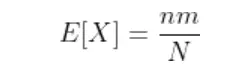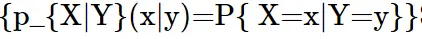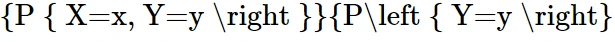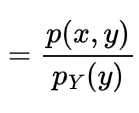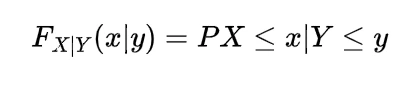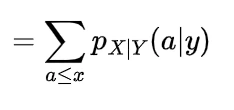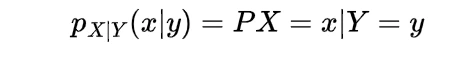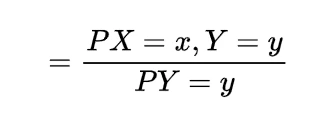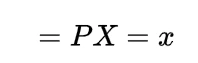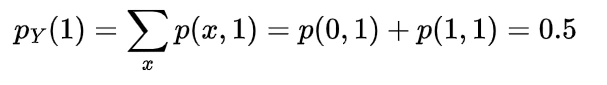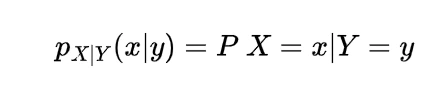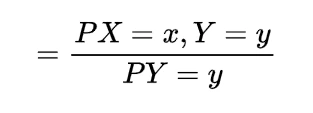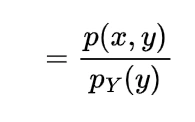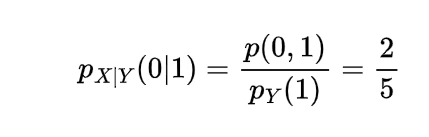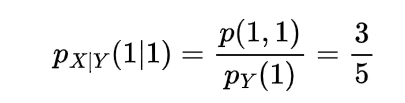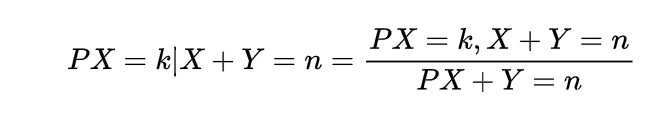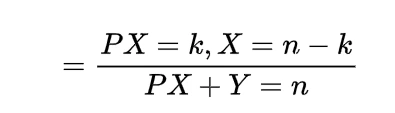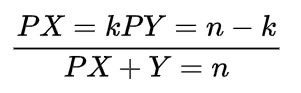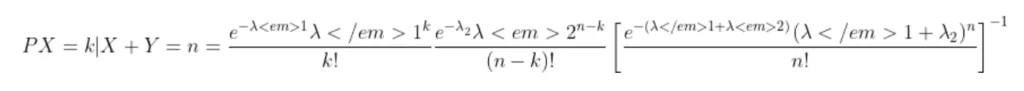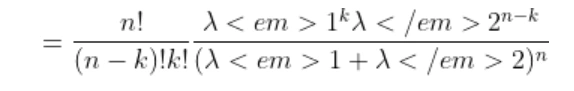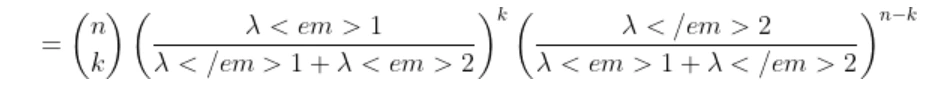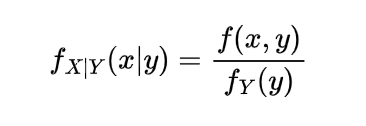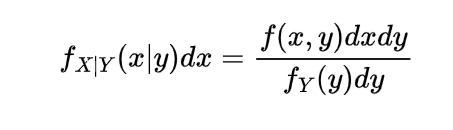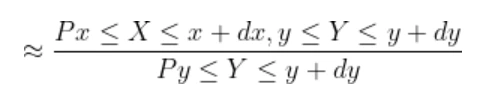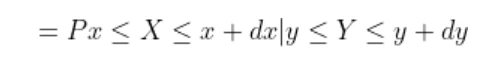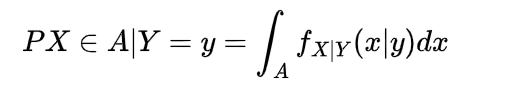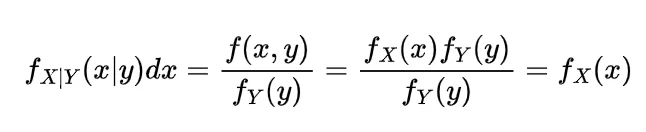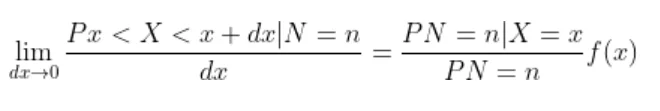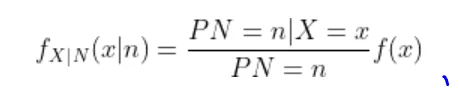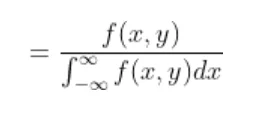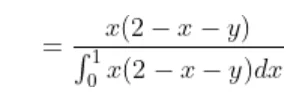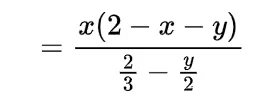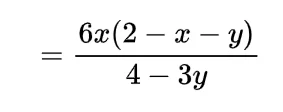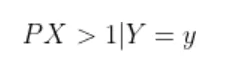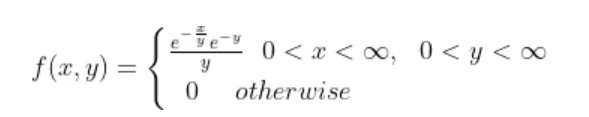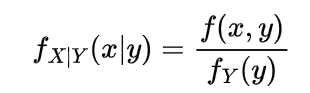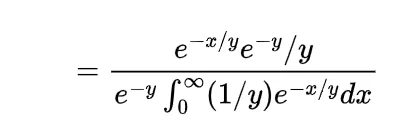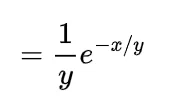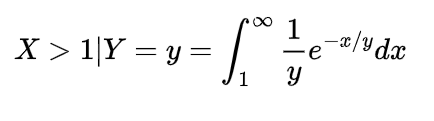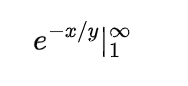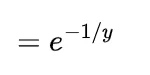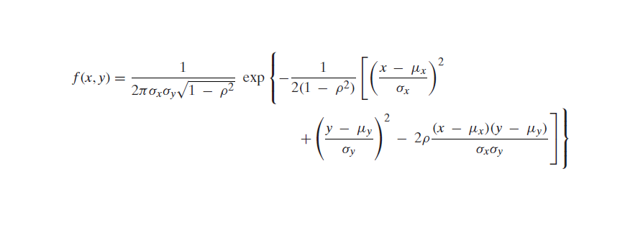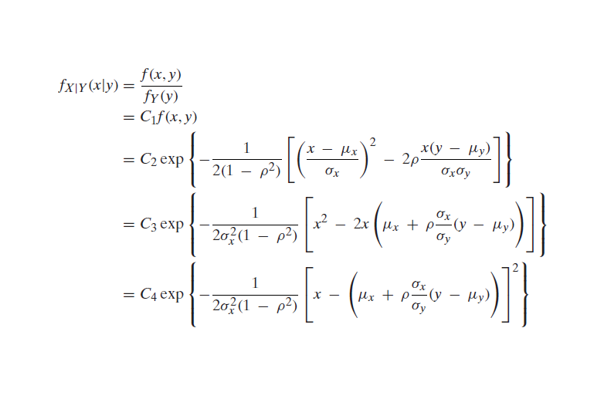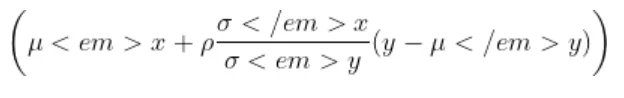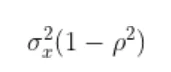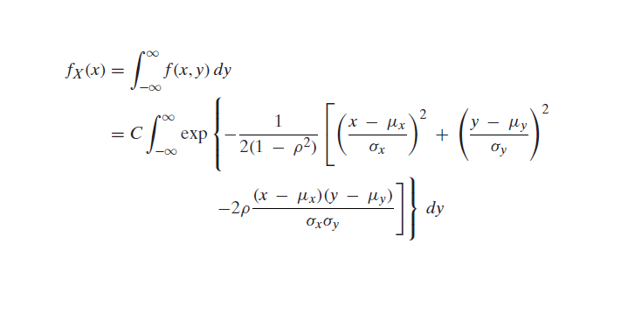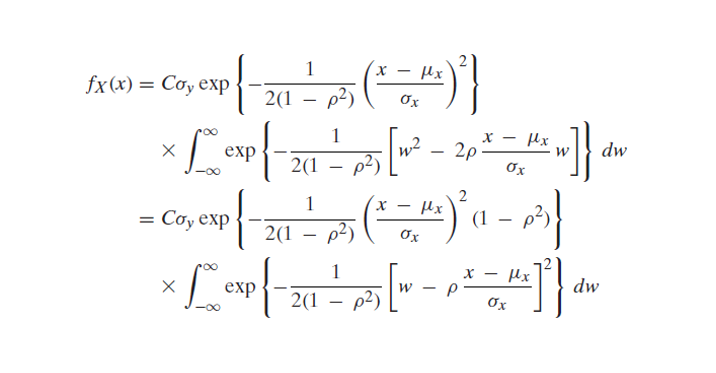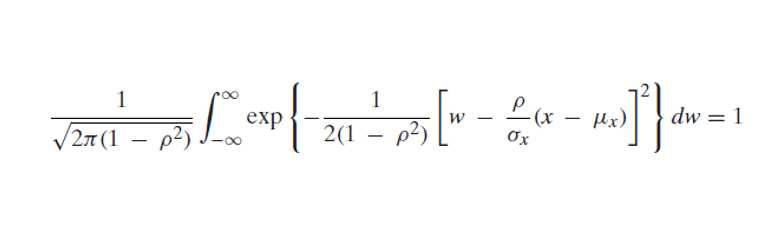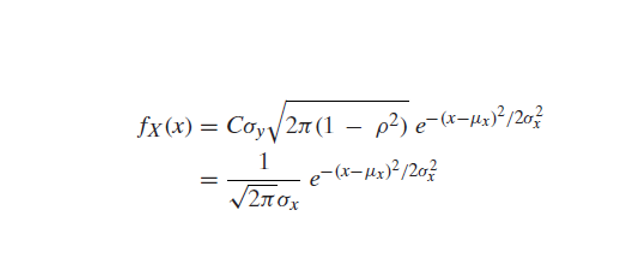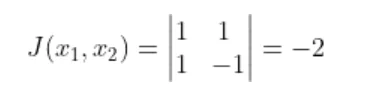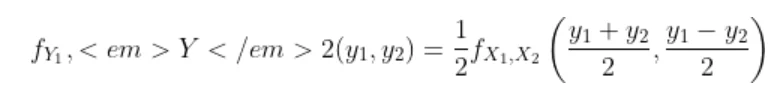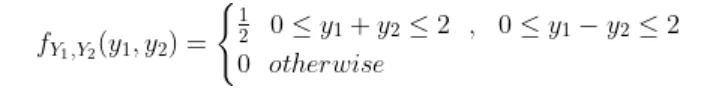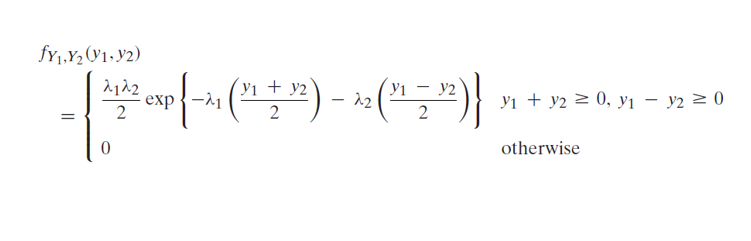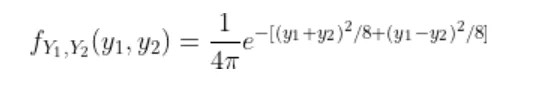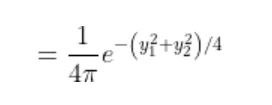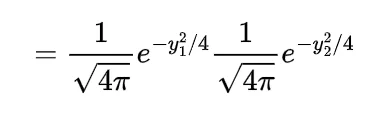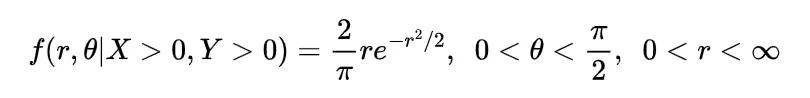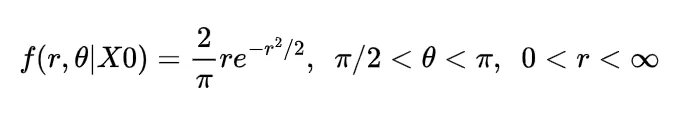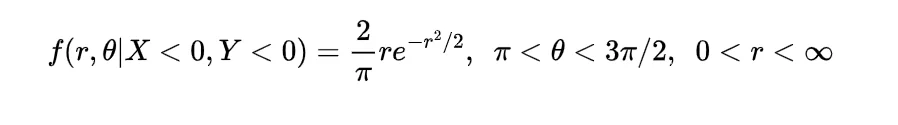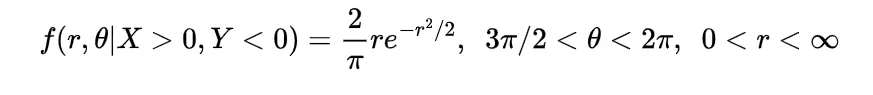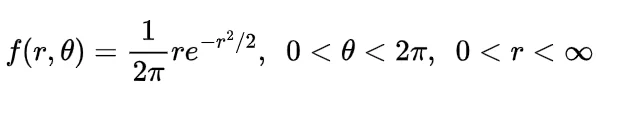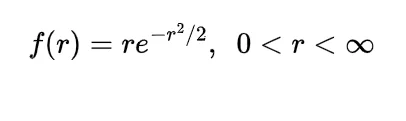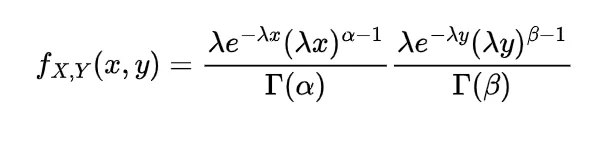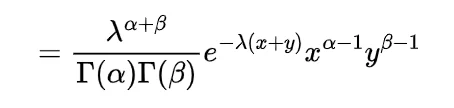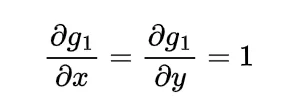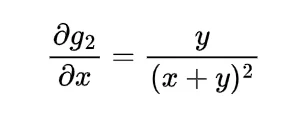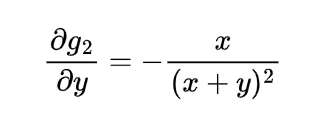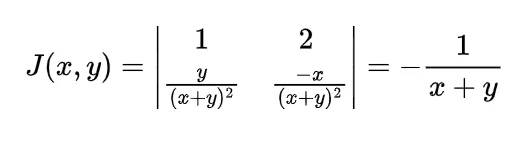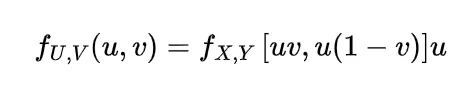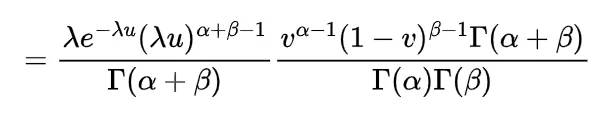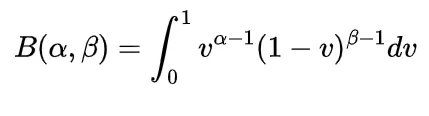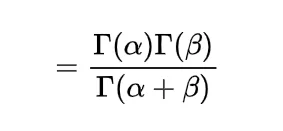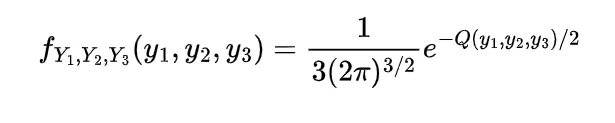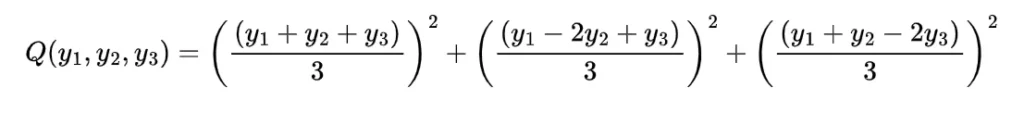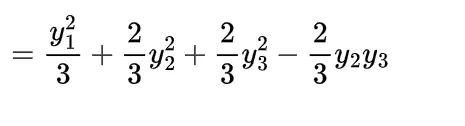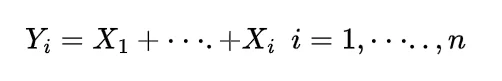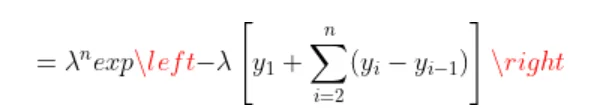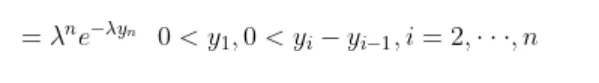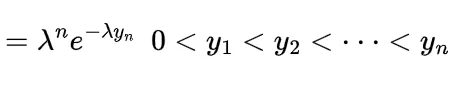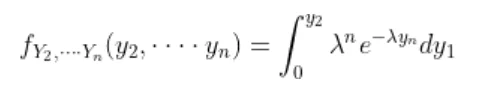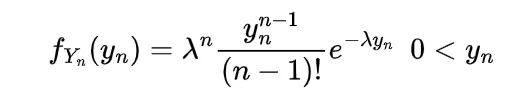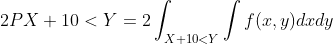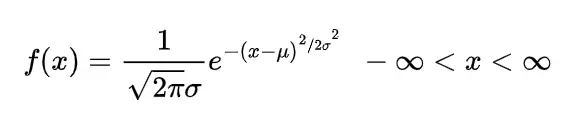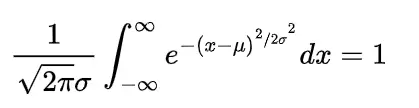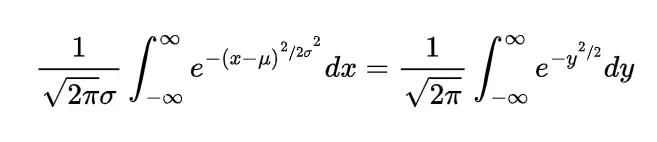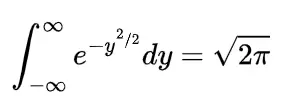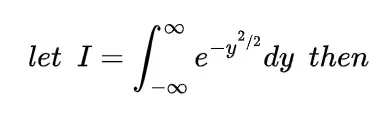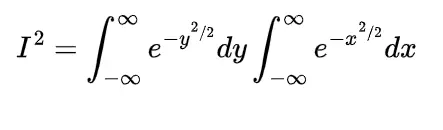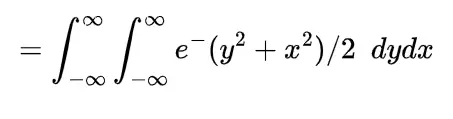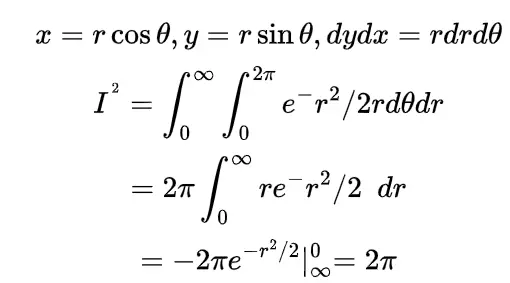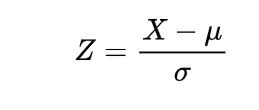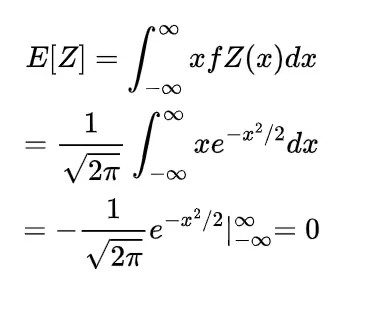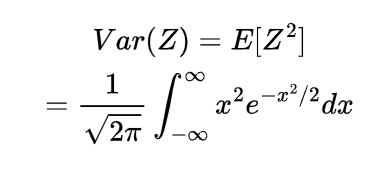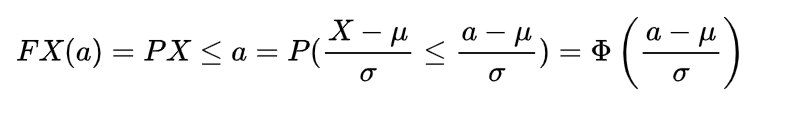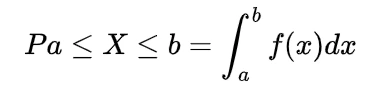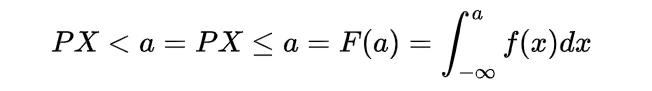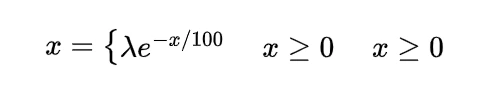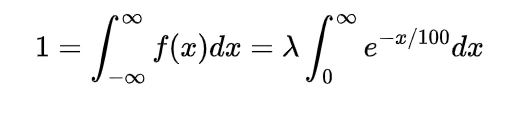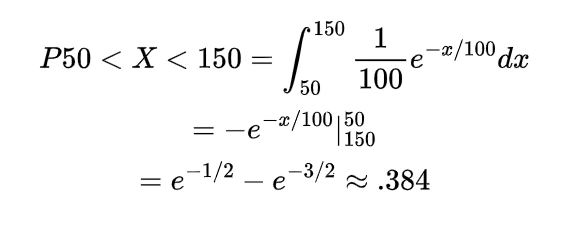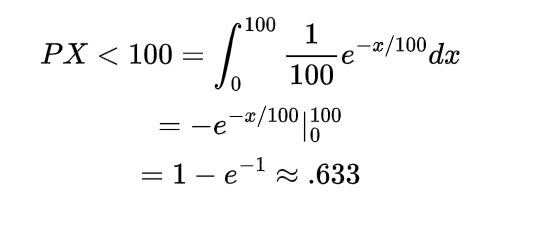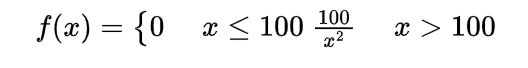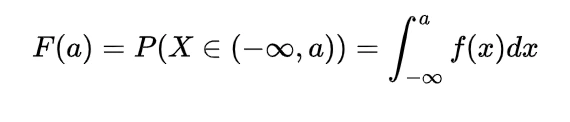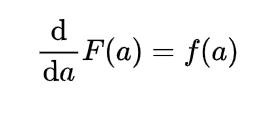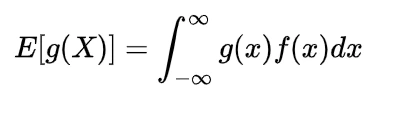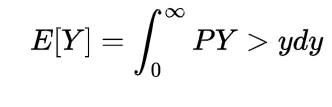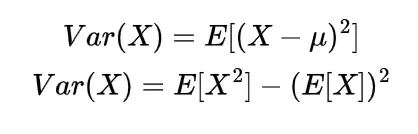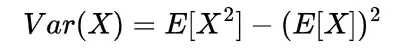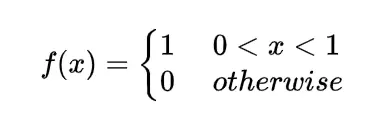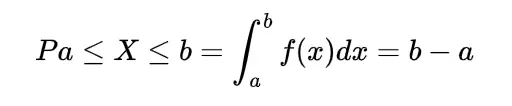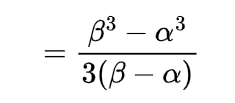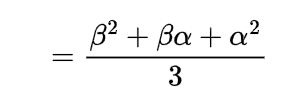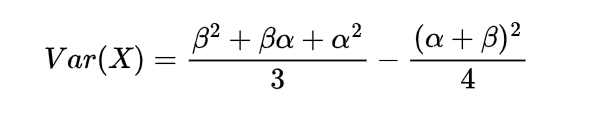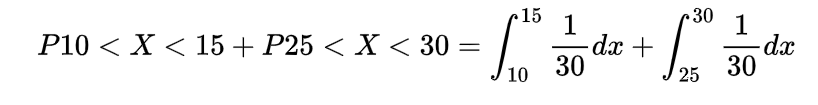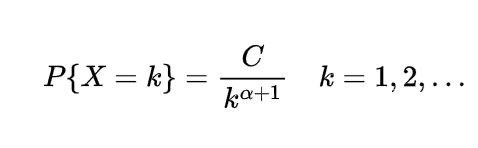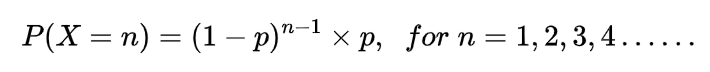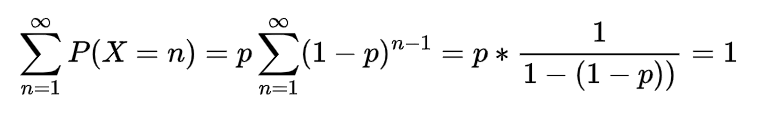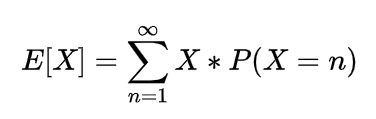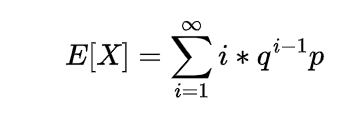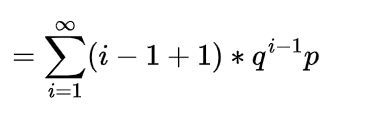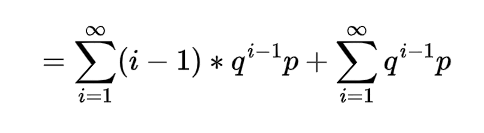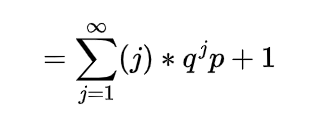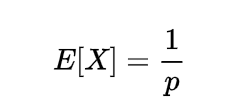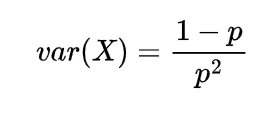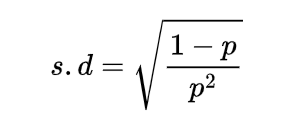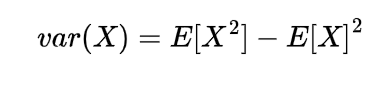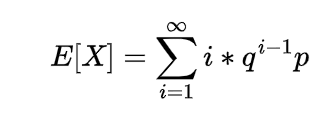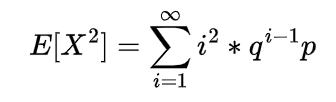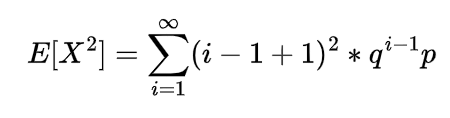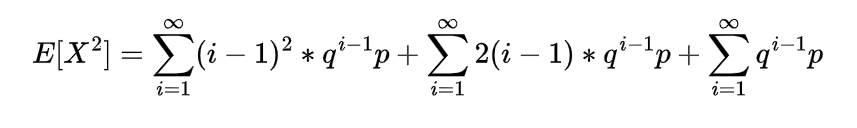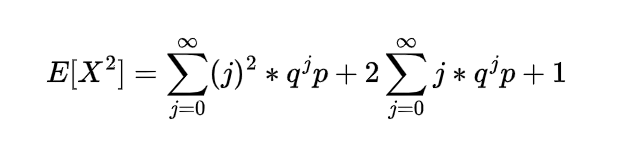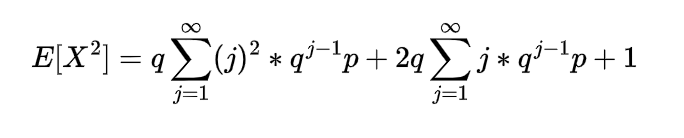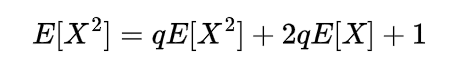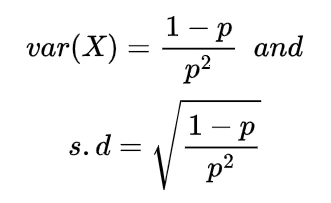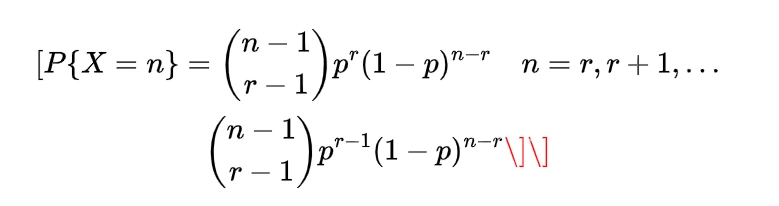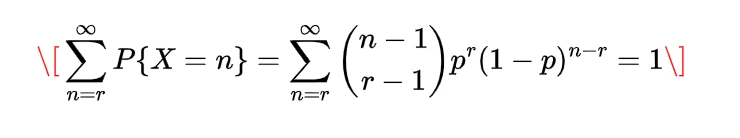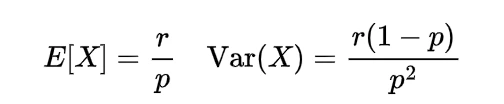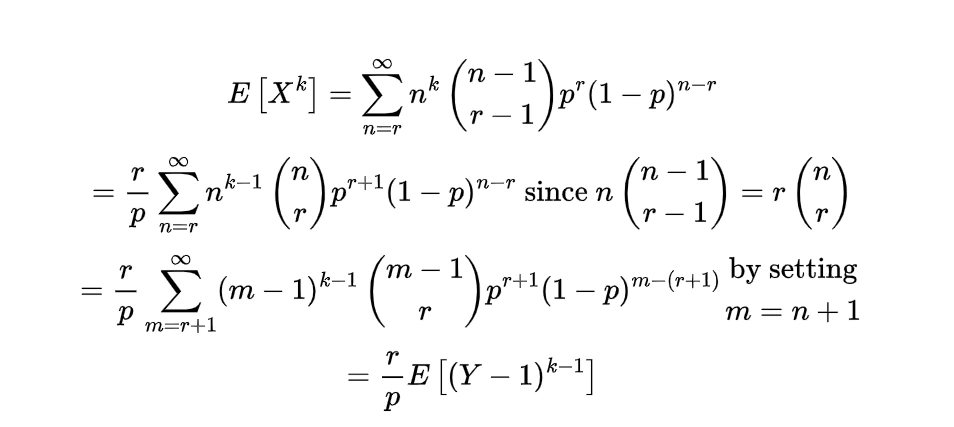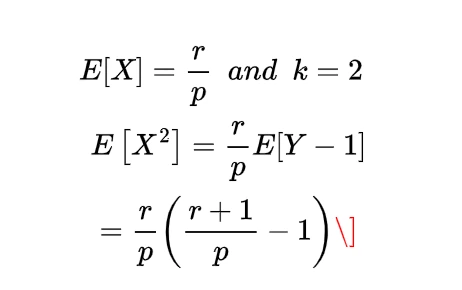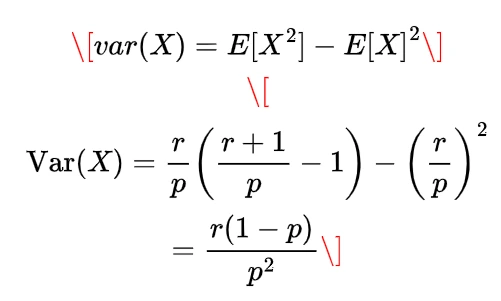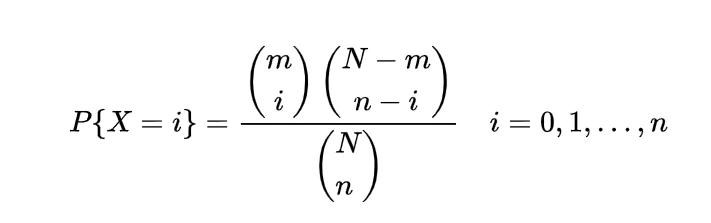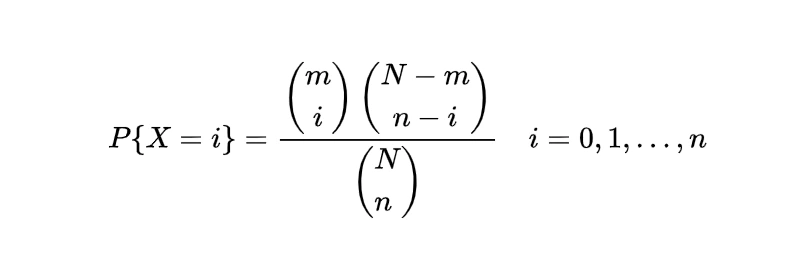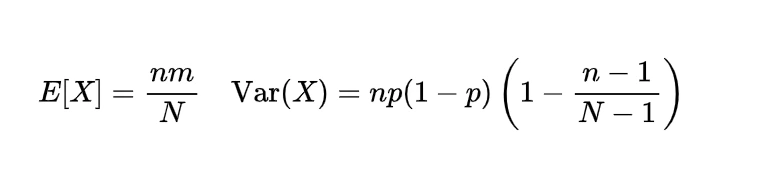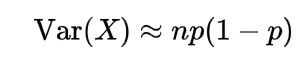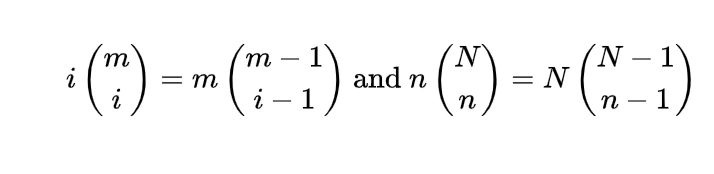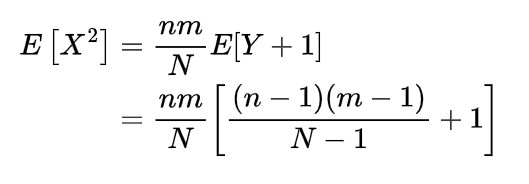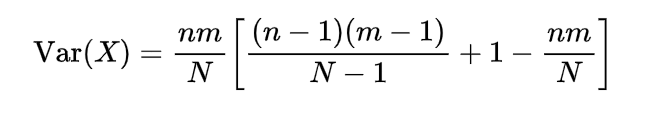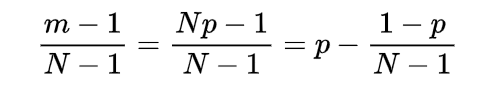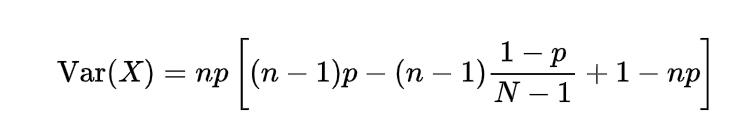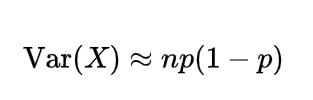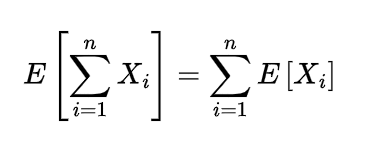Mathematical Expectation and random variable
The mathematical expectation plays very important role in the probability theory, the basic definition and basic properties of mathematical expectation already we discussed in previous some articles now after discussing the various distributions and types of distributions, in the following article we will get familiar with some more advanced properties of mathematical expectation.
Expectation of sum of random variables | Expectation of function of random variables | Expectation of Joint probability distribution
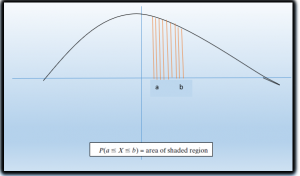
We know the mathematical expectation of random variable of discrete nature is


and for the continuous one is
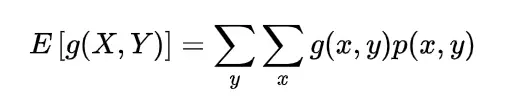
now for the random variable X and Y if discrete then with the joint probability mass function p(x,y)
expectation of function of random variable X and Y will be
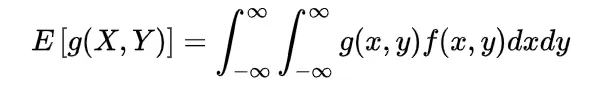
and if continuous then with the joint probability density function f(x, y) the expectation of function of random variable X and Y will be
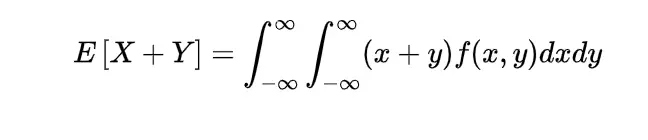
if g is addition of these two random variables in continuous form the


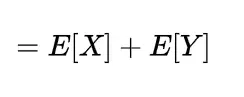

and if for the random variables X and Y we have
X>Y
then the expectation also
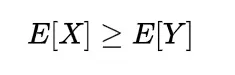
Example
A Covid-19 hospital is uniformly distributed on the road of the length L at a point X, a vehicle carrying oxygen for the patients is at a location Y which is also uniformly distributed on the road, Find the expected distance between Covid-19 hospital and oxygen carrying vehicle if they are independent.
Solution:
To find the expected distance between X and Y we have to calculate E { | X-Y | }
Now the joint density function of X and Y will be
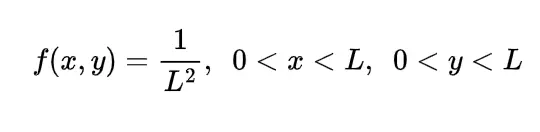
since
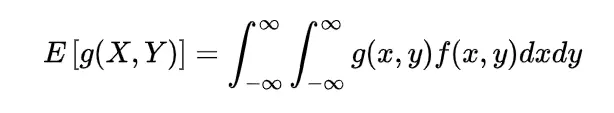
by following this we have

now the value of integral will be
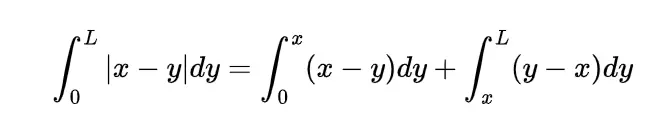


Thus the expected distance between these two points will be
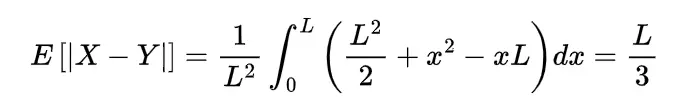
Expectation of Sample mean
As the sample mean of the sequence of random variables X1, X2, ………, Xn with distribution function F and expected value of each as μ is

so the expectation of this sample mean will be
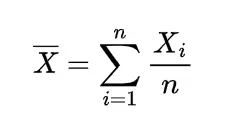
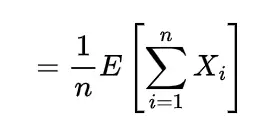
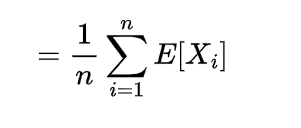

which shows the expected value of sample mean is also μ.
Boole’s Inequality
Boole’s inequality can be obtained with the help of properties of expectations, suppose the random variable X defined as
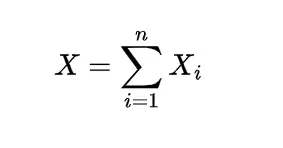
where

here Ai ‘s are the random events, this means random variable X represents the occurrence of the number of events Ai and another random variable Y as
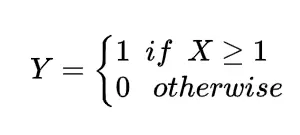
clearly
X>=Y
E[X] >= E[Y]
and so is
now if we take the value of random variable X and Y these expectation will be

and
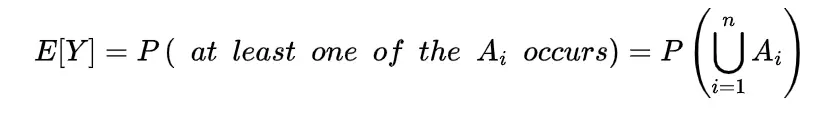
substituting these expectation in the above inequality we will get Boole’s inequality as

Expectation of Binomial random variable | Mean of Binomial random variable
We know that the binomial random variable is the random variable which shows number of successes in n independent trials with probability of success as p and failure as q=1-p, so if
X=X1 + X2+ …….+ Xn
Where

here these Xi ‘s are the Bernoulli and the expectation will be

so the expectation of X will be
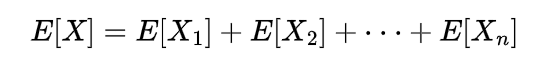
Expectation of Negative binomial random variable | Mean of Negative binomial random variable
Let a random variable X which represents the number of trials needed to collect r successes, then such a random variable is known as negative binomial random variable and it can be expressed as
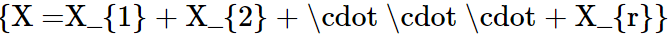
here each Xi denote the number of trials required after the (i-1)st success to obtain the total of i successes.
Since each of these Xi represent the geometric random variable and we know the expectation for the geometric random variable is

so
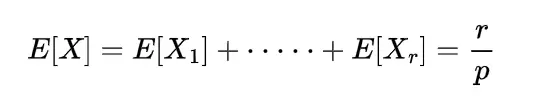
which is the expectation of negative binomial random variable.
Expectation of hypergeometric random variable | Mean of hypergeometric random variable
The expectation or mean of the hypergeometric random variable we will obtain with the help of a simple real life example, if n number of books are randomly selected from a shelf containing N books of which m are of mathematics, then to find the expected number of mathematics books let X denote the number of mathematics books selected then we can write X as

where

so
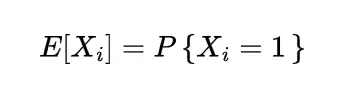
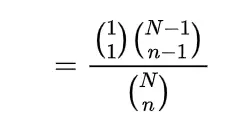
=n/N
which gives
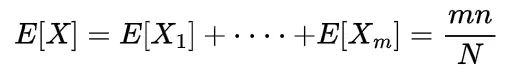
which is the mean of such a hypergeometric random variable.
Expected number of matches
This is very popular problem related to expectation, suppose that in a room there are N number of people who throw their hats in the middle of the room and all the hats are mixed after that each person randomly choose one hat then the expected number of people who select their own hat we can obtain by letting X to be the number of matches so

Where
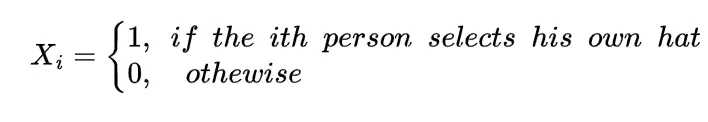
since each person has equal opportunity to select any of the hat from N hats then
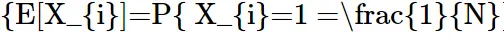
so

which means exactly one person on average choose his own hat.
The probability of a union of events
Let us obtain the probability of the union of the events with the help of expectation so for the events Ai

with this we take
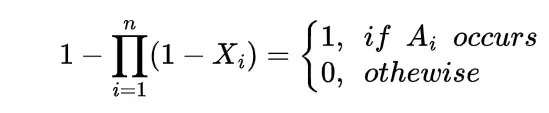
so the expectation of this will be

and expanding using expectation property as
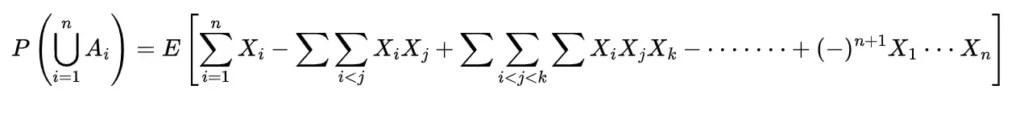
since we have
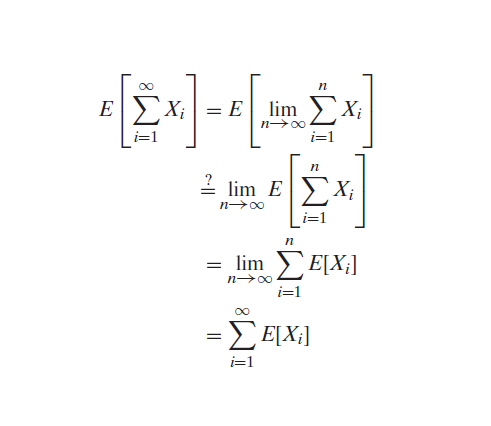
and
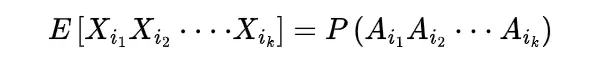
so

this implies the probability of union as
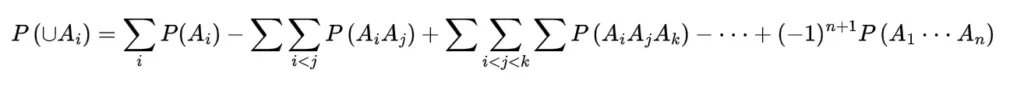
Bounds from Expectation using Probabilistic method
Suppose S be a finite set and f is the function on the elements of S and
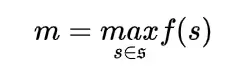
here we can obtain the lower bound for this m by expectation of f(s) where “s” is any random element of S whose expectation we can calculate so


here we get expectation as the lower bound for the maximum value
Maximum-Minimum identity
Maximum Minimum identity is the maximum of the set of numbers to the minimums of the subsets of these numbers that is for any numbers xi
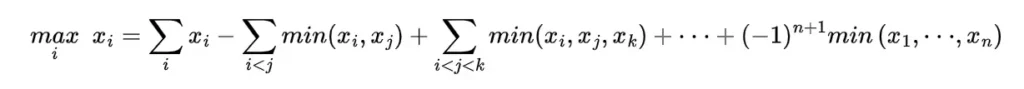
To show this let us restrict the xi within the interval [0,1], suppose a uniform random variable U on the interval (0,1) and the events Ai as the uniform variable U is less than xi that is

since at least one of the above event occur as U is less than one the value of xi
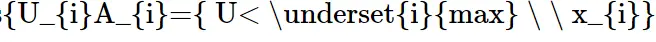
and
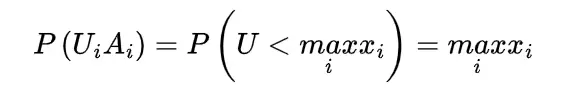
Clearly we know

and all the events will occur if U is less than all the variables and
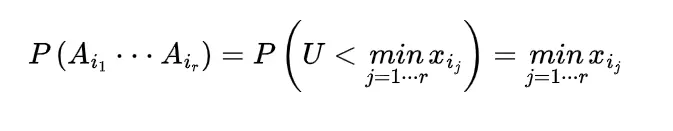
the probability gives

we have the result of probability of union as

following this inclusion exclusion formula for the probability
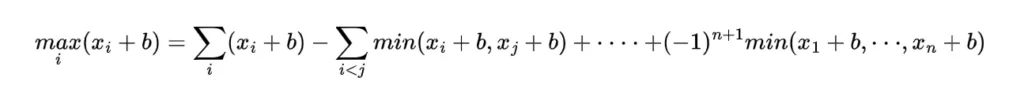
consider

this gives
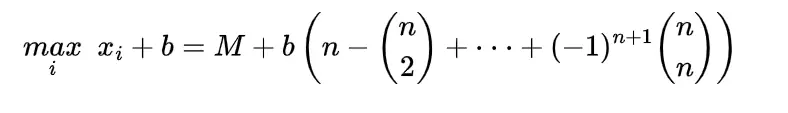
since

which means
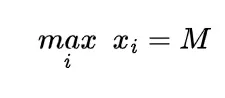
- hence we can write it as

taking expectation we can find expected values of maximum and partial minimums as

Conclusion:
The Expectation in terms of various distribution and correlation of expectation with some of the probability theory concepts were the focus of this article which shows the use of expectation as a tool to get expected values of different kind of random variables, if you require further reading go through below books.
For more articles on Mathematics, please see our Mathematics page.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expectation
A first course in probability by Sheldon Ross
Schaum’s Outlines of Probability and Statistics
An introduction to probability and statistics by ROHATGI and SALEH