Protease enzymes are present ubiquitously and represent a pivot role in all physiological processes. Out of three industrial enzymes, protease is the major one. Proteases are also known as peptidases or proteolytic enzymes that are involved in protein catabolism. This article discusses some protease enzyme examples.
Some plant-derived protease enzyme examples
Protease enzymes present in animals
Microbial based protease enzyme examples
Papain
It is obtained from papaya. This enzyme is used as a meat tenderizer, denture cleaner.

Caricain
It is also obtained from papaya. These enzymes are extensively used in gluten-free food processing.
Bromelain
It is obtained from pineapple. This enzyme play an important role as an anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer agent.
Ficin
This enzymes is isolated from fig. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Actinidin
It is naturally present in various fruits such as kiwi, banana, mango, and pineapple. It is mostly used as dietary additives.
Zingipain
It is derived from ginger. These enzymes act as anti-proliferative agents.
Cucumisin
Mostly these enzymes are obtained from musk melon. These are involved in the hydrolysis of proteins.
Oryasin
This is obtained from rice and involved in milk clotting.
Phytepsin
This is obtained from barley. Similar to oryasin, it is also used in milk clotting.
Neprosin
This protease enzyme is derived from Nepenthes (the tropical pitcher plant). This plant-derived enzyme is widely used as a proteolytic agent in mass spectrometry, and histone mapping.
Trypsin
These are present in the small intestine, aids in protein digestion

Chymotrypsin
This is a proteolytic enzyme produced by the pancreas which is used in small intestine
Elastase
This is present in the pancreas which helps to breakdown proteins and fats.

Collagenase
It helps to the breakdown of peptide bonds present in collagen.
Pepsin
This endopeptidase is present in the stomach and aids in digestion.
Renin
It is secreted from juxtaglomerular kidney cells and helps to control blood pressure.

Thrombin
It is a kind of serine protease that act as a procoagulant and anticoagulant.
Plasmin
This is another example of a serine protease that functions in a fibrinolytic mechanism.
Alcalase
Isolated from Bacillus licheniformis and widely used in the detergent industry.
Savinase
It is isolated from Alkalophilic Bacillus sp.. It is used in the detergent and textile industry.
Neutrase
It is obtained from Bacillus amyloliquefa-ciens.
Novozyme 3403
This is obtained from Bacillus licheniformis and substantially used as denture cleaner.
Novozyme 4551
This protease enzyme is isolated from Bacillus licheniformis and used largely in the leather industry.
Protease enzyme structure
Protease enzyme shows substrate and product specificity. Thus, these enzymes take part in a highly regulated cascade of cellular processes.
The protease enzyme consists of a single polypeptide chain. The polypeptide chain consists of 250 amino acid residues without any sulfhydryl groups.
Depending upon the pH range, protease enzyme can be of three types
Acidic
It functions at 3.8-5.6 pH; used as a seasoning agent in soy sauce, clearing agent in beer and fruit juices; mostly produced by fungal species Aspergillus niger, and Aspergillus oryzae secret extracellular acidic proteases known as Aspergilla opepsins. Other fungal members produce acidic proteases are Penicillium, Rhizopus, and Mucor.
Neutral
The pH of this protease enzyme ranges from 5-8; used in the brewing industry; obtained from Bacillus.
Alkaline
The optimal pH of alkaline protease ranges from 9 to 11; used in the detergent and leather industry; synthesized by Bacillus, mushrooms, and other bacterial species. Streptomyces sp. produces a type of alkaline protease that has keratinolytic activity.
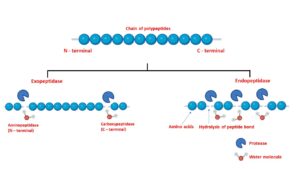
Proteases can be further classified into two groups depending upon the site of cleavage.
Exopeptidases
It usually hydrolyses the ends of a polypeptide. Based on the ends of a polypeptide i.e., C or N terminal is known as carboxy and aminopeptidases respectively. Carboxypeptidases usually hydrolyze the C-terminal end of the polypeptide releasing a single amino acid or a dipeptide while aminopeptidases act on the N-terminal end resulting in dipeptide or tripeptide.
Endopeptidases
The active site of these enzymes are the internal regions of a polypeptide chain. Depending upon the catalytic site and the mechanism, they can be divided into serine protease, cysteine protease, aspartic protease, and metalloprotease.
Serine proteases are denoted by the presence of a serine at the site of hydrolysis. These are low molecular masses and remain active at neutral to alkaline pH. Example- trypsin, chymotrypsin
Aspartic acid protease is also known as acidic protease consists of aspartates at the active site. These are active in acidic pH. Pepsins, cathepsins, and renins are aspartic acid proteases present in eukaryotes.
Cysteine proteases consist of cysteine and histidine in a catalytic triad or dyad. These are active in presence of reducing agents such as HCN or cysteine. Example – pepsinogen, papain.
Metalloprotease is a type of protease enzyme that requires divalent metal ions for its catalytic activity. Some require zinc while others use cobalt.
What is a protease enzyme?
To maintain the growth and development of every animal an array of enzymes play significant roles, among which protease enzymes perform regulatory roles in all cellular processes.
The peptide bond that constitutes the polypeptide chain is hydrolyzed by these protease enzymes and results in the breakdown of protein into smaller polypeptides and amino acids. These are synthesized by animals, plants, fungi, and also bacteria. They cleave and result in smaller molecules or give rise to newer protein products.
Also Read:
- Native species examples
- Dna replication enzymes
- Purine metabolism importance in human physiology
- Cell wall and vacuoles
- Enzymes and photosynthesis
- Different types of pcr
- Extracellular enzyme example
- Is a chromosome an allele
- Polygenic traits examples
- Fibrous protein function

I am a doctoral student of CSIR- CIMAP, Lucknow. I am devoted to the field of plant metabolomics and environmental science. I have completed my post-graduation from the University of Calcutta with expertise in Molecular Plant Biology and Nanotechnology. I am an ardent reader and incessantly developing concepts in every niche of biological sciences. I have published research articles in peer-reviewed journals of Elsevier and Springer. Apart from academic interests, I am also passionate about creative things such as photography and learning new languages.
Let’s connect over Linkedin