In this article, we will discuss the effect of wavelength on refraction, how does the refraction of the waves affect by the wavelength with detailed facts.
The wavelength governs the speed of the propagating wave in the medium. Depending upon the speed of the wave and the refractive index of the medium, it bends in the medium and gets refracted.
Does Wavelength Affect Refraction?
The wavelength of the propagating wave is directly correlated to the velocity of the light or a particle traveling in a wave.
The incident wave on the medium having a refractive index ‘n1’ traveling at a speed ‘v’ and wavelength λ will refract according to the variations of the wavelength while propagating in the medium of a refractive index ‘n2’.
The refractive index of the medium is related to the speed of the light by the equation
n=c/v
Where n is a refractive index of the medium
C is a speed of light, c=3*108m/s
And v is velocity of the light on refraction
If the wavelength of the beam of particles increases, then the frequency, and thereof the energy of the particles decrease. It is evident that the wavelength of the light on refraction does not change, that is the wavelength of the light before and after the refraction of the same light is the same.
But, the speed of the propagation of the wave depends upon the wavelength of the light. The relation between the speed and the wavelength of the light is formulated as
f=v/λ
Where f is a frequency of light
V is a velocity and
λ is a wavelength of the light
The energy of the particle is directly proportional to the frequency of the oscillating particle, and is given by the equation,
E=hf
Where ‘h’ is a Planck’s Constant, h=6.626*10-34J.s
The longer the wavelength, the less will be the energy associated with the particle, and thus the speed of the particle will be less. The particle traveling with a smaller wavelength will have higher energy pertaining to the particle and hence will travel with higher velocities.
Read more on Effect Of Refraction On Wavelength: How, Why, Detailed Facts.
Example: A photon of energy 0.58 MeV is incident on the medium having refractive index 1.33. Find the wavelength of the incident photons.
Given: n=1.33
E=0.58MeV=0.58*106*1.6*10-19=0.93*10-13Joules
h=6.626*10-34 J.s
The energy of the photon is equal to
E=hf
Hence, the frequency of the photon is
f=E/h
=0.93*10-13/6.626*10-34
=0.14*1021
=140*1018
=140EHz
The frequency of the photon is 140EHz.
The refractive index of the medium is the ratio of change in the speed of light.
n=c/v
Hence, the velocity of the light is
v=c/n
=3*108/1.33
=2.25*108m/s
The speed of the photon is 2.25*108m/s
Therefore, the wavelength of the photon is
v=fλ
λ=v/f
=2.25*108/140*1018
=0.0161*10-10
=1.61*10-12=1.61pm
Hence, the wavelength of the photon in the medium of refractive index 1.33 is 1.16 pm.
Read more on Effect Of Refraction On Frequency: How, Why Not, Detailed Facts.
How does Wavelength affect Refraction?
The propagation of the wave in any medium is defined by the length of the wave, its time period, and the frequency of the particle in a wave.
Though the wavelength does not change drastically on refraction, the speed of the particle relies upon the wavelength. If the wavelength is more, the speed will be less; and the speed acquired by the particle is high if the wavelength is very less.
If the light of the greater wavelength is incident, then the refracted beams of particles will possess less energy, and hence the speed of light will be reduced and refract at smaller angles.
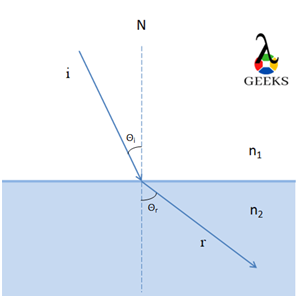
If the beam of the particle of a smaller wavelength is incident, then the particle will possess higher energy, and hence on refraction, the beam of the particle will have a sufficient speed to travel at a certain speed and refract at greater angles.
Read more on Types Of Refraction: Comparative Analysis.
How does Wavelength affect Angle of Refraction?
The wavelength of the light affects the speed and the frequency of the wave.
If the wavelength is bigger, then the speed of the light will be smaller and the light will reflect at a smaller angle; and if the wavelength is small then the light will reflect at the greater angle.
Consider a light incident from the medium 1 of refractive index ‘n1’ on the surface of the object having a refractive index ‘n2’. The refractive index is the ratio of change in the speed of light while propagating from medium 1 to medium 2.
n12=v2/v1
Where n12 is the ratio of the refractive index of the medium 1 to medium 2,
v1 is a speed of light in medium 1
v2 is a speed of light in medium 2
The velocity of the light is related to the wavelength by the relation
v=fλ
At a constant frequency of light, if λ1 and λ2 are the wavelength of the light traveling from medium 1 to medium 2 respectively, then the refractive index of the medium is related to the wavelength as,
n2/n1=λ2/λ1
By Snell’s Law,
n1sin θi = n2 Sin θr
n1/n2=sin θi/sin θr
Hence, relating to the above equation,
λ2/λ1 =sin θi/sin θr
sin θr=λ2λ1/sin θi
θr=Sin-1 λ2λ1/sin θi
The refractive angle depends upon the variations in the wavelength of the light and the incident angle of the beam as per the above equation.
Read more on Refraction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the angle of refraction if the light beam of a wavelength of 450nm is incident on the medium of refractive index 1.33 at an angle of 45 degrees?
Given: n1=1
n2=1.33
λ1 =450nm
We know that,
n1/n2=λ2/λ1
1/1.33=λ2/ 450nm
λ2=450nm/1.33
λ2=338.34nm
Hence, the wavelength of the light in the medium decreases to 338.34.
The refractive angle of the light is
θr=Sin-1 λ2λ1/sin θi
θr=Sin-1 338.34*450/sin 45
θr=Sin-1 338.34*450/ (1/√2)
θr=Sin (-1)/ (0.53)
θr=35.56
The light refracts at 35.56 degree angle.
How does the speed of the wave change on refraction?
As the light enters the denser medium, the speed of the wave decreases.
The frequency of the light decreases on entering the denser mediums and hence the energy reduces reducing the speed of light.
Does the angle of refraction depend upon the speed of the light?
If the wavelength of the particle is small, then the particle possesses high speed.
The greater the speed of the wave, the light will bend at a bigger refractive angle.
Also Read:
- Doppler effect examples
- Effect of refraction on wavelength
- Doppler effect for light
- Effect of refraction on frequency
- Robot end effector
- Ozone layer depletion effects
Hi, I’m Akshita Mapari. I have done M.Sc. in Physics. I have worked on projects like Numerical modeling of winds and waves during cyclone, Physics of toys and mechanized thrill machines in amusement park based on Classical Mechanics. I have pursued a course on Arduino and have accomplished some mini projects on Arduino UNO. I always like to explore new zones in the field of science. I personally believe that learning is more enthusiastic when learnt with creativity. Apart from this, I like to read, travel, strumming on guitar, identifying rocks and strata, photography and playing chess.