Metabolic enzymes are loosely defined enzymes involved in various metabolically important reactions necessary for life and homeostasis.
Some Metabolic enzymes examples include:
- Phosphofructokinase
- Pyruvate kinase
- Pancreatic lipase
- Hepatic lipase
- Lysosomal lipase
- Phospholipases
- Amylases
- Bromelain
- Papain
- Trypsin
- Chymotrypsin
- Alkaline phosphatase
- Alanine transaminase
- Aspartate transaminase
- Lactase
- Maltase
- Enterokinase
They are the proteins involved in many cellular functions and at organ levels and hence are necessary for survival.
1. Phosphofructokinase
It belongs to the sugar kinase family. It is involved in a catabolic reaction in glycolysis. It is also called the pacemaker of the glycolysis pathway. Its deficiency leads to glycogenosis IV, which makes this enzyme clinically significant. The symptoms of its deficiency are muscle cramps, vomiting, and nauseated also might lead to myoglobinuria.
2. Pyruvate Kinase
It is the last enzyme involved in the glycolysis pathway. Genetic defects causing deficiency of this metabolic enzyme lead to chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anaemia (CNSHA). There are four tissue-specific isozymes of this enzyme. Any mutation in the gene coding this enzyme might lead to a lack of mitochondria in the tissue.
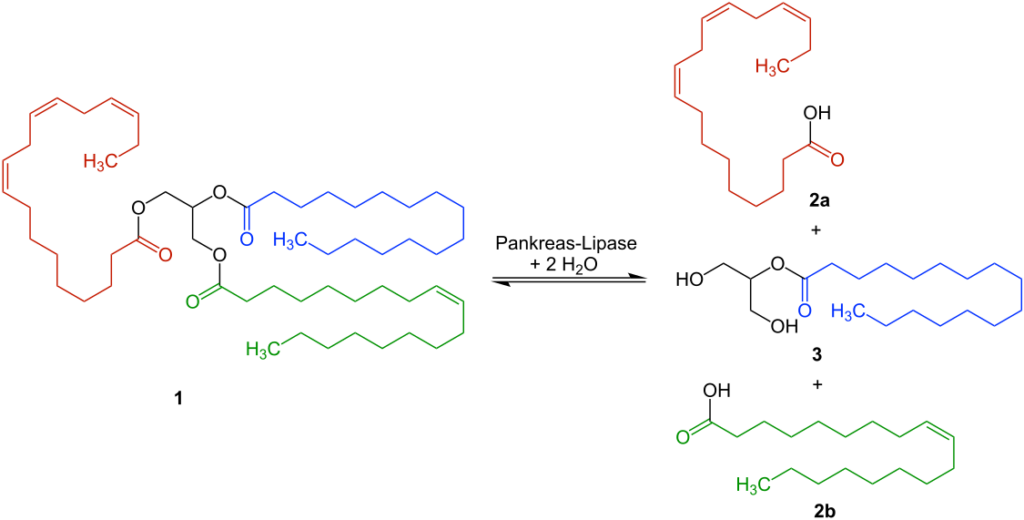
3. Pancreatic Lipase
It is an essential enzyme of the digestive system involved in the digestion of triglycerides. It does so by digesting the ester linkage in the triglycerides. It is a clinically significant protein since its level serves as a diagnosis for tissue/organ functionality.
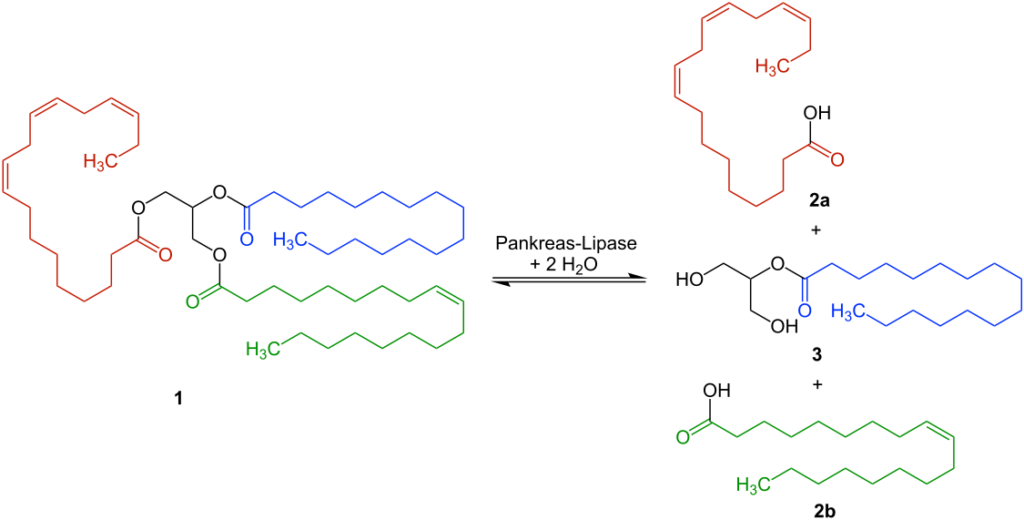
4. Hepatic Lipase
It is also called hepatic triglyceride lipase (HTGL). As the name suggests, it is involved in the hydrolysis of triglycerides. These enzymes are expressed in the hepatocytes of the liver. One of its primary roles includes the conversion of intermediate-density lipoprotein to low-density lipoprotein.
5. Lysosomal Lipase
Its role is mainly in lipid catabolism. However, it acts intracellularly. It is also involved in the hydrolysis of cholesterol. However, they are involved in the metabolic reprogramming of memory T-cells.
6. Phospholipases
They are the lipolytic enzymes that hydrolyze the phosphate group of the lipid at the ester linkage. Along with its role in lipid metabolism, it has roles in metabolite digestion and signals transductions within cells. Based on their function, they are classified into four types – namely Phospholipase A1, Phospholipase A2, Phospholipase Cand Phospholipase D.

7. Amylases
It is involved in the hydrolysis of starch into sugar. In humans, it is mainly found in saliva. Thus, we get a sweet taste from starch-rich foods like rice and potato. Pancreas also secrete amylase, which further breaks down the starch in the GI tract
8. Bromelain
It is a group of an enzyme belonging to plants. It is found abundantly in fruits, specifically the stem of the pineapple plant. It is widely used as a dietary supplement for problems related to the digestive system and inflammation and pain.
9. Papain
It is a protease enzyme found in papaya, from where it also got its name. This enzyme is of clinical importance due to its medicinal properties. It is also widely used dermatologically.
10. Trypsin
It is the enzyme secreted by the pancreas but acts in the small intestine. It is metabolically vital because it starts the protein digestion in the GI tract. The process of digestion by trypsin is referred to as trypsinization. Deficiency in this enzyme can lead to meconium ileus, which means obstruction of the intestine. Also, the hyperactivity of this enzyme leads to pancreatitis, where the enzyme leads to the self-digestion of the pancreas.
11. Chymotrypsin
It is an enzyme secreted by the pancreas but acts in the duodenum to digest the proteins. It is secreted as an inactive enzyme by the pancreas and activated by enterokinase secreted by the small intestine.
12. Alkaline phosphatase
Commonly referred to as ALP, is a crucial liver enzyme active at basic pH. Its physiological role includes dephosphorylation of the substrate. It is also involved in skeleton development. Levels of ALP serve as a check for liver activity. Abnormal levels of ALP in circulation lead to liver stones, gall bladder stones or kidney stones.
13. Alanine transaminase
Famously known as ALP or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), the most common test for liver failure and function. In liver failure conditions, the levels of ALP increase in blood circulation. Therefore it is considered a clinical biomarker for liver health. It carries a transamination reaction in liver cells, essential for the urea cycle.
14. Aspartate transaminase
Like ALP, it is a liver enzyme involved in the urea cycle. However, it is also found in muscles. Blood tests generally include Aspartate transaminase levels (AST) as liver and kidney health indicators.
15. Lactase
In humans, this enzyme is produced by the brush border cells of the small intestine and is involved in the complete digestion of milk. This enzyme is a deficit in infants and also in older people. Some people suffer from its deficiency. This cannot digest milk products. This condition is called lactose intolerance.
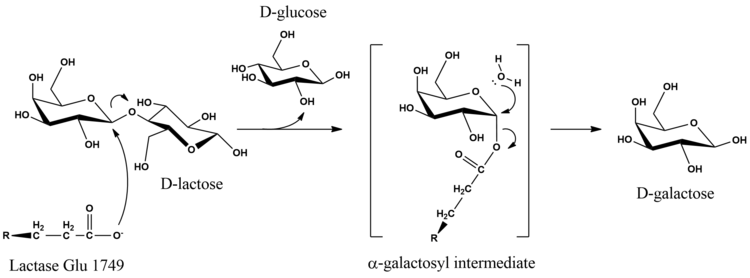
16. Maltase
It is a type of glucosidase. It breaks down maltose to glucose. In humans, it is secreted by the brush-bordered cells of the small intestine.
17. Enterokinase
Also called enteropeptidase. The small intestine secretes it, but it acts on the pancreatic enzymes by converting the various inactive peptidases to their active form.
Conclusion
Metabolic enzymes are proteins which act on a different forms of substrates and aid in physiological pathways necessarily at organ levels. Due to their importance in maintaining the homeostasis at organ level, any deficiency in metabolic enzymes leads to defects in organ function and sometimes failure. Our article summarizes some of the important metabolic enzymes along with facts regarding their function and clinical imporance.
Also Read: