Cyanate ion has the chemical formula OCN-. It is also known as isocyanates. It is an ambidentate ligand which forms complexes.
Cyanate is a colorless liquid substance with small odor. If treated with water it creates toxic fumes and also if heated at high temperature until decomposition can produce cyanide and nitiric oxides fumes which are toxic to health. In this editorial we are learning about OCN- lewis structure and its detailed facts.
How to draw lewis structure for OCN-?
Some points to be remember while drawing any lewis structure
- Structure’s total valence electrons calculation
- Element needs lowest electronegativity to occupy central position
- Connecting all elements with bonding
Chemical formula for cyanate ion is OCN-.
Molecular weight of OCN- is 42.017 g mol-1.
Molecular geometry of OCN- is linear in shape.
OCN- has sp hybridization.
OCN- is polar in nature.
The isomer of less stable fulminate anaion is the cyanate. It also has various salt forms like ammonium cyanate. Cyanate is an anion consisting of three different elements i.e. oxygen, carbon and nitrogen. Most of cyanate compounds toxic to inhale, flammable and also can cause irritation to eyes, skin and mucous membranes.
It is a bridging and ambidentate ligand (ambidentate means it can coordinate with either of its two different elements).
In OCN- lewis structure, there is a single covalent bond between carbon and oxygen atom and a triple bond within oxygen and nitrogen atoms. The nitrogen atom in OCN- lewis structure bears a negative charge on it.
OCN- valence electrons
- OCN- Structure’s total valence electrons calculation
Let us calculate the total valence electrons on OCN- ion. As we know that the OCN- ion involves three elements oxygen, carbon and nitrogen, we have to check the position of group of these three elements in the periodic table. The oxygen atom belongs to 16th group, carbon atom belongs to 14th group and the nitrogen atom belongs to 15th group of the periodic table.
Therefore, O atom contains 6 valence electrons, C atom contains 4 valence electrons and N atom contains 5 valence electrons in their valence shell. As OCN- ion have one O atom, one C atom and one N atom, let us first calculate the total valence electrons for OCN- ion.
Oxygen atom valence electrons = 6 x 1 (O) = 6
Carbon atom valence electrons = 4 x 1 (C) = 4
Nitrogen atom valence electrons = 5 x 1 (N) = 5
Now, add extra one electron for negative (-) charge present on OCN- ion
So, OCN- ion total valence electrons = 6 (O) + 4 (C) + 5 (N) + 1 (-) = 16
Therefore, total valence electrons on OCN- lewis structure is sixteen.
Let us find the total electron pairs on OCN- lewis structure by dividing total valence electrons by two.
OCN- total electron pairs = OCN- total valence electrons / 2 = 16/2 = 8
Hence, there are total eight electron pairs on OCN- lewis structure.
- Element needs lowest electronegativity to occupy central position
The atom with least electronegativity will occupy the central position of the OCN- lewis structure. O atom has electronegativity 3.44, C atom has electronegativity 2.55 and nitrogen atom has electronegativity 3.04. So, carbon atom is least electronegative from all the three elements. Then carbon atom will occupy the central position of the OCN- lewis structure.
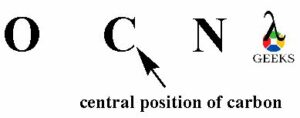
- Connecting all elements with bonding
Now, connect all the three elements O, C and N with each other by linking with a single covalent bond between them. There is the involvement of two valence electrons in each single covalent bond.
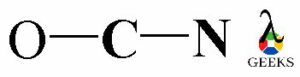
OCN- lewis structure octet rule
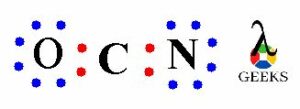
We have total 16 valence electrons in OCN- lewis structure, out of which four electrons involved in bonding between O-C and C-N i.e. two bond pairs. Now we are left with more 12 valence electrons for distribution on OCN- lewis structure to complete the octet of all the three elements present in the ion.
To complete the octet we have to put the eight electrons in the atoms valence shell. Now we have to complete the octet of outer elements i.e. oxygen and nitrogen atom.
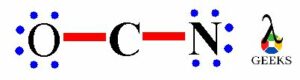
The above structure shows the remaining electrons get shared on O an N, there are six electrons on oxygen and six electrons on nitrogen atom get distributed. So we can see that the O and N atoms has complete octet i.e. two bond pairs and three lone pairs. Similarly, N atom also has teo bond electrons and three lone electrons.
Thus, the O and N atom has complete octet with eight electrons but the C atom has only four electrons i.e. bond pair electrons.
So, carbon atom is not satisfied as its octet is not complete and the structure is unstable. Then we have to move the electrons from nitrogen and oxygen atoms to complete the octet of central carbon atom and also to form double or triple bonds to get a stable OCN- lewis structure which we see further in the explanation of resonance structure.
OCN- lewis structure formal charges
The atoms in any lewis structure having small formal charge give more stable structure. There is a formula to count formal charges on atoms in a lewis structure as follows.
Formal charge = (valence electrons – non-bonding electrons – ½ bonding electrons)
Let we count the formal charges on OCN- lewis structure. So, first we count the formal charge for oxygen atom.
Oxygen atom: Oxygen’s valence electrons = 06
Oxygen’s non-bonding electrons = 06
Oxygen’s bonding electrons = 02
Formal charge on oxygen = (6 – 6 – 2/2) = -1
Carbon atom: Carbon’s Valence electrons = 04
Carbon’s Non-bonding electrons = 00
Carbon’s Bonding electrons =04
Formal charge on carbon = (4 – 0 – 4/2) = +2
Nitrogen atom:Nitrogen’s Valence electron = 05
Nitrogen’s Non-bonding electron = 06
Nitrogen’s Bonding electrons =02
Formal charge on nitrogen = (05 – 06 – 2/2) = -2
Hence, the oxygen atom has -1 formal charge, carbon atom has +2 formal charge and nitrogen atom has -2 formal charge in OCN- lewis structure.
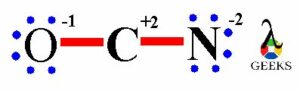
OCN- lewis structure lone pairs
In OCN- lewis structure, after the completion of both the outer elements i.e. O and N there are total twelve non-bonding electrons on both the atoms. It means total six lone electron pairs are present on OCN- lewis structure in unstable form.
Thus, the oxygen atom has three lone electron pairs, carbon atom has zero lone electron pairs and nitrogen atom has three lone electron pairs on OCN- lewis structure.
OCN- lewis structure resonance
OCN- lewis structure shows three non-equivalent resonance structures with the formation of multiple (double / triple) bonds by transfer of electrons within the ion.
In OCN- resonance structure, the charge distributions and bonding’s are vary and having energy levels differ from each other. Some resonance structure shows more stability than other resonance structures. As per the resonance structure rules, if the structure has less energy than it is more stable in nature.
We have already seen in the formal charges topic that the OCN- lewis structure basically consisting three charges -1 on O, +2 on C and -2 on N. Now we have to convert the lone electron pairs of N atom rather than O atom, as O is more electronegative than N atom. Nitrogen being less electronegative can provide more valence electrons for sharing.
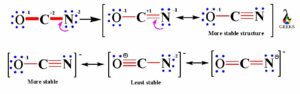
To get the more stable resonance structure, the negative charge should be on the element with more electronegativity. So, in the above structure oxygen having negative charge on one resonance structure, which is more stable as oxygen more electronegative than C and N.
We have to convert the nitrogen atoms lone electron to bond pair to make C-N bond within C and N atom. As there are more charges on atoms so we have to convert more lone electron pairs of N atom into bond pair to get a triple bond between C and N, creating negative charge on O atom to give more stable structure.
Now, in the above more stable structure we can see that carbon atom now has eight electrons in four bond pairs i.e. carbon atom is satisfied with complete octet. As well the negative charge is on O atom as it is more electronegative and shows good lewis structure.
So, finally we conclude that, OCN- lewis structure shows three resonances after minimization of charges on it. One resonance structure shows single bond between O-C and triple bond between C-N, second resonance structure shows triple bond between O-C and single bond between C-N and the third resonance structure shows double bonds between O-C and C-N.
OCN- lewis structure shape
As we already seen in above resonance structure explanation, that the O atom bears -1 negative charge as it is more electronegative. Also O and C have a single covalent bond and C and N atom has triple bond showing a stable form of structure. So, there are zero lone electron pairs on central carbon atom. The VSEPR theory generic formula for OCN- ion is AX2.
As per the above structure and its valence electrons, the OCN- atoms arrangement looks planar; also there are no lone electron pairs present and also the geometry s not in bent shape. Then according to VSEPR theory The OCN- lewis structure is linear in shape.
OCN- Hybridization
Hybridization of any molecule can be determined by the electron density present on the atom. In the above OCN- lewis structure we discussed, central carbon atom is creating bonds within oxygen and nitrogen atom, now let us discuss about its hybridization.
There is a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen which shows a one electron density, also carbon has a single covalent bond with oxygen atom shows second electron density. As there are two electron densities for carbon atom in OCN- lewis structure, the two hybrid orbitals can form by carbon atom to form bonding with oxygen and nitrogen atoms.
Therefore, the carbon atom can form one ‘s’ hybrid orbital and one ‘p’ hybrid orbital during formation of single bona and triple bond with oxygen and nitrogen atom. Thus, the central carbon atom has ‘sp’ hybridization in OCN- lewis structure.
OCN- polar or nonpolar
Some points to be noted, while considering any molecule is polar or non-polar in nature as follows.
- If two atoms have more electronegativity difference then tha molecule is polar in nature.
- Symmetry or assymetrical molecular shape, if symmetrical then non-polar and if assymetrical then it is polar molecule.
- Dipole moment creates due to more electronegative central atoms.
Let us discuss the polar or non-polar nature of OCN- lewis structure. Electronegativity of C atom is 2.55, electronegativity of O atom is 3.44 and electronegativity of N atom is 3.04. The differences of electronegativities of all three elements are clearly seen.
In case of OCN- lewis structure, carbon and oxygen (C-O) and carbon and nitrogen (C-N) bond creates dipole on it due to their electronegativity differences. Basically we know that, the molecule is polar when it has one or more lone electron pairs on central element and having different outer elements.
Thus, central carbon atom of OCN- ion has no lone electron pairs and also OCN- ion have assymetrical geometry. So, OCN- ion is polar in nature.
OCN- lewis structure bond angle
OCN- lewis structure has three elements arranged in a single horizontal plane and having assymetrical distribution of electrons which shows linear shape of OCN- ion.
So, the OCN- lewis structure has 180 degree bond angle.
OCN- lewis structure electron geometry
We have already discussed about the leis structure, formal charges, valence electrons and resonance structure of OCN- ion. From which we can see that there are 16 total valence electrons are present on OCN- ion.
From these 16 valence electrons we can create two double bonds between O-C and C-N or we can create one triple bond between either O-C or C-N. But the stable form of OCN- resonance structure show a single bond between O and C atom and a triple bond between C and N atom with negative charge on O atom. Also there are three lone pairs on O atom and two lone pairs on N atom due to which this ion is termed as ambidentate ligand.
So, OCN- ion shows tetrahedral electron pair geometry.
OCN- Uses
As the cyanate ion (OCN-) is toxic in nature i.e. it is flammable, also cause irritations to human skin, eyes and mucous membrane. We have not seen the cyanate ion in our general use of day to day life. It could be used in only high level chemical factories and industries.
Also Read:
- Nh4 lewis structure
- Nsf lewis structure
- Mg3n2 lewis structure
- Chf3 lewis structure
- Sicl2br2 lewis structure
- Ncl3 lewis structure
- Ch2n2 lewis structure
- Clo lewis structure
- Bacl2 lewis structure
- Baf2 lewis structure

Hello everyone, I am Dr. Shruti M Ramteke, I did my Ph.D. in chemistry. I am passionate about writing and like to share my knowledge with others . Feel free to contact me on linkedin