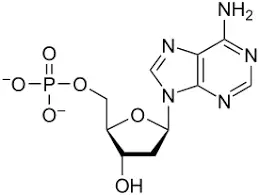
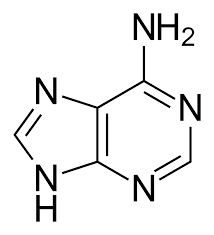
Adenine and guanine are formed during purine metabolism. The nucleotide inosine monophosphate (IMP) is the source of both adenine and guanine.
The nucleotide which is called the inosine monophosphate is composed of atoms that are derived from amino acids, gluatamine, aspartic acid, Coenzyme teteahydrofolate and as well as glycine and is thus made from the already existing ribose phosphate. H2O and NH3 ice is mixed and thus how is adenine formed.
When is adenine formed?
Adenine is just like an amine product that is added to the purine after the addition of the initial amino group. Adenine is only formed when a mixture of H2O-NH3 ice is present.
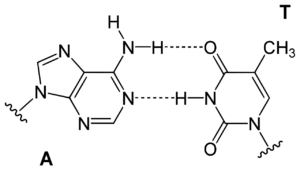
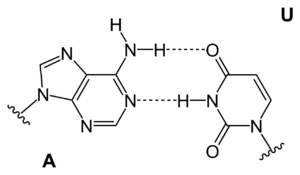
In the structure of DNA, adenine gets combined to thymine with the help of two hydrogen bonds that will make the nucleic acid structures stable. Whereas in RNA, adenine gets to bind to uracil. RNA helps in the synthesis of protein.
Adenine forms a nucleoside called adenosine when it gets attached to ribose. When attached to deoxyribose, adenine forms deoxyadenosine. Adenine is joined with thymine in the structure of DNA by two hydrogen bonds, resulting in a stable nucleic acid structure.
Adenine forms a chemical bond with uracil in RNA. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Amino acids are synthesized by the four-letter code. These four-letter codes include the two purine and two pyrimidine nucleobases. Adenine (A) and thymine (T) with cytosine (C) and guanine (G) together form the code that helps in the cellular synthesis of amino acids.
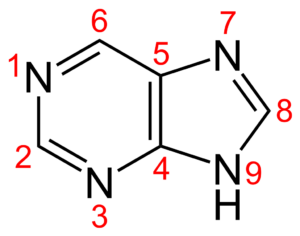
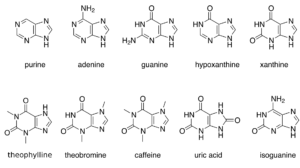
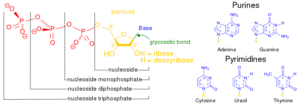
The DNA and RNA in cells are made up of five different types of nucleotides. The purine derivatives of these five bases are adenine (A) and guanine (G). The other bases, such as thymine (T), uracil (U), and cytosine (C), are referred to as pyrimidine derivatives. Purines are found in animals and plants, and they are used to make adenine. Some organs and fishes are likewise high in purine. The pyrimidines are a different sort of nucleotide group. Pyrimidines are smaller than purines because they only have one nitrogen circle.
Where is adenine formed?
The nitrogenous base adenine is present in DNA. It is the nucleotide building block of DNA, consisting of two joined rings. Thymine is invariably paired with adenine.
When DNA is joined, a covalent connection is formed. The deoxyribose sugar and nitrogen form this connection. The hydrogen atom is thus removed by the link created. The new structure formed is known as adenine residue, as a fragment of bigger molecule.
There are two types of purine nucleobases out of which adenine is useful for the formation of nucleotides which are present in the nucleic acids of DNA and RNA. The bits of RNA and DNA that are required for pairing are known as “nucleobases.” On the other hand, “nucleotides” are the chemical compounds that comprises of a heretocyclic base, a single or more than one phosphate groups and a sugar.
DNA and RNA present in the cells comprise five main bases. Out of these five bases, adenine (A) and guanine (G) are known as the purine derivatives, whereas the other bases, thymine (T), uracil (U) and cytosine (C), are known as the pyrimidine derivatives.
Purines are generally present in animals and plants, from where we can obtain adenine. Foods which are rich in purines include some organs like kidneys, liver and brain. Fish is also a major source of purine, for example mackerel, anchovies and herring.
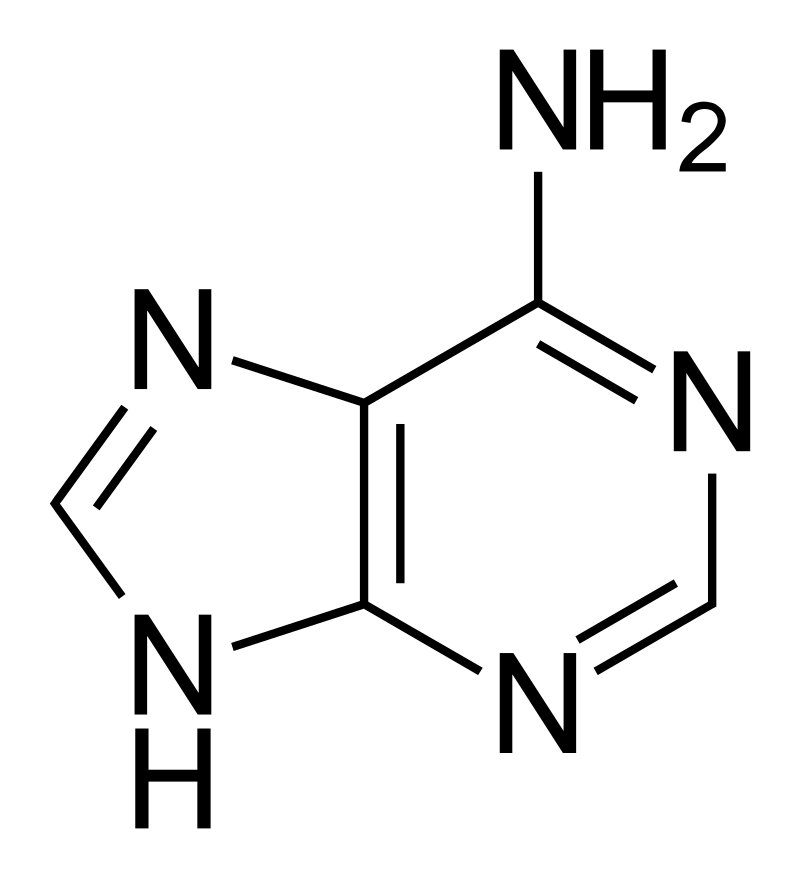
Structure of adenine:
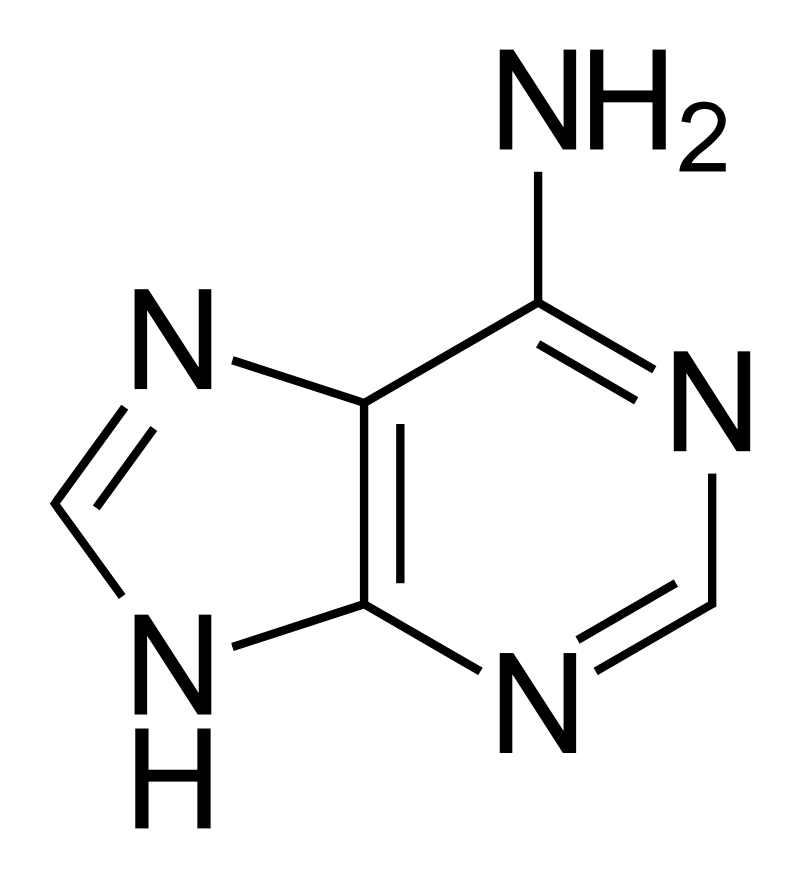
Adenine is a chemical compound which comprises of nitrogen, atoms of hydrogen and carbon. The chemical formula of adenine is C5H5N5. A nucleotide is created when a purine like adenine gets linked up with phosphate and ribose.
DNA and RNA are made up of four nitrogenous bases, with adenine serving as the genetic code for living creatures. Adenine is a key component of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which provides energy to cells.
The fundamental building blocks or small elements often make up the complex structures. For instance, the construction of a house comprises bricks, windows, and doors, which are generally smaller components. In a similar way, living creatures are also built up of molecules that consist of atoms and other smaller molecules.
On considering how is adenine formed, adenine is an essential and fundamental building ingredient required in life. The genetic code of all the biological beings like plants, humans, fungi and several microorganisms are stored in DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). Both acids contain adenine, which aids in the stabilization of nucleic acid in molecules.
With regards to the question how is adenine formed we know that when a purine, such as adenine, is joined to phosphate and ribose, a nucleotide is formed. Adenine fits in the nucleotide family known as the purines. A purine’s fused structure combines a six-membered nitrogen circuit with a five-membered nitrogen circle. There is another type of nucleotide group known as the pyrimidines. These comprises of one nitrogen circle, thus the size of pyrimidines are less than purines.
Detailed facts:
Several experiments were done in the purpose of studying the adenine production.
Erwin Chargaff, an Austrian biologist, provided another important piece of DNA structure information. Chargaff investigated the composition of A, T, C, and G bases in DNA from various animals.
Adenine was referred to as Vitamin B4 in the early literature. The reason behind it was that adenine is being produced inside the body and it was not necessary that adenine must be taken with diet. But later, the facts related to adenine’s being called a vitamin do not link up with the description given to the vitamin. Thus adenine has been removed from the group of Vitamin B.
Hermann Emil Fischer was one of earliest scientist to do research about adenine. He discovered that the two Vitamin Bs namely riboflavin and niacin, forms a chemical bond with adenine to bring the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinuleotide (FAD) respectively.
In 1960, Oró produced adenine in his first experiment. The procedure includes less than 1.0 M of ammonium cyanide (CH₄N₂). Adenine was manufactured in 0.5% yield by warming up the mixtures of ammonium cyanide at a temperature of 70 degree Celsius for many days. After the experiment was done the abiotic production of adenine from the HCN polymerization has been attained several times under various situations. 20% adenine is the highest yield that resulted from the reaction between HCN and liquid ammonia in a sealed-tube.
In today’s world, the most popular way used in the industry for the production of adenine is an advanced form of formamide method. In this method the formamide is being heated up at a temperature which is lower than 120 degree Celsius in a sealed flask for about five hours to obtain adenine as a final product. Using phosphorus oxychloride (phosphoryl chloride) or phosphorus pentachloride, which works as an acid catalyst, and sunshine or ultraviolet conditions, the quantity of the response, is considerably increased.
Also Read: