Metallic oxide example is very much self-explanatory. It can be defined as a crystalline solid made up of oxygen and metal. In metal oxide example formation oxygen exists as an anion with a -2 oxidation state and metals exist as cations. They are usually found as solid oxides in the earth’s crust where there is an oxide coating on the metal.
There are many metallic oxide examples where oxygenation has happened in air, water and earth. Some of the metallic oxide examples are:
- Lithium Oxide is a metallic oxide example
- Magnesium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Sodium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Calcium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Silver Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Iron (II) Oxide as metallic oxide example
- Iron (III) Oxide as metallic oxide example
- Chromium (VI) Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Titanium (IV) Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Zinc Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Copper (I) Oxide as metallic oxide example
- Copper(II)Oxide as metallic oxide example
- Potassium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
- Manganese Oxide as a metallic oxide example
Lithium Oxide is a metallic oxide example
Lithium Oxide (Li2O) is an inorganic chemical compound which is a white crystalline solid. There are many ways by which this metallic oxide example can be prepared. Lithium oxide can be prepared by thermal decomposition of lithium peroxide at temperatures of 200-300 degrees Celsius. Another common method is the burning of lithium metal in the air in the presence of oxygen.
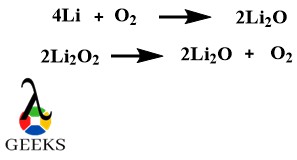
Magnesium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
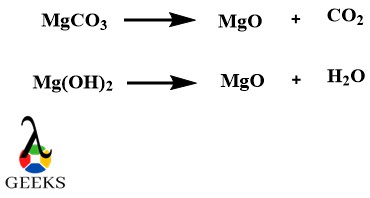
Magnesium Oxide (MgO) also called magnesia is a white hygroscopic metallic oxide example with Mg2+ and O2- ions. It is synthesized by many methods. The laboratory preparation or the most common method of synthesis is the burning of magnesium wire in dazzling light which produces ash-like metallic oxide. Another method is calcination of magnesium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide at a very high temperature of 1000-2000 degrees Celsius.
Sodium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
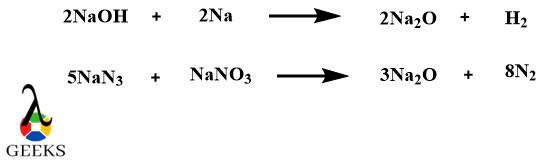
Sodium Oxide (Na2O) is one of the most common metallic oxide examples which is used in ceramics and glasses. There are many ways of producing sodium oxide. For instance, the burning of sodium metal in the air gives impure sodium oxide contaminated with sodium peroxide. The second method is the reaction of sodium metal with sodium hydroxide. One more common method is heating sodium azide and sodium nitrate mixture.
Calcium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
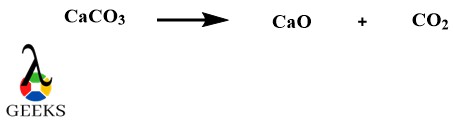
Calcium Oxide (CaO) is one of the oldest metallic oxide examples with historical significance in European history. It is odourless and colourless and is usually prepared by heating limestone in a lime kiln at a high-temperature range. This is called calcification.
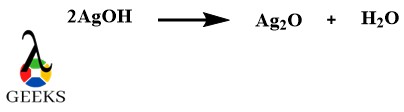
Silver Oxide as a metallic oxide example
Silver Oxide (Ag2O) is a black powdery or dark brown metallic oxide example. There is only one main method to prepare silver oxide which is the reaction between silver nitrate and alkali hydroxide but it is not favorable in nature.
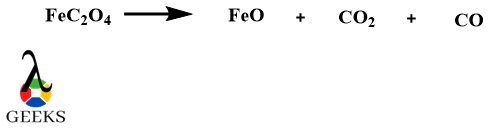
Iron(II)Oxide as metallic oxide example
Iron(II)Oxide (FeO) is a metallic oxide example which is found in nature. Naturally, it is formed because of partial or incomplete oxidation of iron in the air. Artificially or synthetically it can be synthesised by heating iron oxalate(FeC2O4). But the products of this reaction are impure.
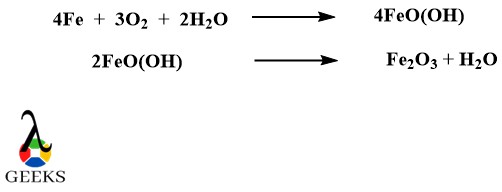
Iron(III)Oxide as metallic oxide example
Iron(III)Oxide or ferric oxide is a metallic oxide example with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the 3 iron oxides and can be synthesized easily. This metallic oxide example can be synthesized in the laboratory by electrochemical reaction where sodium bicarbonate solution is used along with iron anode and inert electrode. The hydrated iron(III)oxide is dehydrated at 200 degrees Celsius.
Chromium(VI)Oxide as a metallic oxide example
Chromium(VI) Oxide or CrO3 belongs to the family of transition metals. Its laboratory preparation is a little complex where a sulphuric acid solution is added to chromate or dichromate solution which in turn releases chromic acid which is soluble in liquid and forms many chromate-related compounds.
Titanium(IV)Oxide as a metallic oxide example
Titanium dioxide or titania is also a naturally occurring metallic oxide example and is found in the earth’s crust or other mineral ores of iron and calcium. It is a very important element and is chemically inert.
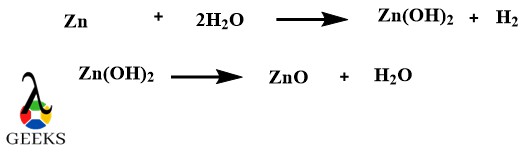
Zinc Oxide as a metallic oxide example
Zinc oxide is a white powdery crystalline metallic oxide example and its laboratory synthesis is very easy. It can be prepared by electrolysis of sodium bicarbonate solution with a zinc anode. This produces zinc hydroxide which upon heating decays into zinc oxide.
Copper(I)Oxide as metallic oxide example
The Cu2O metallic oxide example is formed by the oxidation of copper. It can appear in many colours ranging from red to yellow. Different kinds of additives affect its reaction rates.
Copper(II)Oxide as metallic oxide example
The CuO metallic oxide example is a black powdered solid and is a product of copper mining. There are many methods for its synthesis which involve both industrial and laboratory synthesis. The heating of copper in the air at 300 to 800 degrees celsius and methods of pyrometallurgy are its industrial manufacturing methods. Laboratory synthesis involves the heating of other copper compounds.
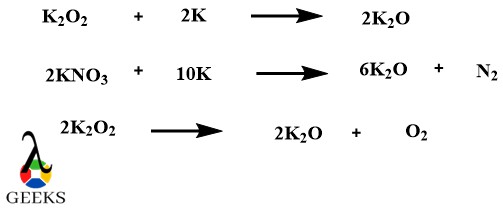
Potassium Oxide as a metallic oxide example
Potassium Oxide formulated as K2O is an alkali metallic oxide example. There are many ways to prepare this metallic oxide example the direct reaction between potassium and oxygen or the reaction of potassium peroxide with elemental potassium.
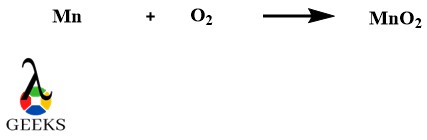
Manganese Oxide as a metallic oxide example
Manganese Oxide or MnO2 metallic oxide example is very easy in terms of its preparation. As manganese does not exist in its elemental form in nature so it exists in its oxide form where it reacts with air oxygen and exists as a stable MnO2 metallic oxide example.
Conclusion
In nutshell, there are many metallic oxide examples where metals being a cation react with oxygen dianion and give different elements synthesized by varied methods performing various reactions and having a whole lot of usages and applications. All the metallic oxide examples are ionic in nature and behavior.

Hello, I am Mansi Sharma, I have completed my master’s in Chemistry. I personally believe that learning is more enthusiastic when learnt with creativity. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Chemistry.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/mansi-sharma22