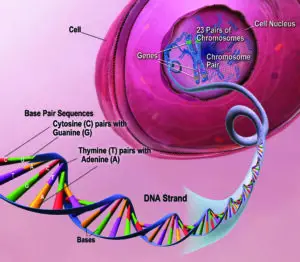
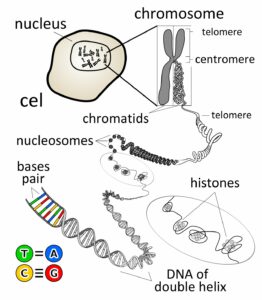
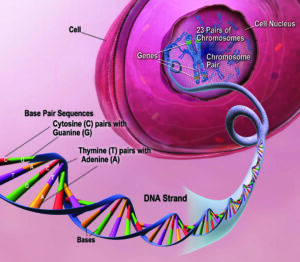
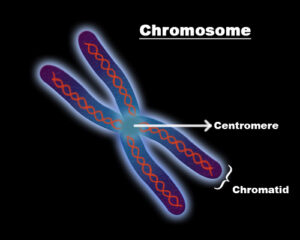
In this article, you will get to know about the seed plant examples. Seed plants are phanerogams(currently not in use) and also known as spermatophytes, a collection of gymnosperm & angiosperms.
Seed plants evolved from cryptogams by the occurrence of seed habit. The first step towards this is shown by the formation of two types of spores i.e. megaspores producing female gametophytes and microspores producing male gametophytes.
- Cycas revoluta
- Cycas circinalis
- Cycas pectinata
- Cycas rumphii
- Cycas beddomei
- Cycas siamensis
- Ginkgo biloba
- Pinus roxburghii
- Zamia fufuracea
- Ephedra sinica
- Welwitschia mirabilis
- Gnetum costatum
- Gnetum gnemon
- Sequoia sempervirens
- Thuja occidentalis
- Araucaria hetrophylla
- Agathis australis
- Agathis robusta
- Pinus radiata
- Pinus gigardiana
- Pinus sylvestris
- Pinus khasya
- Pinus wallichiana
- Pinus merkushi
- Abies balsemea
The first seed plant is a gymnosperm, having a naked seed without fruit. They are flowerless and lack the enclosure of fruit. They have cones or strobili as reproducing organs. They are the most abundant group of plants in the class. It includes a wide range of plants from shrubs to trees. It ranges from the smallest wolfia to the longest sequoias.
They are divided into 4 main domains:
- Cycadophyta
- Ginkgophyta
- Coniferophyta
- Gnetophyta
Are any of the Seed Plant Examples also Monoecious?
Yes, several seed plant examples are also monoecious. Monoecious plant examples include corn, pumpkin, and oak trees. These plants possess both male and female reproductive organs on separate parts of the same plant. As a result, they are capable of self-fertilization and cross-pollination, promoting genetic diversity within their species.
Cycadophyta
The genus Cycas includes about 20 species distributed worldwide, cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions over the planet. It is found in Australia, New Zealand, Japan, China, Burma and other pacific islands. In India, it is found in Orissa, Bengal, Madras etc. It looks like a small palm tree in appearance and two species are planted for ornamental purposes in gardens (ex: Cycas revoluta and Cycas siamensis). Other four species also found in India are Cycas circinalis, Cycas pectinata, Cycas rumphii, and Cycas beddomei.
They are having slow growth process, unbranched stem and soft-wood trunks i.e. manoxylic type
Anemophilous type of pollination is found, having no female cones and devoid of double fertilization.
They possess coralloid roots with a normal root system. Some members of cyanobacteria occupied the internal spaces in between roots for better absorption of water and minerals by developing a symbiotic relationship with them. Example: Nostoc and Anabaena
Cycas revoluta
It is commonly known as Sago palm or King Sago. They are native to Japanese islands and southern china. It is drug-tolerant and requires very little maintenance.

The height of the plant lies between 2-9feet. Due to slower growth, it can be used as ornamental at home. They are common as Bonsai plants. Leaves are arranged in a rosette fashion and are deep green.
Cycas circinalis
It is restricted to the southwest zone of India. Commonly known as Queen Sago. The height of the plant is 4-5 metres. It is found in rocky geographical regions as well as near coastal regions. It is considered “Endangered” in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species,2010 due to a population reduction.
Cycas rumphii
It is native to Australia and Indonesia. The height of the tree is up to 10 metres. This species is classified as the “Near-threatened species” in the IUCN Red List of Threatened species in 2011. It is commonly known as Bread palm. The gum extracted from the plant is used for the making of glues/adhesives.
Cycas beddomei
It is native to Tirumala Hills near Andhra Pradesh and the northwest of Madras. Pollens are narcotic so are seeds as well. Gum is used as an antidote for snake and other animal bites. It is also one of the threatened plant species of India.
Cycas pectinata
It is found in the northeast region of the country. Native to China, Bangladesh and some parts of Nepal. They are most probably 10-12 metres long in height. Stems are mostly used to make toys and cosmetics for hair-related issues. Species are classified as “Vulnerable” in IUCN Red List Data, 2010.

Cycas siamensis
Native to Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam and some other nearby countries. It is commonly known as Thai Sago. It is approx 100-150 cm long. Only young leaves are edible while seeds are not edible due to toxicity. Because it contains a toxic phytochemical “cyacin” which is a hepatotoxic agent. It is also categorised under the vulnerable species in the IUCN list.
Ginkgophyta
Two of the three genera become extinct i.e. Ginkgogoites and Baiera while the only living genus is Ginkgo. The single species of this genus is Ginkgo biloba also known as the maidenhair tree. It has been found in the Jurassic period (the era of dinossaraus). It is native to China but also found in some regions of America, Central Europe, Australia and North America etc. It is approx 60-90 meters long in height. They possess a specific feature of fire resistance.
Ginkgo biloba
The only surviving plant of this division with a height of ~156 meters. Deciduous in nature and has hard woody trunks with proper growth rings. As per the specific name, leaves are bilobed and become golden during autumn.
Reproductive parts are dioecious as they are present on different plant bodies. They are highly rich in flavonoids and terpenes & specially used in the treatment of pre-menstrual syndromes, vertigo and cognitive impairment.
CONIFEROPHYTA/PINOPHYTA
Commonly known as conifers i.e. cone-bearing plants. Over 700 species are present over the earth. They are dominant in the colder regions worldwide and cold zones of the north of the country. From the largest tree to the oldest ones all are lying in this group of gymnosperms.
They have needle-like leaf structures with xerophytic characteristics like the presence of sunken stomata with a thick cuticle layer over the leaf surface to prevent the process of transpiration. Stems are mostly tall and branched in nature due to the rich deposition of lignin in stems, that’s why they are so hard and represent the pycnoxylic type of woody trunks. Tap-root system is found with the mutual relationship of ectotrophic mycorrhiza.
Male and Female cones are present and are monoecious, which helps in the process of reproduction. They can reach up to the height of 3-50 metres. They appear pyramidal or conical like a “Christmas tree’ due to radial branching. This shape helps in the slipping of snow from the trees to prevent them from being overweight on ice on them.
Some of the common examples are Sequoia, Thuja, Abies, Firs, hemlock and spruces etc.
Thuja occidentalis
- Native to Europe and North America.
- Commonly known as White cedar
- Highly used for homoeopathic medicines
Zamia furfuracea
- Native to Mexico
- Common name-Cardboard palm
- Drought tolerance

Araucaria hetrophylla
They are endemic to Norfolk Islands and also found in Brazil, Argentina and New Guinea. These trees are also know as monkey-puzzle trees.They can reach up to 200 feet in length. they posses beautiful whorls and exactly looks like a Christmas trees decorated with snow.
Araucaria hetrophylla
Abies balsemea
- Also known as Canada balsam
- Gum is used as a fixative agent to form permanent slides in laboratories.

Sequoia sempervirens
- Also known as Redwood
- Tallest gymnosperm with a height of 110-120 metres.
- It cannot tolerate atmospheric pollution.
Pinus roxburghii
- This is also called “Chir pine”
- Native to North-America
Pinus wallichaina
They are native to Himalayan & Hindi-kush mountains and reach a height of 55-60 metres long. They fall into the threatened species of IUCN Red List Threatened Species. They are also called Himalayan White Pine.
Pinus gigardiana
- Commonly known as the Chilgoza tree
- Used as the most expensive dry fruit.
- They are the only edible pine-nuts
- Native to Chamba district of Himachal Pradesh

Agasthis australis
They are native to New Zealand and other northern regions of the world. They are the oldest species in the family as they are a follow-up from the Jurassic era. Wind pollination is observed in the flowers of the plant. The height of the tree is 45-50 metres.

Agasthis robusta
- These are also known as Kauri pine. Trees are up to a height of 25-30 metres. They are native to Australia and Budapest. The canopy is almost cylindrical. Woods and trunks are used for furniture, pencils and bats making purposes.
Pinus merkushi
They are native to Myanmar and Vietnam. Leaves are needle-like in shape and are long up to 20-25 metres.
Pinus sylvestris
They are also known as Scotch-pine and are native to Russia, China, Finland, Germany and many other countries. Trees are long up to 30-40 metres. They also have mycorrhizal interaction in their roots for proper water and mineral absorption.

Pinus radiata
They are native to California and Mexico. They are the evergreen conifer of the family. Flowers bloom in the season in bright and beautiful yellow colour that’s why termed as yellow showering of the pinus. In roots, they show mycorrhizal interactions as Verbicular-Arbuscular mycorrhizae(VAM) along with the normal root system.
Pinus khasya
As the name suggests, they are found on the Khasi hills of Meghalaya in India that’s why are named Pinus khasya. They are used for timber purposes and the production of turpentine. They can grow up to 45 metres. Initially, they are conical in shape but as time passes away it becomes rounded. These plants are categorised as “Least concern” in IUCN Red List Book.
GNETOPHYTA
Almost 65 species are found in these genera. They are specifically found in the Himalayan regions of India. It includes the living plants close to angiosperms by having the flower-like arrangement of sporophylls. Gnetales are the highest gymnosperm as they act as the connective link between gymnosperms and angiosperms group of plants. Most are extinct while the living plants are
Ephedra (E.sinica, E.nevadenis); Gnetum(G. gnemon, G.costatum); and Welwitschia(Welwitschia mirabilis).
Ephedra sinica
They are sun-loving and mostly found in arid regions i.e. regions of Asia, Europe and North Africa. It is an evergreen shrub with scaly leaves and is used in the treatment of cough and cold. Ephedrine is the phytochemical extracted from the plant which is similar to adrenalin. Some of the deaths were observed during the trials which is why it was banned by US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in 2004.
Gnetum
It is generally found in some regions of Africa and South America. The tree is about 20 metres long and has pulm-like edible fruit. It inhabits humid, tropical and swampy rainforest and possesses angiosperms like leaves having margined lamina with pinnate venation. Examples: Gnetum gnemon, Gnetum costatum
Welwitschia mirabilis
Dessert-dwelling and confined to dry-region of the world. They show extremely xerophytic features. The plant is mostly dioecious and has an unbranched stem. They have a unique characteristic of slow growth as two leaves grow for the entire lifespan of the plant.
Please click to learn about Polycarpic Plant Example.
Also Read: