This article explains the Lewis structure of barium fluoride, resonance, shape, formal charge, angle, octet rule, lone pairs of BaF2 Lewis structure. Hybridization, solubility, ionic, polar nature, acidic and valence electron of barium fluoride is also explained.
BaF2 is also called Barium fluoride. Barium has two electron in its outermost shell. It donates one electron with each fluorine atom and this electron is accepted by fluorine. BaF2 Lewis structure shows that two Fluorine atoms and one Barium bonded by this method.
How to draw BaF2 Lewis structure?
Below steps are followed to draw Lewis structure of BaF2:
Step 1: Count the available valence electron
Fluorine and Barium are part of halogen present in the 17th group in periodic table, and second group consists of alkaline earth metals.
Two electrons are available in the outermost shell of barium hence, electron dot structure of barium is represented by Ba which is having two dots and fluorine has got seven electrons in its outermost shell, therefore electron dot structure of fluorine is written as F with seven dots.
Outermost valence shell electron of barium atom in BaF2 = 2
Outermost valence shell electron of fluorine atom in BaF2 = 7
Barium fluoride consists of two fluorine atoms therefore total available valence electrons= 2+7(2) = 16.

Step 2: Choose least electronegative atom and insert in the center of the molecule.
In the periodic table electronegativity value increases across a row that is left to right. Therefore, alkaline earth metal have lowest electronegativity while halogens have the highest.
Fluorine is the smallest halogen element with more electronegative than barium. The electronegative value of the barium is lower than that of the fluorine atom in the BaF2 molecule. Hence Barium atom is kept in the center of the molecule due to its electronegative nature.
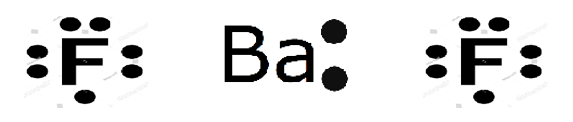
Step 3: The metal atom donates electron while the nonmetal atom accept them in ionic compound.
In BaF2, barium is the metal which donate one electron with each fluorine atom and forms barium (ΙΙ) cation, whereas fluorine is the non-metal, each fluorine atom accept one electron from barium and forms fluoride anion.
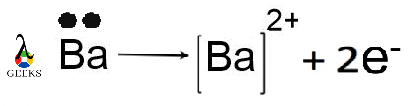
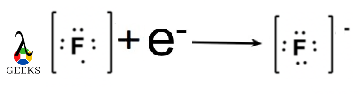
Step 4: Combining two opposite charges, to get BaF2 Lewis structure.
Barium atom donates one electron to each fluorine atom and each fluorine atom receives one electron from barium to bring the stability and as a result of this both ions will have full valence shell due to which it exhibits noble gas electron configuration.
BaF2 Lewis structure can be represented as Ba2+ and F- with eight dots.
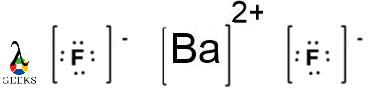
BaF2 Lewis structure resonance:
A multiple Lewis structure represents the different ways of placing electron on the atom in a molecule. Resonance structure is possible for a molecule if there are multiple bonds and also it has formal charge with the presence of lone pair on the atoms of molecule.
BaF2 Lewis structure does not show any resonance structure as there is not bonding between the barium fluoride molecule. In addition to this, barium fluoride is a molecule containing barium as metal and fluorine as non-metal. Therefore resonance structure of BaF2 is not possible.
BaF2 Lewis structure shape:
BaF2 is an ionic compound and there is no bonding between barium and fluorine ion, there is complete transfer of electrons within the molecule. Therefore BaF2 Lewis structure do not have any shape.
BaF2 Lewis structure formal charge:
Formal charge nothing but the charge which is assigned to an atom so that equally shared electrons exists between the atoms in a molecule.
Formal charge= [Total number of valence electron in free state]-{[total number of lone pair
electron] + 1/2[total number of bonding electron]}
In the case of Barium:
Number of valence electron in potassium =2
Total number of lone pair electron = 0
Total number of bonding electron = 0
Formal charge of barium= 2-{0+1/2(0)}
= +2
Formula charge on barium atom in barium fluoride Lewis structure is +2
For fluorine:
Number of valence electron in fluorine =7
Total number of lone pair electron in fluorine= 8
Total number of bonding electron = 0
Formal Charge of fluorine=7-{8+1/2(0)}
=-1
The fluorine atom in BaF2 Lewis structure has a formal charge of -1.
BaF2 Lewis structure angle:
Lewis structure of BaF2 molecule does not have any bond angle as there is no bond present between the molecule as it is originally an ionic compound with the presence of metal and non-metal.
BaF2 Lewis structure octet rule:
In BaF2 Lewis structure, barium metal belongs to the alkaline earth metal and it has 2 valence electron.
As there is no eight electron present in the barium atom so it has incomplete octet whereas each fluorine atom accepts one electron from barium so fluorine has eight electron with complete octet as a result negative charge for fluorine.
BaF2 Lewis structure lone pair:
Pair of electrons that are not involved in bonding are termed as lone pair electrons.
Lone pair electron of Barium in Barium fluoride Lewis structure = 0
Lone pair electron of fluorine in barium fluoride Lewis structure = 4
BaF2 valence electron:
Electronic configuration of barium is 1s22s22p63s23p6 3d104s24p64d105s25p66s2
Outermost electron present in the barium is 2
Electronic configuration of fluorine is 1s22s22p5
Outermost electron present in the fluorine is 7
Two fluorine atom present in the barium fluoride therefore, the total number of valence electron of BaF2 is 2+7(2) =16.
BaF2 hybridization:
BaF2 Lewis structure does not show any hybridization as there is no mixing and recasting of atomic orbitals within the molecule, there is complete transfer of electrons between Ba metal and fluorine non-metal ion creating +2 charge on Ba and -1 charge on fluorine.
BaF2 solubility:
Barium fluoride is slightly soluble in
- water
- calcium hydroxide
- lead dichloride
Barium fluoride is soluble in
- Hydrochloric acid
- Nitric acid
- Hydrogen cyanate
- Hydrofluoric acid
- Ammonium chloride
Barium fluoride is insoluble in
- Silver chloride
- Silver carbonate
- Calcium carbonate
- Lead dichloride
How BaF2 is soluble in hydrochloric acid than water?
In aqueous solution barium fluoride is dissociate into Ba2+ and 2F– ions.
BaF2(s) ⇌ Ba2+ (aq) + 2F− (aq)
F– is a basic anion thus it can react with the acid, such that production of ions are formed is more than the formation of insoluble salt. Hence Barium fluoride is found to be less soluble in water compare to dilute hydrochloric acid.
F−+HCl → HF + Cl−
Why BaF2 is soluble in hydrochloric acid than water?
Fluorine is highly electronegative in nature in BaF2. Hence Barium gets partial positive charge and Fluorine gets a partial negative charge.
More is the ionic character present in a compound more readily it will dissociate into ions. Hydrochloric acid contains hydrogen ions. When BaF2 dissolvesin HCl more ions are formed Hence barium fluoride is more soluble in acidic solution.
Is BaF2 ionic?
Yes barium fluoride is an ionic compound and is made up of barium (ΙΙ) cation and fluoride anion. As there is no presence of covalent or pi bonds within the molecule. There is only presence of charges on Ba metal and fluorine ion which makes the BaF2 an ionic compound.
Why BaF2 ionic?
In BaF2, the interaction between barium and fluorine is ionic in nature because complete transfer of ions is observed and there is no shared bonding. Therefore barium fluoride is ionic in nature.
How BaF2 ionic?
Barium has two electrons in its outermost shell and it donates one electron with each fluorine atom and forms barium (ΙΙ) cation, whereas fluorine is the non-metal, and each fluorine atom accepts one electron from barium and forms fluoride anion. Hence ionic bond is formed by complete transfer of electron as stated above.
Is BaF2 polar or nonpolar?
Barium fluoride is polar in nature. Due to the presence of polar bonds with barium and fluorine it is polar in nature.
Why BaF2 polar?
Barium fluoride is ionic in nature which contains the positively charged cation that is Ba2+and negatively charged anion that is F–on it, which creates a dipole within the BaF2 molecule which makes it polar.
How BaF2 polar?
Due to the presence of polar bond within positively charged Ba cation and negatively charged fluorine anion in BaF2 molecule, there is the formation of polar bond within Ba and F– ion, makes it a polar molecule.
Is BaF2 acidic or basic?
BaF2 is weakly acidic in nature.
Why BaF2 weakly acidic?
Barium fluoride is a weak acid because it is a salt of barium hydroxide which is a weak base and hydrofluoric acid which is a strong acid. This reaction is called acid-base reaction.
Ba (OH)2 + 2HF → 2H2O + BaF2
How BaF2 weakly acidic?
Weak acid is the one which partially dissociates in water. In the case of Barium Fluoride when reacts with water, it does not fully dissociate its ion hence BaF2 is termed as weak acidic in nature.
Summary:
BaF2 consists of two ions i.e. Ba2+ cation and F– anion. Ionic bond is formed between these two ions and it has got polarity and weak acidic nature. BaF2 is found to be soluble acids such as in nitric acid, hydrochloric and is slightly soluble in water.
Also Read:
- Carbonic acid lewis structure
- Hio3 lewis structure
- Baco3 lewis structure
- Cos lewis structure
- No3 lewis structure
- Nh2 lewis structure
- Hno2 lewis structure
- Sio2 lewis structure drawings
- Hco2 lewis structure
- Chcl3 lewis structure

Hi….I am Supriya Upadhya, a Post Graduate in Organic chemistry with good understanding of Chemistry concepts and worked as Junior research fellow in synthesis of anti cancer agent. Also worked on Anti-Microbial Polymer synthesis as part of Post graduate thesis.