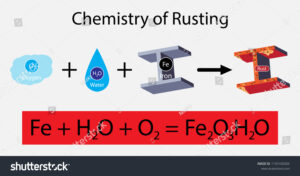
Example 5: Rusting of Iron
Rusting is the best example of oxidation reaction as a well as the displacement reaction. When things made of iron metal are kept into open air the oxygen gas oxidise the Iron metal and a reddish brown layer is formed by the as the effect.
In this reaction the metal (Iron) is replaced by the action of oxygen gas and through this displacement reaction rust forms that is Fe2O3, H2O. The moist air is the reason behind oxidising the metal ions.
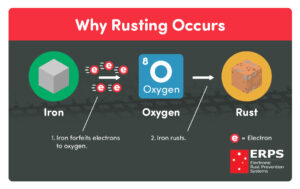
As this oxidation reaction occurs through replacement of metal with its oxide, this reaction is considered as one of the practical displacement reaction examples.
Example 6: The reaction of baking soda and vinegar
The reaction of baking soda and vinegar is one of the best examples of displacement reaction. This reaction happens in two steps, the first reaction is the reference of double displacement reaction.
Acetic acid present in vinegar reacts with sodium carbonate in baking soda. This reaction happens through replacement of both acetic acid and carbonate. Therefore, it is happened by maintaining the principles of double displacement reaction.
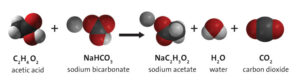
The products come out from the reaction are Sodium acetate and carbonic acid. The unstable carbonic acid then decomposes and the next reaction takes place as decomposition reaction.
Equation:
NaHCO3 + HC2H3O2 = NaC2H3O2 + H2CO3
This is a simple example of double displacement reaction.
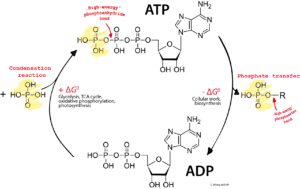
Example 7: Photosynthesis
Single displacement reaction happens in photosynthesis process. This is the main process of making food of the plants. Single displacement reaction takes place during Calvin cycle. In the light reaction when hydrogen molecules get separated from the water molecule to replace the carbon dioxide molecules to form the Glucose.
Equation:
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
As only one reactant is replaced by the other one, this reaction comes under the single displacement reaction category. This reaction is also taken as the example of combination reaction. However, replacement reaction is quite intense in photosynthesis.
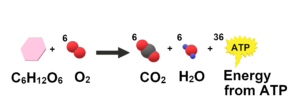
Example 8: Cellular respiration
Double displacement reaction takes place in cellular respiration. This is not a single reaction. Both oxidation and reduction reactions are noticed to be take place here. Therefore, it is it is a great example of redox reaction.
On the other hand, this reaction is reliable I absorbing exergonic reaction properties. That is it releases a certain amount of energy with the products. The double displacement properties can be shown in cellular respiration as well.
When glucose is oxidised and oxygen gas is reduced, each of the reactant is replaced with the help of other reactant. Therefore, it is a double displacement reaction.
Equation:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Question 1: Is there any possibility of displacement reaction when a less reactive metal is made to react with a compound contains more reactive metal?
Answer: A less reactive metal cannot displace a more reactive metal as more reactive metal have tendency to create stable bond with ions. It becomes harder to break that bond for a less reactive metal. Therefore, displacement reaction cannot take place in this kind of reaction.
Question 2: Are Acid-Base reactions considered to be displacement reaction? If yes, then which type of displacement reaction happens in Acid-Base reactions?
Answer: The neutralization reaction between an acid and a base is a great example of displacement reaction. Exchanging the ions with each other to produce neutral salt is the main fact of displacement reaction between acids and bases.
These reactions are double displacement reaction as both the acid and bases replace each other by exchanging the ions.
Question 3: How does displacement reaction depend on reactivity of metals?
Answer: When the more reactive metals are made to react with the compound containing less reactive metals, that more reactive metals show its tendency displace the less reactive metal from the compound and it take the place of that less reactive compound and firms new compound. In this way, displacement reaction depends on the reactivity of metals.
Question 4: What type of displacement reaction can be noticed in photosynthesis?
Answer: Single displacement reaction is noticed to be happening in photosynthesis when glucose is formed by the replacement of oxygen gas from Carbon Dioxide.
Question 5: In which step double displacement reaction can be found to be happened when Vinegar is mixed with baking soda? Which reaction happens in second step?
Answer: In the first step of reaction double displacement takes place. Vinegar contains acetic acid is replaced with the sodium and make sodi8um acetate and the carbonate is replaced into carbonic by getting the hydrogen molecule.
Due to unstable nature of carbonic acid it decomposes and decomposition reaction takes place in the next step.
Know more about decomposition reaction
Also Read: