Protists are mostly single-celled or unicellular organisms mostly live in aquatic ambience.
Protists are eukaryotic mostly single-celled or unicellular organisms. Though they are relatable to other organisms they aren’t considered as true animals, plants or fungi this is why they fall into a different category.
Why are protists eukaryotic?
Now we know that protists are mostly single-celled organisms but still what makes them fall under the category of eukaryotes.
Protists have a nucleus and other complex organelles in them which makes it fall under eukaryotes.
Why are protists eukaryotes and not prokaryotes?
Protists are mostly single-celled organisms and still, they come under eukaryotes. We know that prokaryotes are simple and eukaryotes have complex structures. But protists are eukaryotes, how?
The presence of a nucleus inside them and other complex membrane-bound organelles make protists fall under eukaryotes.
Image credits: Wikimedia
Are protists simple or complex organisms?
Protists, though they are mostly unicellular organisms, they are not simple organisms.
Yes, protists are complex organisms. They have complex organelles in them which are similar to plants, animals, fungi and other bigger organisms.
Are protists haploid or diploid?
Protists can be haploid or diploid.
Protists transform themselves from being haploid to diploid.
Most of the protists are unicellular which are haploid. Multicellular protists are diploid. This may change from one species of protists to another depending on their morphology and other components.
Are protists motile or nonmotile?
Motility or movement of small organisms is based on the presence of flagella, cilia, pseudopodia (False feet) in the protists.
Most of the protists have flagella and have the capability to move.
Eg: Flagellum- Euglena, Pseudopodia- Amoeba, Cilia- Paramecium.
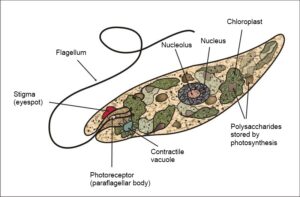
Image credits: Wikimedia
How do protists obtain energy?
Based on their nutrition uptake, protists are classified into 3 types
Ingestion protists:
This group of protists engulf the minute food particles and ingest them. The food particle is then digested in the organelle called vacuoles.
Eg: Amoeba

Image credits: Wikimedia
Absorption protists:
This group of protists are called decomposers. The food particle is absorbed into the organism by the process of diffusion.
Eg: spirogyra
Photosynthetic protists:
Photosynthetic protists are the group of protists that are able to prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis in which light is used as a primary source. They are the producers and are majorly present in the aquatic system.
Eg: Algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates etc.
What protists are decomposers?
Protists are producers majorly. Few protists are decomposers too.
Slime moulds are decomposers. Other than slime moulds, chytrids, Oomycetes, labyrinthulomycetes are other examples of protists being decomposers.
Are protists aerobic or anaerobic?
Protists can be aerobic or anaerobic. Few protists are obligate aerobes. Few are anaerobic organisms
Characteristics of protists:
- Protists are mostly single-celled organisms or commonly known as Unicellular organisms.
- There are few multicellular protists too.
- Protists are complex organisms as they have nuclei inside them.
- Protists have other membrane-bound organelles like endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, vacuole etc
- Protists are mostly motile. They have flagellum, cilia or pseudopodia which is commonly called “False feet”.
- Protists require a moist environment to survive. So they are aquatic organisms.
- Few protists have symbiotic relationships. They live like a parasite inside other organisms like plants, humans etc.
- Based on their nutrition uptake, protists are classified into 3 types: Ingestion protists, Absorption protists, Photosynthetic protists.
Importance of protists in Ecology:
- They involve themselves as a major part in food chain
- Protists have the capability to consume/ ingest bacteria and other microbes. This way the microbe population will be under control.
- The photosynthetic protists play a vital role in ecology as they aid in reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- The major protists, Phytoplankton is the basic component of marine food chain.
- Protists aid in building coral reefs.
- Protists aid in recycling nutrients in the ecosystem.
Importance of protists in the Economy:
- By the process of photosynthesis, Protists release oxygen. This can be used for biofuel preparation.
- Few protists like Red algae etc. have medicinal value.
- Protists like seaweeds are consumed in many countries like Japan etc. They can also be used as a fertilizer as they are rich in potassium, nitrogen etc.
- Diatoms are used in making paper, cement, dental impressions etc.
- Agar agar is a red algae used in growth media in microbiology and as a thickening agent in food industries (Jams, jellies etc.)
Read more on Eukaryotic examples
Also Read:
- Endonuclease enzyme example
- Crustacean characteristics
- Is adenine an amino acid
- Red algae examples
- Are bacteria prokaryotic or eukaryotic
- Is exocytosis active
- Nucleotide structure insight and significance
- Intracellular enzyme examples
- Enzymes and substrates
- Nonvascular plants examples

Hello, I am Sugaprabha Prasath, a Postgraduate in the field of Microbiology. I am an active member of the Indian association of applied microbiology (IAAM). I have research experience in preclinical (Zebrafish), bacterial enzymology, and nanotechnology. I have published 2 research articles in an International journal and a few more are yet to be published, 2 sequences were submitted to NCBI-GENBANK. I am good at clearly explaining the concepts in biology at both basic and advanced levels. My area of specialization is biotechnology, microbiology, enzymology, molecular biology, and pharmacovigilance. Apart from academics, I love gardening and being with plants and animals.
My LinkedIn profile-