Welding is the method which has been around us from a long period of time and different types of welds are introduced over the decades.
The weld joints can be classified according to the way the pieces of metal are placed together or align with each other. Each type of welds are different from each other by design, quality and cost wise. Selection of an appropriate weld type as per requirement needs special attention and skill of the welder.
The welding process is all about using heat to melt separate metal pieces so that their molten portion flow together and fuse to form a single seamless piece.
Different Types of Weld Joints
Welds can be geometrically prepared in many different ways.
According to American Welding Society(AWS), Welding Joints can be classified basically as below :
The above mentioned weld joints cover different weld types.
Welders have to select a weld type observing certain criterions like welding method and thickness of the members to be welded. Generally, welds are described by their shapes when we observe their cross sections.
In a weld joint different members are joined together to form a single part so that the stresses acting on them are distributed. A weld joint has to withstand different types of stresses like tensile stress, compressive stress, bending, torsion and shear stresses. The capability of a welded joint to overcome theses stresses depends on both the design and integrity of the weld.
The welding method and the joint design are inter related, depending on the welding method we have to select the joint type and vice versa.
A particular welding method results a particular type of weld accurately and efficiently. The characteristic of the welding method like the rate of travel, penetration, deposition rate, heat input etc affect its performance and resulting weld.
Butt joint
Butt welds are very common and simple to weld, here metal pieces are placed near to each other in the same surface and pieces are joined edge to edge. Most common applications of butt weld are fabrication industry and piping system.
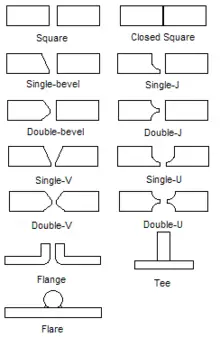
Different types of butt welds(variation in groove shape, applications, width of the gap etc.) in butt welding are listed below:
- Square
- Single bevel
- Double bevel
- Single J
- Double J
- Single V
- Double V
- Single U
- Double U grooves

.
Because the orientation of the material usually presents only one end to a long gluing or welding surface, the resulting joint is inherently weak.
Accumulation of slag, porosity, cracking etc are certain drawbacks of butt welds which make it weaken. Butt welds can be fed through automatic welding machines accurately due to their simplicity in design.
Corner joint
Corner joints are common in sheet metal industries to weld frames, boxes, tanks etc. It is similar to butt welds, two plates at right angles to each other in the ‘corner’ in either an open or closed manner, giving an L shape.
In the case of light weighted flexible sheets accurate alignment is quite difficult. To avoid the occurrence of air trap, try to get rid of air pockets, pits, surface irregularities at the weld joint.
Different geometric patterns of corner welds in corner joints are as below:
(i) Fillet weld
(ii) Spot weld
(iii) Square-groove weld or butt weld
(iv) V-groove weld
(v) Bevel-groove weld
(vi) U-groove weld
(vii) J-groove weld
(viii) Flare-V-groove weld
(ix) Edge weld
(x) Corner-flange weld
Edge joint
In edge joint, the metal pieces are placed in such a way that the edges give an even surface and then one or both the surfaces are bent at an angle to form the joint. In case of applications to withstand heavy loads, additional filler metals are applied to fuse the edges completely.
The various weld types in this welding joint are:
Square-groove weld or butt weld
Bevel-groove weld
V-groove weld
J-groove weld
U-groove weld
Edge-flange weld
Corner-flange weld
Lap joint
In case of lap welds the two ends of the metal pieces of different thicknesses are placed in such a way that one piece can overlap the other one. Depending on the necessities, welds have done only on one side or on both the sides.
This type of joints are generally avoided for thicker materials and preferred for sheet metals. Corrosion is the main issue associated with lap welds, however using modern techniques and changing variables this problem can be prevented. Since, Lap joints have the characteristics same as Fillet welds, so it is considered as a Fillet Weld also.
The Various weld types in lap joint are
(i) Fillet weld
(ii) Bevel-groove weld
(iii) J-groove weld
(iv) Plug weld
(v) Slot weld
(vi) Spot weld
(vii) Flare-bevel-groove weld
Tee Joint
In T welds two pieces are welded at a 90-degree angle to each other, one piece is generally attached to the center of another one giving a T shape. This type of joint is frequently seen in welding a pipe on a base plate.
Different welding styles that can be used to create a tee joint are as follows
- Plug weld
- Slot weld
- Bevel-groove weld
- Fillet weld
- J-groove weld
- Melt-through weld
- Flare-bevel-groove weld
A groove is introduced when the base metal piece is thick and welding on both sides unable to withstand the load, the joint must support. In case of T joints effective penetration into the roof of the weld must be ensured.
Different Types of Welds are:
Fillet weld
It is one of the most commonly seen weld type in fabrication industries.
Fillet welds have covered almost 70-80% of all the welds made by arc welding method. Tee joint, lap joint, corner joints all come under fillet welding joints. Since there is no requirement of any edge preparation, fillet welds are simpler as well as cheaper than butt welds.
Different types of fillet welds are mentioned below:
Square groove weld
Single -V groove weld
Single -bevel groove weld
Single -U groove weld
Single -J groove weld
Flare V weld
Flare Bevel weld
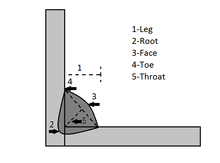
The main difference between Butt and Fillet welds is the surfaces to be joined in butt welds are on the same plane and in fillet welds the surfaces make an angle of 90 degree to each other.
A 45 degree angle is formed between the two parts in case of fillet welds whereas butt joint weld looks like a seam or bead.
When the bolts are not strong enough and wear off easily, welders generally prefer fillet welds, also to join flanges to pipelines and welded fabrications.
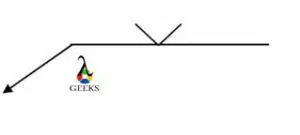
Groove Weld
The Groove weld is a type of joint, where an opening between two members provides a space to deposit the metal.
Two main types of groove welds are single V type and Double V type. Groove welds can resemble butt welds when two members of butt weld are having grooves on them.
Seam Weld
Seam welds are a continuous joint between two overlapping members, similar or dissimilar materials, created by the use of pressure and electric current.
Since metals have th characteristic of conducting electricity and can sustain high pressure, this process is performed on mostly on metals. Resistance seam welding is the most commonly used process for seam welds. Seam welds are very durable and robust in natue because a large area is joined by the weld and the joint is forged due to heat and pressure applied.
Spot Welds
Here two metal sheets are joined together at certain spots. In case of spot welds two sheets are placed in an overlapping position to each other(just like in lap joint), then a rotating tool is pressed with high force on to the top surface.
The frictional heat and the high pressure plastify the sheet metal, the pin of the tool is plunged into the sheets until the shoulder is in contact with the surface of the top sheet.

This tool consists of a pin which rotates and penetrates into the sheet, the shoulder in the tool is the source of high forging pressure which binds the sheets without melting. After a short gap the rotating tool is pull out from the sheet materials to make another spot weld in each 5 seconds.

Plug Weld
Plug welds are mainly used to replace rivets and used to join overlapping surfaces, one of which has holes on it.
These are circular welds used to join two members together through a small hole in one of the members and the hole is generally partially or completely filled with weld metal.
In most of the automotive applications, plug welds replace spot welds when the space required to operate a spot welding equipment is not sufficient. The plug welds give a stronger joint than a spot weld.

Slot Weld
Just like the Plug welds, Slot welds are also used for joining overlapping surfaces one of which has holes on it, round in case of plug welds and elongated for slot welds.
In simple words in case of slot welds one piece of material is connected with another piece of metal through an elongated shaped hole. The elongated hole can be open at one end or may be partially or completely.
Full and Partial Penetration Welds
Full Penetration weld or Complete Joint Penetration (CJP) weld has a special kind of groove that allows the filler material to flow through the entire gap starting from the top to the bottom of the joint.
In case of Partial Joint Penetration(PJP) Welds, the filler material does not reach the root portion of the joint. If you observe the cross section of the joint you will find gap between the two members.
The metal edges are generally beveled properly to assist full penetration or CJP, U,J and V grooves are very common shapes for the full penetrations . A well done CJP gives a strong and durable joint than PJP.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: State differences between Butt and Fillet Welds.
Answer: If two metal pieces are lying on the same plane and they are joined together then we get a butt weld. Butt welds require edge preparation.
If the metal pieces to be joined are making an angle of 90 degrees with each other then we get a fillet weld. Edge preparation is not necessary.
Q2. What are the differences between weld joint and rivet joint.
Answer: The Difference between Welded and Riveted Joint are mentioned below:
| Welded Joint | Riveted Joint |
| For welded Joints, no holes are required on the parent members. | Number of holes on the parent members are required to join them with the help of rivets. |
| A continuous type of joint is obtained. | An intermittent type of joint is obtained due to the existence of gaps between rivets. |
| Joints are generally leak proof | Chances of leakage is quite high. |
| Strength of welded joint is quite high | Riveted joints are comparatively weak. |
| The whole assembly is lighter in weight. | The whole assembly consist of a number of components which make it heavy in weight. |
| Time required for welding is less | Multiple steps are involved in riveting process which consumes long time. |
Conclusion:
To wrap up our post we can state that there are different types of welds and each one has unique characteristics. To achieve specialization in welding we should properly know their qualities and which one will be suitable as per our requirement.