In nature there are several types of bacteria are present. Bacteria are generally classified basing on their structure and shape. Usually bacterial cell is prokaryotic cell.
Bacteria have several classifications according to their shape, structure and number. There are many subclasses in bacteria. Bacterial cell basically contains cytoplasm, genetic material, nucleoid and cell wall. In this topic we shall discuss more on bacterial cell type.
Dormant bacterial cell type
The dormant bacterial cell is commonly known as an endosperm. The endospore is usually referred as a spore.
An endospore is likely to be tough and non-reproductive cells. Endosperms are formed from bacteria. In this stage the bacterial is in non-reproductive stage for days or even for several months too.
The temperature can also determine the reproduction stage of bacteria. For example at -18 degrees centigrade the bacteria cannot undergo reproduction and will be in dormant stage. At 0-5 degrees the bacteria will be sleeping stage and the reproduction will be very slow. But at 5-63 degrees the bacteria can reproduce at faster rate.
What is the most common type of bacterial cell?
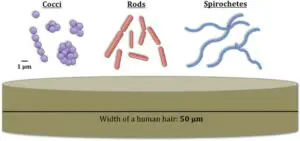
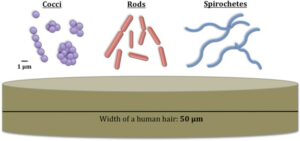
The most common type of bacteria are cocci, spirilla, bacilli, and comma forms.In this section we shall discuss bacterial cell type.
Bacteria are typically classified in to five types basing on their shape. They are cocci, bacilli, spirilla, vibrios and spirocheates.
The rod shaped is commonly known as bacilli. The spherical shaped bacteria is known as cocci. The common examples of cocci are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The spiral shaped bacteria is known as spirilla. Campylobacter jejuni is the example for spiral bacteria. The comma shaped bacteria is known as vibrios. Vibrio cholera is example for vibrio bacteria it causes cholera in humans. It leads to diarrhea.
The cocci bacteria are sub classified depending on the arrangement of cells. They are diplococcus, strepto cocci, staphylo cocci, tetrads and sarcina.Diplococcus bacteria means a pair cocci are present. For example streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae).
Streptococci means that the cocci are present in string like structure. Example for this type is streptococcus pyogenes.Staphylo coccus bacteria means that the cocci are present in colonies in irregular manner.Example for staphylo coccus bacteria is Staphylococcus aureus.
If we found four cocci together then it is said to be tetrad. Example for tetrad is Micrococcus species.If eight cocci are found together it is said to be sarcina bacteria.An example for this type is Sarcina ventriculi.
The spiral bacteria can be sub classified into two types basing on the cell flexibility, cell mobility, number twists present in a cell. There are two types of spiral bacteria. One is spirillum and the an other one is spirochetes. The spirillum and spirochete is differentiated basing on the presence of flagella. Usually the spirilla are short and rigid cells whereas spirochetes are relatively long and flexible cells. The spirilla have external rigid flagella whereas spirochetes have internal flexible flagella.
Camphylobacter species are the best examples of spirilla. They are pathogenic and may cause food borne camphylobacteriosis.
Borrelia species are the best examples of spirochetes. These are also pathogenic in nature. For example Borrelia recurrentis may cause relapsing fever in humans. These are the common bacterial cell type.
What bacterial cell type is a flexible spring-like structure?
The spirochetes are the flexible spring like structure bacteria having internal flagella.
Among all the species of bacteria the spirochetes are the more flexible bacteria. They contain internal periplasmic flagella which help the bacteria in locomotion. Flagella are the locomotors in bacterial cells. They stick the bacterial cells in liquids or to the surface so that a cell can move freely in the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are cocci bacteria gram positive or gram negative?
The cocci bacterial cells are gram positive in nature. Because they contain peptidoglycan in their cell membrane.
Cocci bacteria like streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci are gram positive bacteria.
How can we indicate whether the bacteria is gram positive or gram negative?
By using gram staining we can differentiate the bacteria.
In gram staining the gram positive bacteria turns purple and gram negative bacteria turns red or pink.
Why the gram positive bacteria turns purple in gram staining?
The gram positive bacteria turns purple in gram staining because of the presence of peptidoglycan in the cell membrane.
The gram negative bacteria do not contain peptidoglycan layer.
What are common infectious bacteria in humans?
- Coliform bacteria, bacterial vaginosis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia, syphilis, E. coli, Salmonella are the common infectious bacteria.
- For example Coliform bacteria can cause urinary track infections. E.coli and salmonella are common food poising bacteria.
Also Read: