Protein in liberal terms are a good for the diet of people. They are made of the building blocks called the amino acids.
Any enzyme is a protein that helps in getting the metabolism speed up or also helps the chemical reactions on the bodies to heat up. There are many enzymes that are protein with very few non protein enzyme example being-
Protein is an essential macronutrient, but not all food sources of protein are created equal, and you may not need as much as you think. In order to get into the basics about protein and shaping our diet with healthy protein foods. Protein is found throughout the body—in muscle, bone, skin, hair, and virtually every other body part or tissue. There are many enzymes that are protein with very few non protein enzyme example.
What is non protein enzyme?
The role of any enzyme is to reach out to the stomach and the hydrochloric acid and then break down the amino acids into smaller particles.
Only few of the proteins do have the capability to bind with the substrate with the help of the activation sites in a manner that shall allow the reaction to occur in a good manner. Thus there are few non protein enzyme example.
The binding of the enzymes shall be needed for the activation of the reaction sites such that it shall allow the reaction to take place in a good manner which makes few enzymes be protein but not proteins are not the enzymes. There are quite a few of the enzymes that are not proteins with they being no biological catalyst seen in body.
There are a few of the RNA molecules that shall help in being a catalyst for a particular fact and shall act as both gene material and also as a biocatalyst. It is also a part of the ribosome that links with the amino acid at the time by protein synthesis. The coenzymes are small protein molecules that are linked with few enzymes making non protein enzyme example few in number.

One of the first law is that the catalyst help speeds up the reactions in the organism a much time faster and are considered to be the proteins. Most of these are 3 dimensional with the globular proteins being tertiary or quaternary and having few non protein enzyme example that are the special species kike hammerhead ones.
The enzymes shall be used to make the everyday life of the people easy. They can be used in the food and also in the beverages that shall be able to processed, animal nutrition and also textiles along with the cleaning of house and car fuel. They shall be able to act as a catalytic and make a holoenzyme or called apoenzyme. There are many enzymes that are protein with very few non protein enzyme example.
Non protein enzyme structure
The site for activation of the protein is the rea that connects the substrates the groups and the co factors heling it to link with substrate.
The site for activation shall mostly take up less than 5% of the tertiary structure of the protein and there is also a change witnessed at the site of activation and also in the enzyme work manner. A protein is a naturally occurring, extremely complex substance that has amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds.
The site for activating for the non protein enzyme example can be classed into two- the catalytic site and the binding site. The cofactor is said to be the molecule that are non-protein and carries the chemical reaction that cannot be done by the amino acids. They can be either inorganic or organic.
There are many coenzymes that are linked with vitamins. The enzymes can be if primary, secondary, tertiary. The secondary refers to the link of the amino acids in a chain manner which is the primary state and is located close. There are then two types of he secondary being the alpha helicase and the pleated sheets.
The structure ranges from the general amino acids the sequence of the 3D state in a protein that is folded. These sequence of acid make non protein enzyme example and make it distinct determining the shape. Further on the enzyme that shall determine the activity of the enzyme. The structure for the non protein enzyme example are mentioned.
Primary structure
The constituents of the amino acids are connected with the bonds of peptide. This bond is seen between the amino chains and one of them and the carboxyl group of the other along with getting the water molecule released has it. This structure tends to depict the 3D structure of the proteins and in many ways the amino acids shall be arranged in the chain that shall influence the proper protein folding for the enzyme to be active representing non protein enzyme example.

Protein is made from twenty-plus basic building blocks called amino acids. Because we don’t store amino acids, our bodies make them in two different ways: either from scratch, or by modifying others. Nine amino acids—histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine—known as the essential amino acids, must come from food.
Secondary structure
The enzyme having this structure refers to the linking of the amino acids in the chain of the primary structure and also are closely packed. There are two types of these called the helical one also the alpha helix and the other the pleated sheets namely the beta pleated sheets. Another example of a secondary structure is that of a nucleic acid such as the clover leaf structure of tRNA. Secondary structures are those that develop in rocks after their formation as a result of their subjection to external forces.
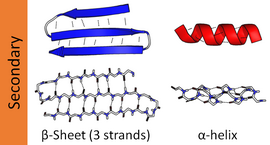
The next level of protein structure, secondary structure, refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone. The most common types of secondary structures are the α helix and the β pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds which form between the carbonyl O of one amino acid and the amino H of another.
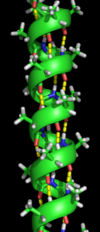
Alpha helix
- This is the helical structure that is kept coiled around in the acid and is also right handed in its nature.
- The alpha helix is also characterized along with the intramolecular bond of hydrogen and in between the oxygen and carbon oxygen bond of which each bond in the strands and the ammine group of the bond show non protein enzyme example.
- The side chain of the substitutes of the amino acids shall be extended to the exterior across the helix.
- The helix has them about 3.6 of the amino acids per turn on its average and also means that it shall be able to have 36 of the amino acids in the turns being 10. The pitch is about 5.4 Armstrong.
- These are more readily made in enzymes that in any non protein enzyme example and make all sort if possible conformations that owes to the optional use of the hydrogen in the bonds and is made in these arrangements for getting stability.

Beta pleated sheet
- The seconds form of the structure that is secondary in the enzymes is the beta pleated sheet. This makes the generation of intermolecular hydrogen bond between the two or more of the straight chains.
- The oxygen atom of the carbon and oxygen of the peptide link has one strand along with the hydrogen bonds with the amine group of the peptide bond in the strands that are adjacent.
- Again there are two of the strands that shall be involved in the making of the beta pleats which can ruin the strands that run parallel to each other it even runs anti-parallel to them.
- If the amine groups of both the chains are kept opposite to each other and on the same side, the sheets are said to be kept running parallel to each other.
- On the rest part of the chains are kept opposite in the non protein enzyme example then the chain seems to run in the opposite direction. Here, the sheet is said to be antiparallel.
- This stands that is anti-parallel shall be able to run and is much more stable than the sheet that are parallel sheet owned that allows greater alignment in the bonds of hydrogen.

Tertiary structure
- The arrangement of the amino acids in the 3D space shall be defined in the space of tertiary structure of the enzymes.
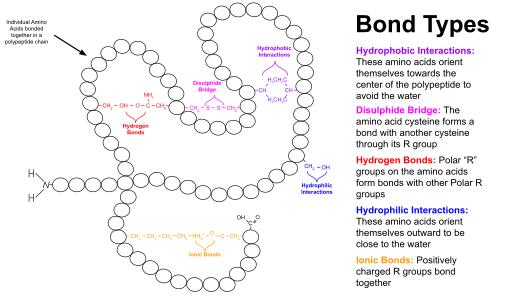
- The molecule of protein shall be arranged itself in 3D manner in making up of the tertiary structure in the bonds of hydrogen also have polar polar interaction, along with having hydrophobic interaction being ionic interaction making disulfide bonds, with Vander der Waals forces.
- Under many conditions that are physiological in its conditions having the side chains of amino acids that are hydrophobic in its nature such as the isoleucine and tend to remain buried in the non protein enzyme example core, owing to the less affinity or having aqueous medium.
- The group that has Ala, Val, Leu, Ileu and are often seen to be hydrophobic link between the other for non protein enzyme example. Acid or base acid of the side chain are polar in its nature and thus shall remain exposed to the surface of enzyme allowing solubility.
Ribozyme
The term ribozyme refers to the activity of the non protein enzyme example and the nature at the same time.
The ribozymes are said to be catalytic and active as a RNA molecules or other protein in RNA complexes in which the RNA shall be solely provided in the catalytic activity.
The examples are small about the ribozymes that shall contain the hammerhead, the hepatitis delta and the varkud RNA satellite. The large ribozymes shall be of much help up to 3000 nucleotides and can make reaction products with being free from the 3-hydroxyl and the 5 phosphate group. They are found in the ribosome.

Deoxyribonucleic
It is also called the DNA enzymes and are catalytic in form are also capable of performing any specific reaction. They are also single stranded molecules that are catalyzed in several reactions. The nature of it is helps in carrying of the genetic material for having the organism grow and function. It is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism.

Collagen
It is the protein that is found in the connective tissue, skin, the cartilage and bone. It helps them give the support to the tissue. It is most of the abundant protein found in the body. It is a fiber that line the structure to make the connective tissue. It means that it connects the tissue the other tissue and is much major component of the skin, tendons and also has skin and cartilages.

Lysine
They are vital amino acids that means that it is vital for human but the body cannot tolerate it. It is much safe for the people yet are not able to make lysine with itself. The sources of it shall be the dairy, eggs, meat and the fish. It is an alpha amino acid and shall be having the alpha lysine. It is used to lessen pain. Lysine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.

Biotin
It is a vitamin that is seen in the foods like the milk, eggs and also in the bananas. The lack of biotin can cause hair to think and also develop rash. It is vital for enzymes in body and shall be able to break down the food substances. Biotin is an important part of enzymes in the body that break down substances like fats, carbohydrates, and others.
Also Read:
- Analogous structures examples
- Do bacterial cells have cytoplasm
- Transplanting plants examples
- Dna replication vs polymerase
- Foot anatomy
- Do prokaryotes have golgi 2
- Do prokaryotes have exons
- Insectivorous plant example
- Do plant cells have lysosomes
- Does lysosome have membrane
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.