In this article we will discuss about Feso4 structure, characteristics and nine must to know facts about Ferrous sulphate which is an iron salt.
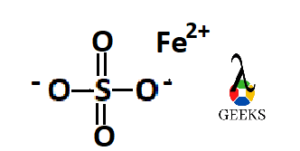
FeSO4 (hydrous) contains Fe2+, SO42-and most commonly seven molecules of water in its crystal structure. Ferrous Sulfate (FeSO4) is more popularly known as green vitriol that is green sulfate (vitriol which is an older name for sulfate).
What is the FeSO4 structure?
The structure of Feso4 (hydrous) consists of Fe2+, SO42- and most commonly seven molecules of water in its crystal. FeSO4 is bluish green in color.
On heating, the crystals of FeSO4 losses water of crystallization and their color changes from bluish green to white color.
Is FeSO4 soluble in water?
Yes, Ferrous Sulfate (FeSO4) is soluble in water. Ferrous Sulfate forms a aquo complex, [Fe(H2O)6]2+ when dissolved in water.
Why is FeSO4 soluble in water?
FeSO4 is an ionic compound. Like dissolves like so ionic compounds can dissolve in polar solvents. Water is a polar solvent so FeSO4 can dissolve in water.
The aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+ has a octahedral molecular geometry.
Is Ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) an acid or base?
Ferrous sulfate (Feso4) is formed by the reaction between sulfuric acid (a strong acid) and ferric hydroxide (a weak base) so Ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) is an acidic salt.

Why FeSO4 is an acid?
When FeSO4 is dissolved in water, the solution formed will have more H+(aq) ions than OH–. Thus Ferrous Sulfate is an acid.
Properties of FeSO4
| Compound name | Ferrous sulfate |
| Other names | Green Vitriol Copperas Iron(ll) sulphate |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| Exists as solid or liquid | Powder or crystalline solid |
| Acidic or basic nature | Acidic salt |
| Odour of FeSO4 | Odorless |
| Colour of FeSO4 (Ferrous Sulfate) | light-green (when hydrous) white (when anhydrous) blue-green (colour of FeSO4 solution) |
| Melting point of FeSO4 | 56-64 degree celsius |
| Molar Mass of FeSO4 | 151.908 g/cm3 |
| Density of FeSO4 | 2.84 g/cm3 |
| Covalent or Ionic Compound | Ionic Compound |
Is Ferrous Sulfate (FeSO4) a strong acid? If not why?
No, FeSO4 is a weak acid. Fe2+ is less polarizing and reacts partially with water to release H+ ion so Ferrous Sulfate (FeSO4) is a weak acid.
Is FeSO4 ionic or covalent?
FeSO4 is an ionic compound because it is formed by the electrostatic force of attraction between the Fe2+ and SO42- ions.
Why is FeSO4 an ionic compound?
An ionic compound is formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one element to another in order to achieve a noble gas configuration. It is formed when the difference between the electronegativities of atoms is large.
In FeSO4, there exists an electrostatic force of attraction between the Fe2+ ion (positively charged) and SO42- (negatively charged). So FeSO4 is an ionic compound.
Is FeSO4 a solid?
Yes, FeSO4 is either a light green (when hydrous) or white (when anhydrous) crystalline solid because in FeSO4, the force of attraction between the particles is stronger than the thermal energy of particles so FeSO4 exists as solid.
Why do FeSO4 exists as solid?
Substances in which the particles are very close to each other, the forces of attraction between the particles of substance are stronger even than the thermal energy of the particles such substances exist as solids so FeSO4 exists as solid
Is FeSO4 a precipitate?Why and why not?
Ans: A precipitate is an ionic solid that is insoluble in water. FeSO4 is soluble in water so FeSO4 is not a precipitate.
Is FeSO4 aqueous or solid?
FeSO4 is a light green (when hydrous) or white (anhydrous) crystalline solid. It is soluble in water.When dissolved in water, it forms aqueous solution.
Why is FeSO4 a solid and why it forms aqueous solution?
Substances in which the particles are very close to each other, the force of attraction between the particles of substance are stronger even than the thermal energy of the particles such substances exist as solid By this definition FeSO4 is a solid.
Aqueous mean dissolved in water. FeSO4 is soluble in water. When FeSO4 is dissolved in water, it forms aqueous solution.
Is FeSO4 a strong electrolyte?Why?
Yes, FeSO4 is a strong electrolyte. A strong electrolyte is a substance which dissociates completely into ions in water. As FeSO4 dissociates completely in water, so it is a strong electrolyte.
These ions conduct electricity in solution.
Frequently asked questions:
1) What does Ferrous mean?
Ans: The meaning of ferrous is “containing iron”. This term is derived from Latin word ferrum which mean iron.
2) How do Fe3+ and Fe2+ differ from each other?
Ans: Fe3+ has diamagnetic properties while fe2+ has paramagnetic properties.
3) What is the important metabolic processes in which iron (Fe) plays an important part?
Ans: Iron plays an important role in various metabolic processes like oxygen transport to cells of our body, DNA synthesis and production of energy in electron transport.
4) Which is dietary iron? Is it ferrous or ferric?
Ans: Dietary iron exists in three main forms – Ferrous iron, Ferric iron and Heme iron
5) Which is the readily absorbed form of iron?
Ans: The readily absorbed form of iron is the heme iron.
6) What is the shape of the crystal of Ferrous Sulfate?
Ans: The Ferrous Sulfate crystal has octahedral molecular geometry. Ferrous sulfate crystals are paramagnetic in nature.
7) Which is correct Ferrous Sulphate or Ferrous Sulfate?
Ans: Sulphate and sulfate both refer to the SO42- salt of iron. The sulphate spelling with ‘ph’ is used in British English while sulfate spelling is recommended by IUPAC.
8) Why is the color of FeSO4 (Ferrous Sulfate) change on heating?
Ans: The colour of ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) change when heated due to the evaporation of water of crystallization and we get anhydrous Ferrous Sulfate.
On heating the colour of crystals change from light green to white in colour.
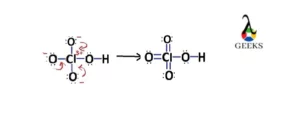
9) How is FeSO4 structure looks like?
Ans: The structure of FeSO4 consists of Fe2+ and SO42-ion.
The structure of FeSO4 is as follows :
Conclusion
Feso4 is an acidic salt which is formed by the reaction between a sulfuric acid (strong acid) and Ferrous Hydroxide (a weak base). FeSO4 is a weak acid. Heme is the readily absorbed form of iron.
More Lewis Structures: