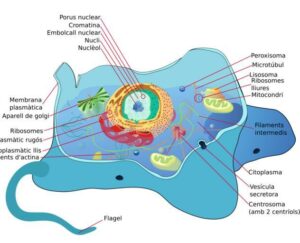
The cytoplasm is the non-nuclear substance of protoplasm within the animal cells. As the cytoplasm is very crucial for cellular activities, here we try to find out the answer of do animal cells have cytoplasm or not.
The cytoplasm is the core part of a cell, consisting of cytosol, organelles and inclusions. Every micro and macro bio molecule, inorganic compounds float within cytoplasm. Every cellular activity is highly dependent on it. So as per the basic requirement of a cell, all animal cells have cytoplasm inside their plasma membrane.
The cytoplasm also contains various enzymes, necessary for biochemical reactions. It moves particles from one side to another side of the cell, and stimulates signaling pathways. It also protects the cell by acting as a buffer.
Features Of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm performs several kinds of activities within a cell. Let’s have a closer look at some common features of cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasm is basically made up of 80% – 85% of water substance. It also composed proteins molecules(10%-15%), lipids substances(2%-4%), inorganic salts and polysaccharides.
- All the cellular organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, lysosome, etc embed within the cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasm also plays a notable role in breakdown of wastes, various cytoplasmic enzymes stimulate cellular digestion procedure within cells.
- Cytoplasm produces cytoskeleton, a filamentous system which helps to stay all the organelles inside to their correct positions.
- Cytoplasm protects the cell as a protective buffer.
Apart from these the cytoplasm has several more features in it.

Features of cytoplasm from Wikimedia
Do Animal Eukaryotes Have Cytoplasm?
Sir Rudolf von Kölliker, a famous Swiss anatomist, physiologist, and histologist first used the word cytoplasm In 1863. It is the main platform of all cellular biochemical activities.
Every animal eukaryote has cytoplasm in their cells. The cytoplasm is the core substance of the cell, having all the essential bio molecules and organelles in it. The cellular functioning mechanisms are highly dependent on cytoplasm. Every living organism, including animal eukaryotes, have cytoplasm in their cells.
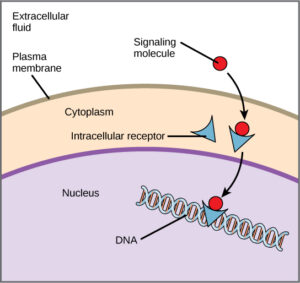
The eukaryotic Cytoplasm structure is more complex than the prokaryotic structure. In a eukaryotic cell the cytoplasm is enclosed by a plasma membrane internally and distinct from the nuclear region externally.

Cytoplasm in animal cell from Wikipedia
To know more about eukaryotes read our article on Eukaryotic Cells Examples: Detailed Insights
Why Do Animal Cells Have Cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is an undivided part of a cell. Every metabolic process directly or indirectly depends on the cytoplasm. Let’s find out why do animal cells have cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm consists of proteins, amino acids, lipids, salts, etc. Most cellular processes occur inside the organelles or after processing from the nucleus most of the metabolites transferred to cytoplasm. It takes part in cell division, holds and protects all over the cell. That’s why animal cells have cytoplasm.
To know more about animal cells read our article on Do Humans Have Animal Cells: Interesting FACTS
Is Cytoplasm Present In Plant And Animal Cells?
Cytoplasm is a term where ‘cyto’ means cell and ‘plasm’ means stuff, so cytoplasm means cell staff. All living organisms have cytoplasm in their cells.
Plant cells and animal cells both have cytoplasm as the interior part of their cell. In both cases the cytoplasm contains cytosol, cellular organelles and cytoplasmic inclusions. Most of the metabolic activities occur in that place.
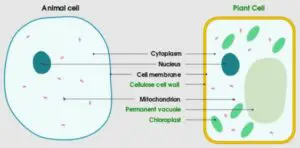
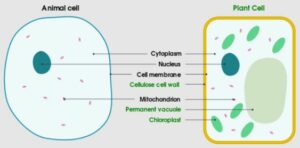
The features of cytoplasm in plant cells and in animal cells are slightly different from each other. The most common difference is in their constitutive organelles. Where plant cells have plastids, chloroplasts the animal cells lacking those organelles in their cytoplasm.
What Are The Differences In Cytoplasm Between Animal Cells And Plant Cells?
As we previously discussed, both the animal and plant cells contain cytoplasm inside their cell membrane. In both cases most of the biochemical reactions of cells are dependent on the cytoplasm. But there are some differences in cytoplasm between the animal cells and plant cells.
- The cytoplasm in animal cells are enclosed by only the cytoplasmic membrane. But in the case of plants the cytoplasm is enclosed by the cytoplasmic membrane and the cell wall as well. The animal cells don’t have the cell wall outside the cell.
- The nucleus is situated at the center part of Cytoplasm in the animal cells but in case of plant cells the nucleus lies on the side of the cytoplasm.
- Most animal cells contain lysosomes in their cytoplasm but in case of plants, the presence of lysosomes in cytoplasm is very rare.
- The cytoplasm in animal cells have centriole which helps in cell division but in plant cells the centrosome or centriole is absent in cytoplasm.
- The cytoplasm in animal cells contain numerous small vacuoles as storage molecules. But the plant’s cytoplasm contains a large centrally positioned, single vacuole inside the cell.
- Mitochondria is present in cytoplasm of animal cells, numerous in numbers. In plant cells the mitochondria is fewer in number.
- The animal cells contain cilia in most of the cases but the plant cells lack cilia.
- The animal cells do not have plastids and chloroplasts in their cytoplasm but the cytoplasm of plant cells have them. These are one of the most important organelles in plant cells that help them in the photosynthesis process.
Despite these many differences both animal cells and plant cells have some similarities in their cytoplasm. In both of the cases the cytoplasm consists of cytoskeleton and cytosol matrix. Both the animal cells and plant cells have similar organelles in their cytoplasm. Those are include the mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes.
To know more read our article on Do Animal Cells Have A Cell Wall: Interesting FACTS
Do Animal Cells Have Free DNA In Cytoplasm?
DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is the main genetic material, consisting of several genes, the basic unit of heredity.
The animals basically possess eukaryotic cells. An eukaryotic cell has their DNA inside the membrane bound nucleus. The cytoplasm is divided by the nuclear membrane from the nucleus of the cell. The nucleus is not a part of cytoplasm. That means it did not have free DNA lying in its cytoplasm.
Only in case of prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm contains free naked DNA or nucleoid in its cytoplasm area.
Do All Animal Cells Contain Cytoplasm?
As we know, the cytoplasm is a very essential part of any cell, whether it is an animal cell or a plant cell. Every living organism must contain cytoplasm in cells. That is, all animal cells contain cytoplasm.
As a whole we can say that the cytoplasm is an undivided part of the cell of every living being. We cannot imagine the cell without the cytoplasm part whether it is an animal cell or a plant cell. We try to give the answer of do animal cells have cytoplasm or not? Hope this article will be informative to you.
Also Read: