Purine are heterocyclic aromatic chemical compounds that are made up of Carbon atom, Hydrogen atom and Nitrogen atom.
The following are the purine examples that we will discuss in this article.
and many more.
In the nucleic acids both DeOxyRibose Nucleic acid which is known as the DNA and Ribonucleic Acid which is known as RNA, Adenine and guanine are the purine compounds present.
Read More on Sequence Of Nitrogenous Bases In DNA: What, Why, Purpose, Detailed Facts
Explanation on Structure of Purine and purine examples:
- Purines are aromatic heterocyclic compounds.
- The base chemical Code of purines is C5H4N4.
- It is a 2 -ring structure made up of a pyrimidine ring and an imidazole ring connected together.
- The pyrimidine ring in purine is a six membered ring and has 2 atoms of nitrogen in the 3, 1 region of the ring.
- The Imidazole ring in purine is a five membered ring and has 2 atoms of nitrogen in the seventh and ninth region of the ring.
- So totally the purine has four nitrogen atoms in it that are in the first, third, seventh and ninth place or position.
Read more on Biosynthesis of Purines and Pyrimidines | An important part of cellular metabolism
Detailed Characteristics of Adenine:
- Adenine is one of the five nitrogenous bases (Adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil, thymine) present in the nucleic acids (DNA, RNA).
- A subunit of Adenine which is called the adenosine triphosphate also called ATP is the energy molecule that is utilized by the cell for biochemical reactions.
- The chemical Code is C5H5N5
- Adenine-purine pairs with thymine which is a pyrimidine.
- The IUPAC Name of Adenine is 9H-purin-6-amine.
- The Molar mass of adenine is 135.13 g/mol and Density of adenine is 1.6 g/ cm3
Read More on Adenine vs Thymine: Comparative Analysis
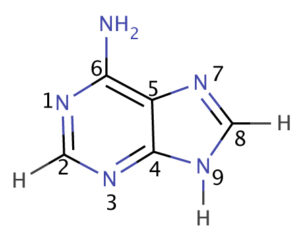
Image Credits- Wikimedia
Characteristics of Guanine:
- Guanine is similar to adenine.
- The chemical code of guanine is C5H5N5O.
- The IUPAC Name of Guanine is 2-amino-1H-purin-6(9H)-one.
- A portion of guanine which is called as Guanosine triphosphate which is an energy molecule and also aids in the cell signaling mechanisms.
- The structure is very similar to adenine with few differences.
- The difference between adenine and guanine is that the presence of amine group in adenine on C6, and an extra double bond between C6 and N1 in its complementary pyrimidine ring whereas the amine group in guanine is on C2 and a carbonyl group on C6 in its pyrimidine ring.
Read more on Is Guanine A Purine :Why And Detailed facts

Image Credits- Wikimedia
Characteristics of Hypoxanthine:
- Hypoxanthine is a purine organic compound that is majorly found in muscle tissues of humans.
- Hypoxanthine has OXO substituent at the 6th position.
- Hypoxanthine is a fundamental metabolite.
- The IUPAC name of Hypoxanthine is 1,9-Dihydro-6H-purin-6-one.
- Hypoxanthine is the product of purine catabolism.
- Rarely they are present in nucleic acids and aid in the salvage pathway for nucleic acid synthesis.
- Hypoxanthine is a PARP-poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)Inhibitor which has anti-inflammatory and cyto-protective effects.
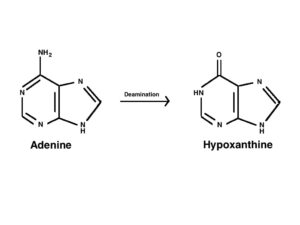
Image Credits- Wikimedia
Characteristics of Xanthine:
- Xanthine is an oxopurine in which the second and sixth positions have an oxo group.
- It is present in the bodily fluids and tissues even in urinary calculi.
- Degradation of adenosine mono-phosphate is performed by xanthine as an intermediate to form uric acid.
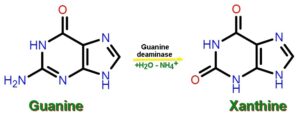
Image Credits- Wikimedia
Characteristics of Theophylline:
- The chemical name of Theophylline is 1,3-dimethylxanthine
- It is used to relax the smooth muscles.
- The chemical code for theophylline is C7H8N4O2.
- It is also called Elixophyllin.
Characteristics of Theobromine
- Theobromine which is also called dimethylxanthine by having 2 methyl groups in the third and seventh position.
- It is a purine derivative that is obtained from the cacao plant commonly known as chocolate.
- It is an adenosine receptor antagonist and also a metabolite.
Characteristics of Caffeine:
- A Xanthine alkaloid that is found in the seeds and other plant parts of certain plants.
- The chemical code of Caffeine is C8H10N4O2.
- It is also a natural pesticide.
- High doses of this compound may lead to enzyme elevation and damage the liver.
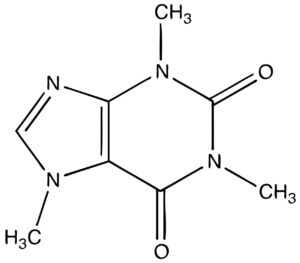
Image Credits- Pixabay
Read More on Adenine structure in RNA: Detailed Facts
Characteristics of Uric Acid:
- The chemical code of uric acid is C5H4N4O3.
- Uric acid is a product of protein metabolism that is found in bodily fluids like urine, blood etc..
- Uric acid is also called 2,6,8-hydroxypurine.
- The IUPAC Name of Uric acid is 7,9-dihydro-3H-purine-2,6,8-trione.
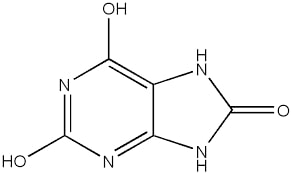
Image Credits- Wikimedia
Read More on Purine metabolism | Importance in human physiology
Characteristics of Isoguanine:
- Isoguanine is an oxopurine as the amino group is positioned at the 6th place.
- Iso guanine is also called 6-amino-7H-purin-2-ol, 6-amino-3,7-dihydro-2H-purin-2-one.
- The chemical code of Isoguanine is C5H5N5O.
- The IUPAC name of isoguanine is 6-amino-1,7-dihydropyran-2-one.
Also Read:
- Does nucleus have chromosomes
- Ecosyetm examples
- Do lysosomes have proteins
- Flower anatomy
- Basidiomycota examples
- Animal cell
- True fruit example
- Enzymes in hydrolysis
- Polymerase chain reaction in molecular biology
- Carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion

Hello, I am Sugaprabha Prasath, a Postgraduate in the field of Microbiology. I am an active member of the Indian association of applied microbiology (IAAM). I have research experience in preclinical (Zebrafish), bacterial enzymology, and nanotechnology. I have published 2 research articles in an International journal and a few more are yet to be published, 2 sequences were submitted to NCBI-GENBANK. I am good at clearly explaining the concepts in biology at both basic and advanced levels. My area of specialization is biotechnology, microbiology, enzymology, molecular biology, and pharmacovigilance. Apart from academics, I love gardening and being with plants and animals.
My LinkedIn profile-