This type of diffusion is the movement of molecules and that is passive in nature and is always along the concentration gradient.
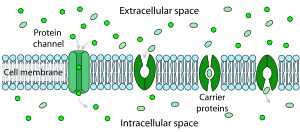
For the facilitated diffusion in cell, the molecules tend to often diffuse across the plasma membrane with the help of the proteins in the membrane which are termed to be either the carrier or the channels proteins. Both of them have the concentration gradient and is for facilitated diffusion in cell.
Any example for facilitated diffusion in cell can be the glucose transport as the molecule of glucose are said to be large an also polar that cannot pass via the lipid bilayer. Thus it tends to need a carrier called the glucose transporters for facilitated diffusion in cell.
The molecules that are associated with facilitated diffusion in cell offer the process of selective passage which means that the membrane does not intend to allow the flow of all the molecule but only specific ones can pass via this and prevents the allowance of the other molecule proving the fact correct.
What is facilitated diffusion in cell?
The method of facilitated diffusion in cell acts to use the molecules that are not able to move on its own. The layer for facilitated diffusion in cell are phospholipid bilayer.
The method for simple transport is the method that has materials that pass via the membrane without the help of the proteins with the facilitated diffusion in cell the materials tend to diffuse across all the plasma membrane with the help of all the protein membrane.
This facilitated diffusion in cell attains the use of energy with not having the substances to move across the membrane as a whole. The method of simple diffusion does not need molecule nor ions and is vital to regulate that goes in or out. Active transport is not the same to that of facilitated diffusion in cell.
The facilitated diffusion in cell allows the molecules that are charged and polar like amino acids, ions, nucleosides and carbohydrates and then crosses the plasma membrane. For facilitated diffusion in cell the amino acid can be a good example for facilitated diffusion in cell.
Where does facilitated diffusion occur?
The facilitated diffusion in cell is the process of having the solutes diffused via the transport proteins in the cell itself.
The location for facilitated diffusion in cell is the plasma membrane. The proteins that are channel ones along with also being the gate channel proteins and also the carrier proteins are the three level of transports proteins that have its uses in this.
The plasma membrane is the place where facilitated diffusion in cell takes place. This is also called to be the cell membrane and this membrane is found in all of the cells that tends to separate the inside material of cell with the outer world. In the plant or the bacterial cells, a cell wall is kept linked with the plasma on its outer area.
How does facilitated diffusion work?
In facilitated diffusion in cell the molecules tend to move along a gradient concerned with concentration for any type of material.
Here in facilitated diffusion in cell the molecule gets moved from the area that has high concentration of solute or bacteria to the area having a lower one and is accompanied by the carrier. The facilitated diffusion in cell is called to be selective.
On the process of facilitated diffusion in cell being selective means that there is entry for only specific molecules and ions that can get via it. The rest of the molecules are prevented from getting through it with the facilitated diffusion in cell being carried forward across the membrane for all the living beings and cells.

What does facilitate diffusion transport?
The facilitated diffusion in cell is not done alone but with help of carrier and also many proteins in the membrane going via the plasma.
At the time of facilitated diffusion in cell there is a concentration gradient that helps in the transfer of materials like that of
- Ions
- Water
- Materials in and out of the cell body.
- Facilitated diffusion in cell also carries solutes
Despite the fact that facilitated diffusion in cell connects with the transport proteins yet this is still a passive method for transportation as the solute keeps on moving downward via the concentration gradient. Small molecules are mostly linked with facilitated diffusion in cell.
When does facilitated diffusion occur in cell?
As said earlier for the process of facilitated diffusion in cell there is always a concentration gradient seen and used for having material transferred.
At the time of facilitated diffusion in cell the rate of hemoglobin tends to fasten up with having the rate of diffusion also getting constantly more for oxygen and also the facilitated diffusion in cell takes place when the molecules of oxyhemoglobin are said to be dispersed on a random manner.
The whole process of facilitated diffusion in cell takes place in the cell membrane along with getting to elate energy for having the molecules moved away. Here in facilitated diffusion in cell the material moves down the gradient from high to low as also in passive diffusion for facilitated diffusion in cell.
Function of facilitated diffusion in cell
As facilitated diffusion in cell takes place in the cell membrane, not every of the molecule that wants to cross the barrier can get in.
The molecules that tend to pass via the facilitated diffusion in cell needs to be small and non-polar in nature to be traverse in its medium. It helps in creating of a gradient for facilitated diffusion in cell the plasma membrane.
For an instance the molecule for glucose can be take in consideration for facilitated diffusion in cell, the function is-
- It allows the exchange of not so large molecules and thus is not able to cross the membrane of cell for this method.
- Transfer of molecules from one place to other
- The ions like the calcium, potassium and also sodium are said to be charged and are thus also repelled by the membrane with rest being polar.
Type of facilitated diffusion in cell
Molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers.
Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. Channel proteins, gated channel proteins, and carrier proteins are three types of transport proteins that are involved in facilitated diffusion in cell with it mostly being of two types that are–
- Carrier proteins
- Ion channels also being a type of its example

Example of facilitated diffusion in cell
The proteins that are involved for the facilitated diffusion in cell are called to be the transmembrane ones being 2 in number.
The transmembrane proteins are carrier protein and also the channel proteins used for facilitated diffusion in cell and helps certain molecules to pass and restrict from entering the area of facilitated diffusion in cell and thus can accelerate the process to get transported as well with some already being there.
The examples of facilitated diffusion in cell are-
- Glucose transporter
- Aquaporins
- Ion channel
Glucose transporter
This tend to fascinate the glucose transport across the membrane. It is seen on the plasma membrane already likin the molecules.
This links with the molecules of glucose that is much large in size and then helps the transports across the lipid bilayer and not the plasma membrane facilitated diffusion in cell. This in the facilitated diffusion in cell are of 2 types.
The two types of glucose transported are the sodium glucose cotransporters that are seen in the small intestine and also tends to bind with the molecules of glucose and are seen in the small intestine and also in the renal tubules with being responsible for having the molecule transported in facilitated diffusion in cell.
Aquaporins
These are also said to be a kind of protein that helps facilitated diffusion in cell along with having the facilitation of water molecules.
If there is a mutation seen for the proteins making aquaporins then it shall result in the problem like that of diabetes insipidus. They are also called as water channels and are large in number for facilitated diffusion in cell making pores in the cell membrane.
The basic function of this in facilitated diffusion in cell is to have the water molecules transported across the membrane of cell in getting the response fir the osmotic gradient that is made by the solute actively being transported. Passive transporters are the water ways moving down the gradient in facilitated diffusion in cell.
Ion channels
These are also called the transmembrane proteins and allow the selective transports of the solutes and the ions across facilitated diffusion in cell.
It also has pumps in it that helps in keeping up with the concentration if the fluid and is different from that of the cytosol. There is also much of the social ion present in the outer area with having many of the potassium ions along with open channel.
There is a small change in violate for this in the facilitated diffusion in cell and then the channel for the sodium ions tend to change along with the opening the barrier or the cell. The ions of potassium are also kept open and them the ions are made to move out of the cell. This is done when there is many sodium ions present.
Is facilitated diffusion irreversible and how?
The process of facilitated diffusion in cell occurs in many species at the time when there needs to be a diffusion of liquids.
This facilitated diffusion in cell is thus subjected to being reversible in nature which is called to be complexation. The molecules diffuse in the plasma membrane with help of carriers and channels along the concentration gradient for moving in and out.
The rate for facilitated diffusion in cell tends to be saturated with the concentration difference in all of the two phases that is much not preferred to diffuse in the linear manner along the concentration difference. The way is from one side of the cell membrane to other which can also be said as high to low.
Is facilitated diffusion highly selective?
The method for facilitated diffusion in cell is said to be a passive molecular movement along the gradient and is also a selective process.
While the facilitated diffusion in cell is a selective method it means that the membrane linked to it allows only few of the membrane to get into it and also thus helps the non useful particles stay out without causing any problem in facilitated diffusion in cell.
The process of having the molecules transferred from one place to other shall be able to take in successfully only when there is the use of active or passive transport. The facilitated diffusion in cell can be only carried out via transmembrane proteins and only with ions or solutes that are small like that of sodium, potassium or calcium.

Why is facilitated diffusion highly selective?
It is always said that the facilitated diffusion in cell is concentrated to be linked up with passive type of transport and thus being selective.
There is always a different in the level of concentration and it is called the concentration gradient and thus facilitated diffusion in cell takes place. The facilitated diffusion in cell can only take place if there is a concentration difference.
The facilitated diffusion in cell tens to stop itself after there is equal amount of concentration in both of the molecules or sides. Thus it is vital to have selectively for the size, charge and polarity of the ions tends to be much of a factor for all of the ions or solutes entering the membrane for facilitated diffusion in cell.
Does facilitated diffusion have a transport maximum?
It is much different to that of the simple diffusion method and thus facilitated diffusion in cell needs a membrane.
The transport maximum in facilitated diffusion in cell refers to the point where on having the concentration increases if the substance there is not change or result in a growth of the movement for the ions across the cell wall or plasma area.
Mostly this is termed with glucose for facilitated diffusion in cell. In facilitated diffusion in cell the carrier protein tends to increase the diffusion arte by having the solute to allow and then enter the cell area. The maximum rate for facilitated diffusion in cell tends to be about the point to which the carrier protein can get itself saturated with the solute.
Does facilitated diffusion transport large molecules?
The method of facilitated diffusion in cell tends to be much selective in its nature for the process needs to be smooth.
The facilitated diffusion in cell has taken up the charge of the molecule that is much small in its size and also tend to take in the molecules that have charge that is non-polar in its structure and shall be not able to induce molecules on it.
The facilitated diffusion in cell tends to have only molecules that are not polar in nature and also do have small ions in them like that of the potassium sodium an also calcium. The charge of the ions tends to influence the flow of facilitated diffusion in cell and thus helps in navigating of the molecules and targeting it in the cell area sharing common traits.
Does facilitated diffusion move water?
Water molecules and ions move through channel proteins. Other ions or molecules are also carried across the cell membrane by carrier proteins.
Water can also cross a membrane incidentally, when ions flow through their channel proteins. But most osmosis involves facilitated diffusion in cell mediated by aquaporins. Some aquaporins only transport water.
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration with the help of a transport molecule. Since substances move along the direction of their concentration gradient, chemical energy is not directly required.
How does facilitated diffusion move water?
A channel protein, a type of transport protein, acts like a pore in the membrane that lets water molecules or small ions through quickly.
In many ways, airport security is a lot like the plasma membrane of a cell. Cell membranes are selectively permeable, regulating which substances can pass through, as well as how much of each substance can enter or exit for facilitated diffusion in cell.
The simplest forms of transport across a membrane are passive. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. In cells, some molecules can move down their concentration.

Does facilitated diffusion move ions?
The mechanism for the facilitated diffusion in cell has the membrane that allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it.
In facilitated diffusion in cell, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. A concentration gradient exists for these molecules, so they have the potential to diffuse into or out of the cell by moving down it.
The cell membrane is selectively permeable, allowing only certain substances to pass through. Passive transport is a way that small molecules or ions move across the cell membrane without input of energy by the cell. The three main kinds of passive transport are diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
Does facilitated diffusion move nonpolar molecules?
Facilitated diffusion tends to be medoum for passive transport alomg with involving the use of all trasnverse proteins.
The materials that are transported via this is the ions, water and many more particles that are not large and also polar in nature. Thus with concern to this, the method does not move any of non polar molecules.
Does facilitated diffusion require a carrier protein?
Carrier proteins are responsible for the facilitated diffusion of sugars, amino acids, and nucleosides across the plasma membranes of most cells.
The method of facilitated diffusion in cell requires a membrane carrier proteins. That is, the carrier facilitates diffusion of the substance to the other side. Facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion in several ways.
The transport relies on molecular binding between the cargo and the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein. Facilitated diffusion in cell is a type of passive transport. Even though facilitated diffusion involves transport proteins, it is still passive transport because the solute is moving down the concentration gradient.
Is facilitated diffusion saturable?
The rate of facilitated diffusion is saturable with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases; unlike free diffusion which is linear in the concentration difference.
The glucose transporters are of two types being sodium-glucose cotransporters which are present in the small intestine and renal tubules and are responsible for the glucose transport against the concentration gradient, and the facilitative glucose transporters which are responsible for the bidirectional movement of glucose.
In other words, facilitated diffusion in cell exhibits saturation kinetics and is therefore similar to the relationship between reaction rate and substrate concentration in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Simple and facilitated diffusion are both non-directional with respect to the membrane; solute can move in either direction.

Why and When is facilitated diffusion saturable?
The transport relies on molecular binding between the cargo and the membrane-embedded channel or carrier protein for the facilitated diffusion in cell.
The rate of facilitated diffusion is saturable with respect to the concentration difference between the two phases; unlike free diffusion which is linear in the concentration difference.
This process is saturable, which means, as the concentration gradient of the substance increases, it will go on increasing until it reaches a point where all the carrier molecules are occupied. One important characteristic that is associated with facilitated diffusion in cell is saturation.
Does facilitated diffusion use vesicles?
This type of transport involves some rearrangement of the cell membrane. Endocytosis is a general term.
Proteins and polysaccharides are examples of very large molecules that need to pass into and out of cells by way of vesicle transport.
In facilitated diffusion in cell, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. A concentration gradient exists for these molecules, so they have the potential to diffuse into the cell by moving down it.
Conclusion
The facilitated diffusion in cell, the molecules here tend to get themselves diffused across the plasma membrane with the help of the proteins in the membrane and they are the ones which are termed to be either the of the transport proteins.
Also Read:
- Animal chromosomes structure
- Purple sulphur bacteria examples
- Scorpion examples
- Are proteins polymers
- Do eukaryotic cells have a cell wall
- Does mitochondria have circular dna
- Independent assortment example
- Simple fruit example
- What is hydrophilic head
- Hard fruit example
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.
