In this article we are going to analyze is hydrogen bond stronger than Covalent or not.
A hydrogen bond cannot be stronger than a covalent bond. The bond energy of a covalent bond is 200 KJ/mole and the bond energy of a hydrogen bond is 8-42 KJ/mole.
Let’s have a closer approach towards the covalent bond, details and Facts.
Basically, a covalent bond is formed between a non metal and non metal by the process of mutual sharing of electrons.
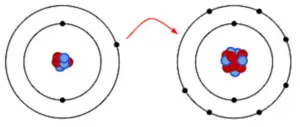
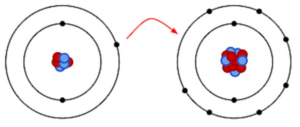
Consider hydrogen atom
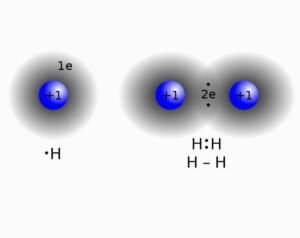
Image credit: Wikimedia
We know it has one atom and needs one more to satisfy its duplet, so what it does is shares its one electron with one more hydrogen atom. In this way through mutual sharing of electron pair the bond is satisfied and the so formed bond is a single bond (as only one pair of electrons are shared for bond formation).
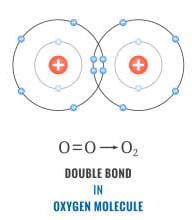
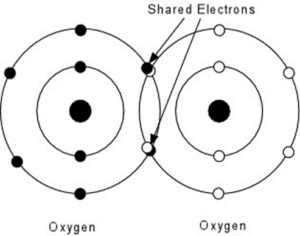
Consider oxygen atom
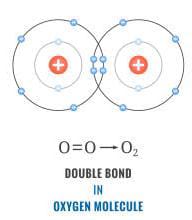
We know that it requires 2 more electrons to achieve it octet. So one oxygen atom shares its pair of electrons with one more atom of oxygen. So in this way a double bond is formed. Hence we can say that oxygen is an example of double covalent bond.
Consider nitrogen atom
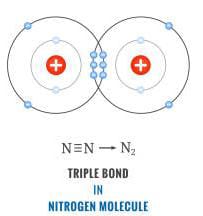
We are aware that Nitrogen had 2,5 as its electronic configuration so in order to stabilize its octet it is in need of another three atoms.
So what it does is shares it electrons with more atom of nitrogen. This mutual sharing of electrons (3 pairs of electrons are shared) gives rise to triple bond. Hence it can be said that Nitrogen is an example of triple covalent bond.
Some Properties of Covalent bond in general:
- Covalent bonds (single, double, triple) are formed from molecules and not from ions.
- They are very bad conductors of electricity (as they do not have ions).
- They have very weak Vander Waal forces (i.e. intermolecular forces of attraction).
- They are quite weak in comparison to ionic bonds.
- They usually exist as gases, liquids and soft solids the reason being intermolecular forces of attraction.
- They have low melting point and low boiling point because of weak Vander Waal forces.
- Most of the times the liquid form is very volatile.
- Talking about the solubility it depends whether the covalent compound is :
Non-Polar Covalent bonds:
They do not conduct electricity and are insoluble in water. Basically they have all the general properties of general covalent bonds.
Polar Covalent bonds:
To understand the concept of Polar Covalent bonds let’s have a look at the example of HCl.
Chlorine is electronegative so it will pull electron pair towards itself. So partial positive charge will be developed on hydrogen and partial negative charge will be developed on the chlorine (this charges are very minimal, so electrons are shared but not equally by both). So this kind of compounds which have difference in the electronegativity have polarity and ate called as polar compounds. This compounds are generally most of the times soluble in water, conduct electricity (as they have some amount of charges present).
Let’s analyze hydrogen bonding:
A hydrogen bond is the type of bonding where a hydrogen atom is attached to a covalently bonded atom (which should be electronegative in nature) and also attached to one more electronegative atom. This bond is the hydrogen bond or hydrogen bonding.
Some Properties of Hydrogen bonding:
- As temperature increases hydrogen bonding strength decreases.
- It has around five to ten percent ionic nature.
- Consider hydrogen bonding in molecule of H2O which has three different states:
- Taking into account solid which is ice has a temperature of around less then or equal to zero degrees Celsius. It has four hydrogen bonds.
- Taking into account liquid, which has a temperature of around zero to four degrees Celsius. It has two hydrogen bonds.
- Taking into account gas, which has a temperature greater or equal to four degrees Celsius. It exists usually in vapor or steam form. It has no hydrogen bond.
- As the electronegativity increases the strength of hydrogen bond also increases.
- Have you ever wondered why alcohol does not dissolve in water? The reason for this is that alcohol forms hydrogen bonding with water. Hydrogen bonding is formed between partial positive hydrogen atom of alcohol and partial negative end of oxygen of water.
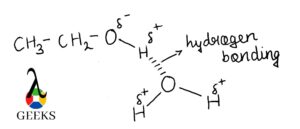
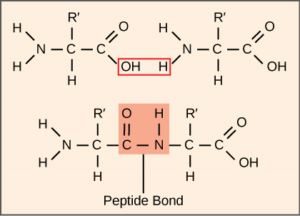
For complete details about hydrogen bonding refer: Is Peptide Bond A Hydrogen Bond: Why, How, Detailed Facts
Why Covalent bond is stronger than hydrogen bond?
We know that the bond energy of hydrogen bonding is very less as compared to that of covalent bond (bond energy of hydrogen bonding is 8-42 KJ/mole and covalent bond is 200 KJ/mole).
Also the covalent bond has shorter bond length in comparison to the hydrogen bond (it has quite longer bond length). We know that bond length and the bond strength are related in inverse manner meaning the two quantities are inversely proportional to each other. Covalent bonding short bond length will have more strength hence covalent bonding is stronger than hydrogen bonding.
Read more about: 15+ Limiting Reactant Problems: And Solutions
Are hydrogen bonds stronger than non polar covalent bonds?
As we have seen in the above section that non polar covalent bonds are the ones which are bad conductors of electricity, possess weak Vander Waal forces, have low melting point and low boiling point and are insoluble in water.
On the other side we can see that hydrogen bonding can conduct electricity, is stronger than Vander Waal forces, has high melting point and high boiling point. We can conclude that covalent bonding and hydrogen bonding both being chemical bond , covalent bond is always stronger than hydrogen bond ( as it is formed as a result of mutual sharing of electrons).
Hence non polar covalent bonds are stronger than hydrogen bonding.
Read more about: 5+E1 Reaction Example: Detailed Explanations
Hydrogen bond v/s covalent bond
| Hydrogen Bonding | Covalent Bonding |
| Hydrogen bonding involves dipole-dipole kind of attraction. | Covalent bonding involves mutual sharing of electrons between atoms. |
| Has the ability to conduct electricity | Does not have the ability to conduct electricity |
| Have higher melting point and higher boiling point. | Has comparatively lower melting point and lower boiling point |
| Are seen to be stronger than Vander Waal forces. | Are weaker Vander Waal forces |
| Bond energy is around 8-42 KJ/ mole. | Bond energy is 200 KJ/mole. |
Also Read: