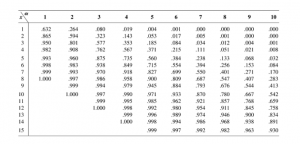
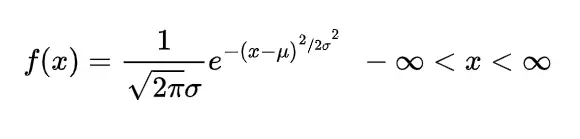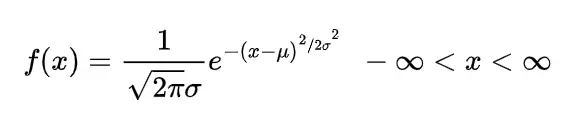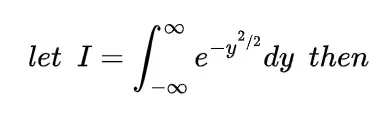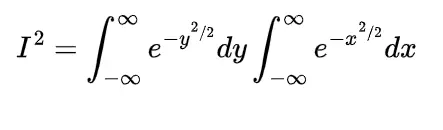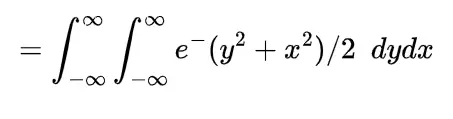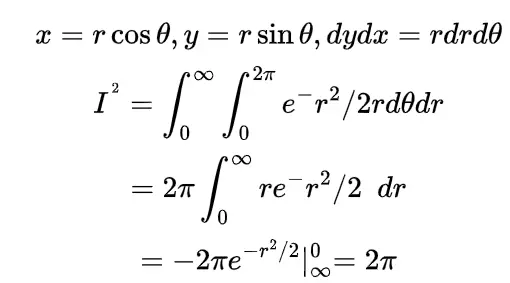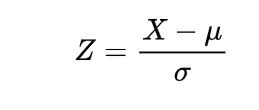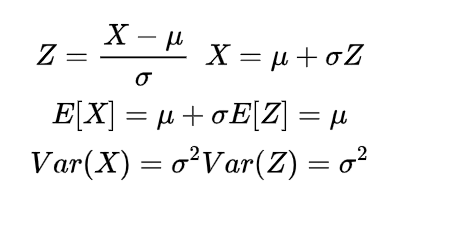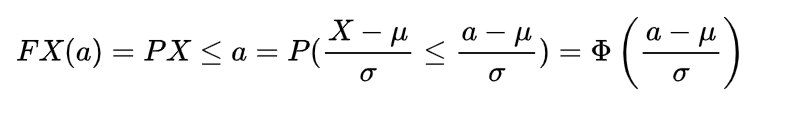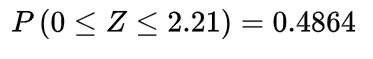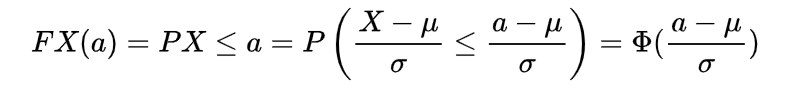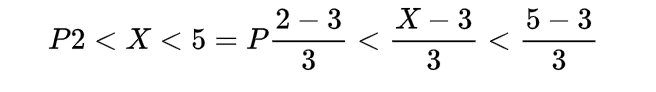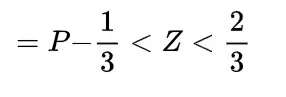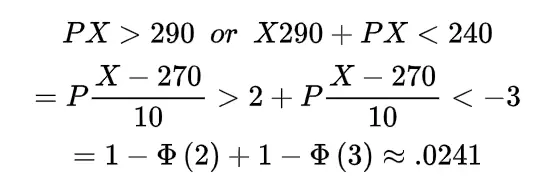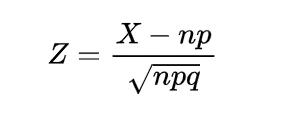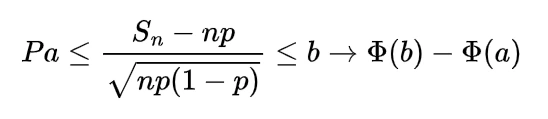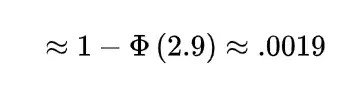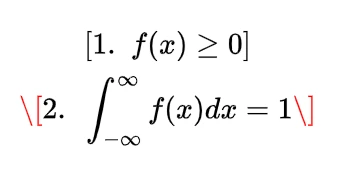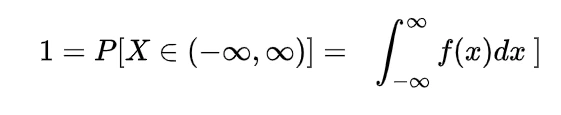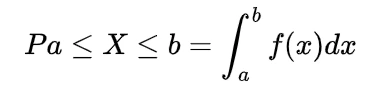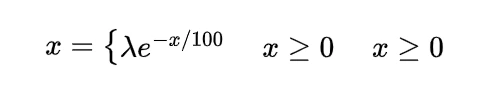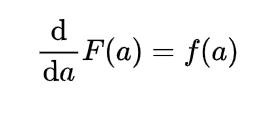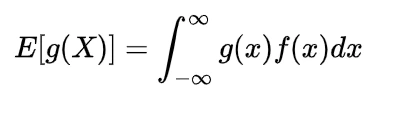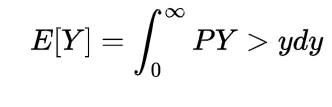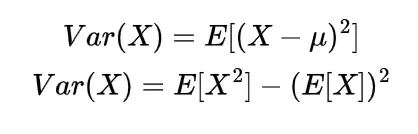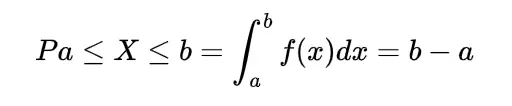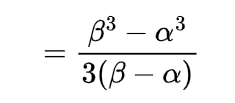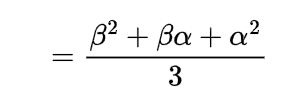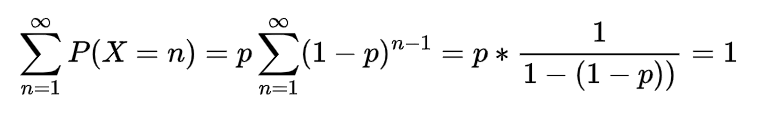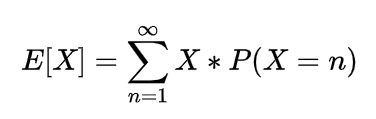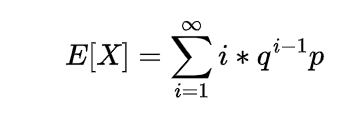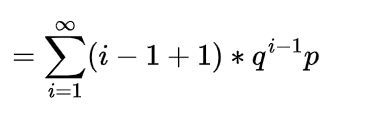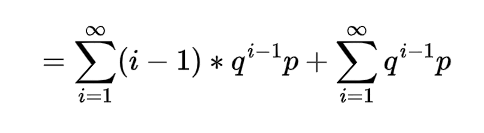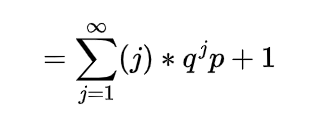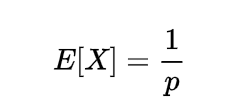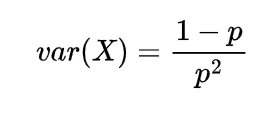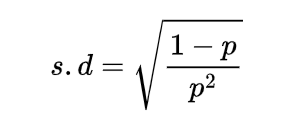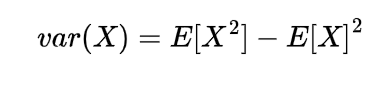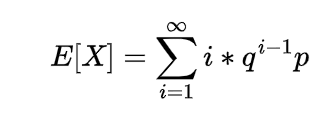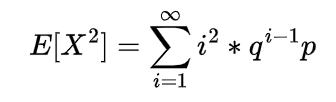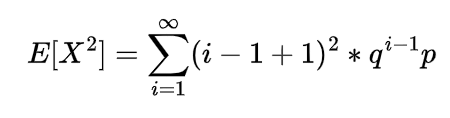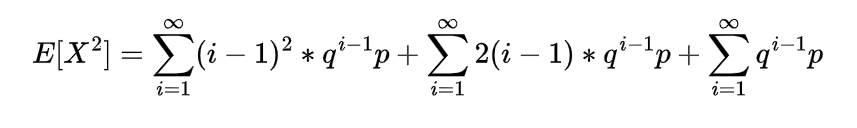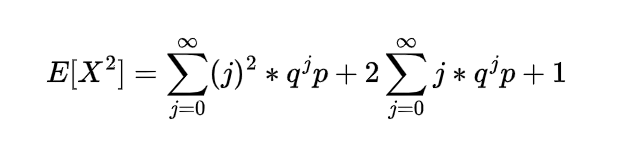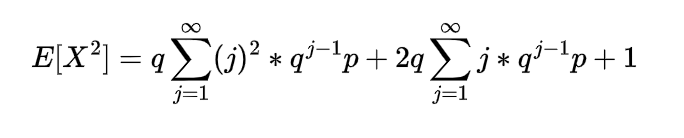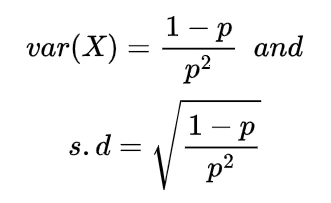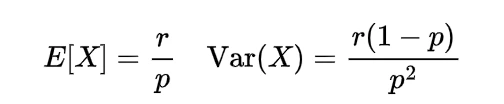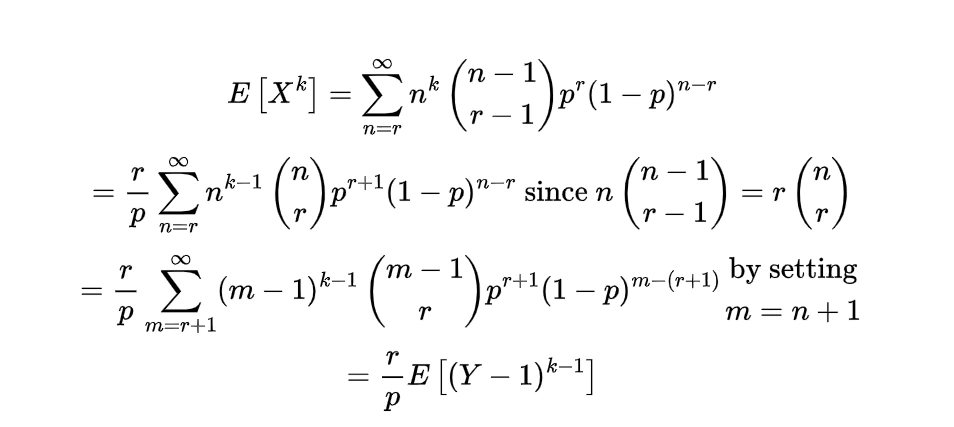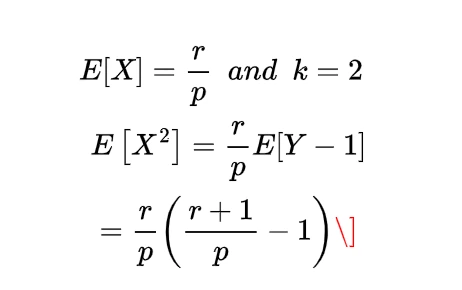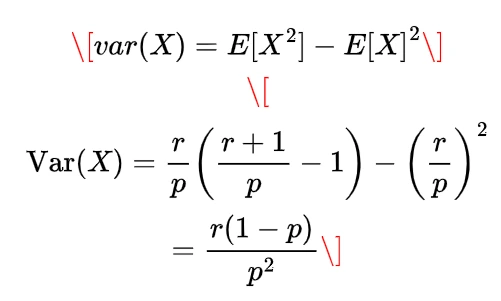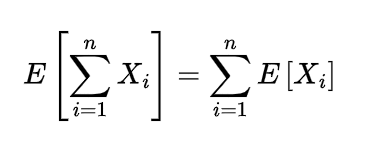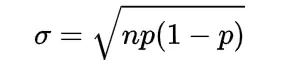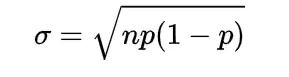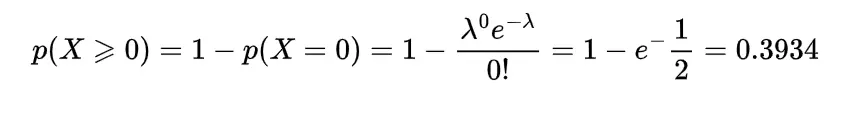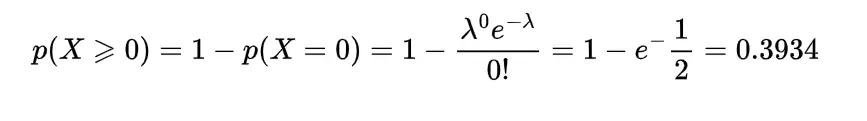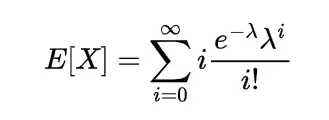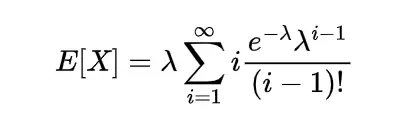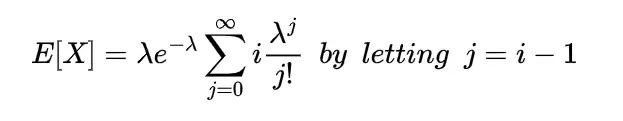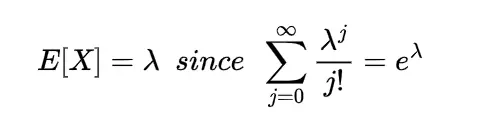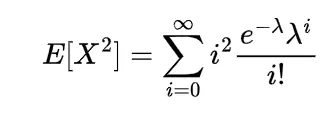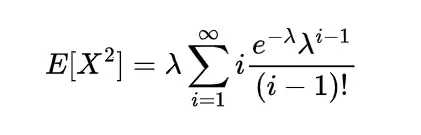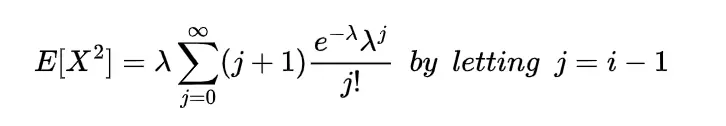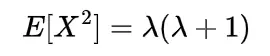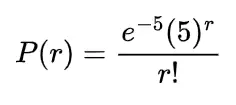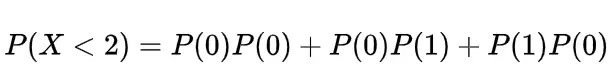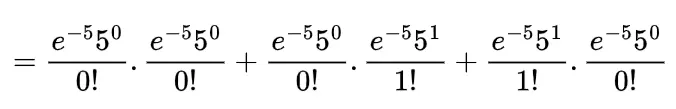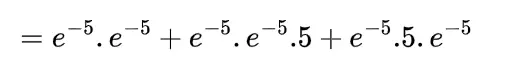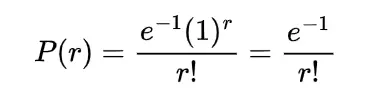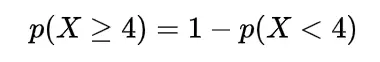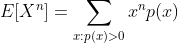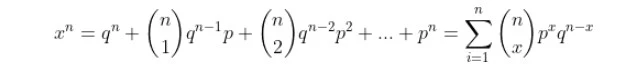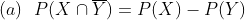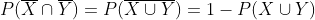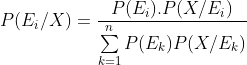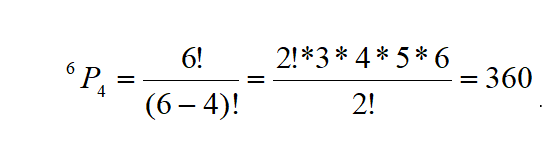Inverse gamma distribution and moment generating function of gamma distribution
In continuation with gamma distribution we will see the concept of inverse gamma distribution and moment generating function, measure of central tendencies mean, mode and median of gamma distribution by following some of the basic properties of gamma distribution.
gamma distribution properties
Some of the important properties of gamma distribution are enlisted as follows
The probability density function for the gamma distribution is
or
where the gamma function is
2.The cumulative distribution function for the gamma distribution is
where f(x) is the probability density function as given above in particular cdf is
and
respectively or
E[X]=α*β
and
- The moment generating function M(t) for the gamma distribution is
or
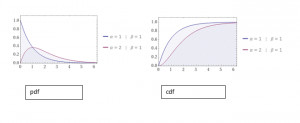
- The curve for the pdf and cdf is

- The invers gamma distribution can be defined by taking reciprocal of the probability density function of gamma distribution as
- The sum of independent gamma distribution is again the gamma distribution with sum of the parameters.
inverse gamma distribution | normal inverse gamma distribution
If in the gamma distribution in the probability density function
or
we take the variable reciprocal or inverse then the probability density function will be
Thus the random variable with this probability density function is known to be the inverse gamma random variable or inverse gamma distribution or inverted gamma distribution.
The above probability density function in any parameter we can take either in the form of lambda or theta the probability density function which is the reciprocal of gamma distribution is the probability density function of inverse gamma distribution.
Cumulative distribution function or cdf of inverse gamma distribution
The cumulative distribution function for the inverse gamma distribution is the distribution function
in which the f(x) is the probability density function of the inverse gamma distribution as
Mean and variance of the inverse gamma distribution
The mean and variance of the inverse gamma distribution by following the usual definition of expectation and variance will be
and
Mean and variance of the inverse gamma distribution proof
To get the mean and variance of the inverse gamma distribution using the probability density function
and the definition of expectations, we first find the expectation for any power of x as
in the above integral we used the density function as
now for the value of α greater than one and n as one
similarly the value for n=2 is for alpha greater than 2
using these expectations will give us the value of variance as
Invers gamma distribution plot | Inverse gamma distribution graph
The inverse gamma distribution is the reciprocal of the gamma distribution so while observing the gamma distribution it is good to observe the nature of the curves of inverse gamma distribution having probability density function as
and the cumulative distribution function by following
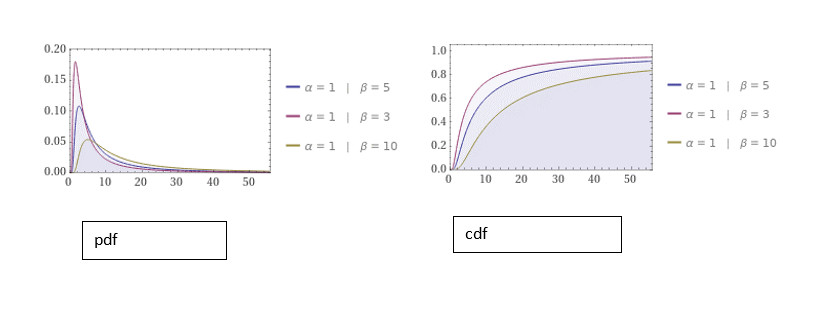
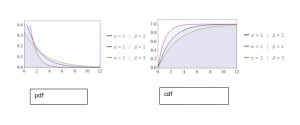
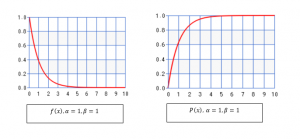
Description: graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function by fixing the value of α as 1 and varying the value of β.
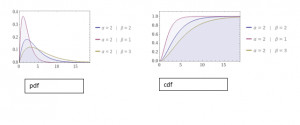
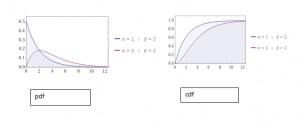
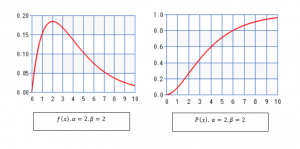
Description: graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function by fixing the value of α as 2 and varying the value of β
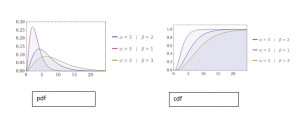
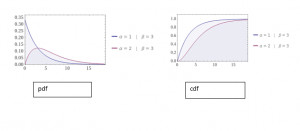
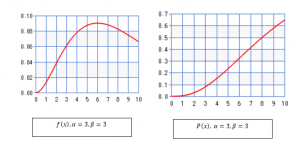
Description: graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function by fixing the value of α as 3 and varying the value of β.
Description: graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function by fixing the value of β as 1 and varying the value of α.
Description: graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function by fixing the value of β as 2 and varying the value of α
Description: graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function by fixing the value of β as 3 and varying the value of α.
moment generating function of gamma distribution
Before understanding the concept of moment generating function for the gamma distribution let us recall some concept of moment generating function
Moments
The moment of the random variable is defined with the help of expectation as
this is known as r-th moment of the random variable X it is the moment about origin and commonly known as raw moment.
If we take the r-th moment of the random variable about the mean μ as
this moment about the mean is known as central moment and the expectation will be as per the nature of random variable as
in the central moment if we put values of r then we get some initial moments as
If we take the binomial expansion in the central moments then we can easily get the relationship between the central and raw moments as
some of the initial relationships are as follows
Moment generating function
The moments we can generate with the help of a function that function is known as moment generating function and is defined as
this function generates the moments with the help of expansion of exponential function in either of the form
using Taylors form as
differentiating this expanded function with respect to t gives the different moments as
on in another way if we take the derivative directly as
since for both discrete
and continuous we have
so for t=0 we will get
likewise
as
and in general
there is two important relations for the moment generating functions
moment generating function of a gamma distribution | mgf of gamma distribution | moment generating function for gamma distribution
Now for the gamma distribution the moment generating function M(t) for the pdf
is
and for the pdf
the moment generating function is
gamma distribution moment generating function proof | mgf of gamma distribution proof
Now first take the form of probability density function as
and using the definition of moment generating function M(t) we have
we can find the mean and variance of the gamma distribution with the help of moment generating function as differentiating with respect to t two times this function we will get
if we put t=0 then first value will be
and
Now putting the value of these expectation in
alternately for the pdf of the form
the moment generating function will be
and differentiating and putting t=0 will give mean and variance as follows
2nd moment of gamma distribution
The second moment of gamma distribution by differentiating moment generating function two times and putting the value of t=0 in second derivative of that function we will get
third moment of gamma distribution
The third moment of gamma distribution we can find by differentiating the moment generating function three times and putting the value of t=0 in third derivative of the mgf we will get
or directly by integrating as
sigma for gamma distribution
sigma or standard deviation of gamma distribution we can find by taking the square root of variance of gamma distribution of type
or
for any defined value of alpha, beta and lambda.
characteristic function of gamma distribution | gamma distribution characteristic function
If the variable t in the moment generating function is purely an imaginary number as t=iω then the function is known as the characteristic function of gamma distribution denoted and expressed as
as for any random variable the characteristic function will be
Thus for the gamma distribution the characteristic function by following the pdf of gamma distribution is
following
There is another form of this characteristics function also if
then
sum of gamma distributions | sum of exponential distribution gamma
To know the result of sum of gamma distribution we must first of all understand sum of independent random variable for the continuous random variable, for this let us have probability density functions for the continuous random variables X and Y then the cumulative distribution function for the sum of random variables will be
differentiating this convolution of integral for the probability density functions of X and Y will give the probability density function for the sum of random variables as
Now let us prove if X and Y are the gamma random variables with respective density functions then there sum will also be gamma distribution with sum of same parameters
considering the probability density function of the form
for the random variable X take alpha as s and for random variable Y take alpha as t so using the probability density for the sum of random variables we have
here C is independent of a , now the value will be
which represent the probability density function of sum of X and Y and which is of the Gamma distribution, hence the sum of the gamma distribution also represents the gamma distribution by respective sum of parameters.
mode of gamma distribution
To find the mode of gamma distribution let us consider the probability density function as
now differentiate this pdf with respect to x, we will get the differentiation as
this will be zero for x=0 or x=(α -1)/λ
so these are only critical points at which our first derivative will be zero if alpha greater than or equal to zero then x=0 will not be mode because this makes pdf zero so mode will be (α -1)/λ
and for alpha strictly less than one the derivative decreases from infinity to zero as x increases from zero to infinity so this is not possible hence the mode of gamma distribution is
median of gamma distribution
The median of the gamma distribution can be found with the help of inverse gamma distribution as
or
provided
which gives
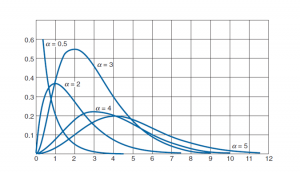
gamma distribution shape
Gamma distribution takes different shape depending on the shape parameter when shape parameter is one gamma distribution is equal to the exponential distribution but when we vary the shape parameter the skewness of the curve of gamma distribution decreases as the increase in the shape parameter, in another words the shape of the curve of gamma distribution changes as per the standard deviation .
skewness of gamma distribution
skewness of any distribution can be observed by observing the probability density function of that distribution and skewness coefficient
for the gamma distribution we have
so
this shows the skewness depends on alpha only if alpha increases to infinity curve will be more symmetric and sharp and when alpha goes to zero the gamma distribution density curve positively skewed which can be observed in the density graphs.
generalized gamma distribution | shape and scale parameter in gamma distribution | three parameter gamma distribution | multivariate gamma distribution
where γ, μ and β are the shape, location and scale parameters respectively, by assigning specific values to these parameters we can get the two parameter gamma distribution specifically if we put μ=0, β=1 then we will get standard gamma distribution as
using this 3 parameter gamma distribution probability density function we can find the expectation and variance by following there definition respectively.
Conclusion:
The concept of reciprocal of gamma distribution that is inverse gamma distribution in comparison with gamma distribution and measure of central tendencies of gamma distribution with the help of moment generating function were the focus of this article, if you require further reading go through suggested books and links. For more post on mathematics, visit our mathematics page.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_distribution
A first course in probability by Sheldon Ross
Schaum’s Outlines of Probability and Statistics
An introduction to probability and statistics by ROHATGI and SALEH