AlF3 is known as aluminum trifluoride with molecular weight of 83.9767 g/mol. It exists in AlF3.xH2O form and sometimes in anhydrous form as well. Let us discuss more facts.
AlF3 exist as hydrates and can be formed from ammonium hexafluoro aluminate by thermally decomposing it. Aluminum fluoride trihydrate occurs as rare mineral rosenbergite. It has a very high melting point at around 12900 C. The hydrates are found as colorless solids with heat capacity of 75.1 J/mol K.
AlF3 exists in rhombohedral crystal structure and used in the making of glasses when mixed together with ZrF. Let us study AlF3 lewis structure, valence electrons, angle, etc.
How to draw AlF3 lewis structure?
Lewis structure is a simple electronic representation of the skeletal structure of a molecule that involves valence electrons. Let us draw the required steps below.
Counting total valence electrons
The first step involves counting total number of valence electrons available. The ground state electronic configuration of Al and F are [Ne]3s23p1 and [He]2s22p5. The outermost electrons in 2s, 3s, 2p and 3p with a total of 3 + 7*3 = 24 electrons are used for constructing AlF3 lewis structure.
Choosing the central atom
Al is chosen as the central atom. The least electronegative atom is the central atom as it could share more electrons and form more bonds than a more electronegative atom. Al and F have electronegativity of 1.61 and 3.98. This makes F to hold its electrons more tightly for sharing or transferring.
Drawing bonds
First two electrons are put between each of the 3 Al-F sets. In this, 3 valence electrons from Al and 1 valence electrons from each of the 3 F atoms are shared to form 3 bonds. The octet is filled for 3 of the F atoms. Al has only 6 electrons in its surrounding thereby staying as electron deficient.
Assigning the lone pairs
The remaining 18 valence electrons are put on each F atom as lone pairs. Each F atom has 3 lone pairs of electrons. This gives 9 lone pairs of electrons shown as two dots on atoms.
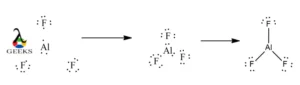
AlF3 lewis structure shape
Shape of a molecule is the structure adopted by the molecule accounting to the total bond pairs and it does not involve the lone pairs. Let us discuss in details.
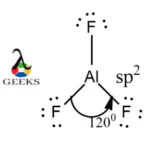
The shape of AlF3 lewis structure molecule is trigonal planar. AlF3 is planar with 3 bond pairs in triangular shape. The central atom, Al, is sp2 hybridized with no lone pair of electrons on it. Each F atom is singly bonded to the central atom at 1200 to avoid maximum repulsion among the bond pairs.
Shape of a molecule will not account for the lone pairs present in F atoms.
AlF3 lewis structure formal charge
Formal charge is the hypothetical imaginary charge acquired by every atoms in a molecule provided electrons sharing take place fairly. Let us discuss below.
Formal charge of AlF3 is zero which has been calculated using the formula ‘Formal charge = (Number of valence electrons in a free atom of the element) – (Number of unshared electrons on the atom) – (Number of bonds to the atom)’.
- Formal charge of Al = 3 – 0 – 3 = 0
- Formal charge of all the 3 F atoms = 7 – 6 – 1 = 0
- All the F atoms are equivalent.
- AlF3 is a neutral molecule.
AlF3 lewis structure angle
Bond angle of a molecule is the angle between a central atom and two adjacent atoms attached to the same central atom. Let us discuss below about AlF3 bond angle.
The bond angle of AlF3 is 1200. In this geometry of AlF3 lewis structure, there are 3 bond pairs which are most stable when they are at maximum distance from one another at an angle of 1200. The lone pairs do not repel each other that strongly at that angle as well.
AlF3 lewis structure octet rule
Octet rule is the general rule adopted by molecules that states every atom tries to accommodate at least 8 electrons in its octet to gain stability. Let us discuss more below.
AlF3 does not obey octet rule. Al is electron deficient with only 6 electrons in its octet. Each F atom obeys octet rule with 8 electrons in its octet. Since AlF3 is an electron deficient species with incomplete octet, it has a tendency to form dimer depending on the surrounding conditions.
AlF3 lewis structure lone pairs
Lone pair of electrons are the valence electrons that do not participate in any chemical bond formation. Let us calculate the total lone pairs of AlF3.
AlF3 has a total of 9 lone pairs of electrons. There are 3 equivalent F atoms and each F atom has 3 lone pairs of electrons. This counts a total of 9 lone pairs. They resides on F atoms and they do not undergo delocalization. The total lone pairs on 3 F atoms complete their octet along with bonding pairs.
AlF3 valence electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons present in a shell of an atom that can participate in a chemical bond formation. Let us discuss more in details.
AlF3 has a total of 24 valence electrons. The ground state electronic configuration of Al and F are [Ne]3s23p1 and [He]2s22p5. Each F atom has 7 valence electrons in its valence shell. This makes a total of 21 valence electrons from F and 3 valence electrons from Al atom.
Out of 24 valence electrons, only 3 bond pairs participate in chemical bond formation and remaining 18 stays as non-bonded electron pairs.
AlF3 hybridization
Hybridization of a molecule is the overlapping of atomic orbitals to obtain hybridized orbitals with lowered energy. Let us discuss in details.
AlF3 has sp2 hybridization. The paired electrons in 3s are excited to occupy two of the 2p subshells. Each of the 3 electrons in 3s, 3pz and 3py undergo hybridization with the atomic orbitals of fluorine and forms sp2 hybridized orbitals. The hybrid orbitals are lower in energy and acquires maximum stability.
Is AlF3 solid?
Solid is a state of matter where all the atoms or ions are tightly packed together with high density and melting point. Let us study more facts below.
AlF3 is a solid material. It takes up crystalline white coloured solid state as it is likely to form a dimer. This happens as AlF3 is not stable due to its electron deficiency. It doesn’t form complete octet making it viable to dimer formation but AlF3 is made stable in gaseous state under elevated condition.
Is AlF3 polar or nonpolar?
Nonpolar molecules are those that have zero dipole moment with symmetric electric charge distribution. Let us look into details if AlF3 is polar or not.
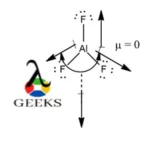
AlF3 is not a polar molecule. This is because the shape of AlF3 is trigonal planar with equivalent bonds. All the F atoms are equivalent and they produce symmetrical charge distribution resulting in no polar bonds formation. Hence, they are not polar molecule.
Why and How AlF3 is nonpolar?
AlF3 is nonpolar as all the three equivalent Al-F bonds produce dipole moment vectors in a direction that cancels each other. The two dipole moment vectors of two of the equivalent bonds produces a net dipole moment in a direction opposite to the dipole moment vector of the third equivalent Al-F bond.
Therefore, the symmetrical dipole moment vectors cancel each other with a magnitude equal to total zero.
Is AlF3 soluble in water?
Solubility of a compound depends on lattice energy and hydration energy. Let us discuss below.
AlF3 is only slightly soluble in water. This is because AlF3 is a non polar species. The dipole moment vectors in AlF3 cancel out each other. There is no charge separation due to symmetric electron cloud distribution. Hence, they cannot form dipoles to attract any polar water solvents.
Only the respective cations and anions are dissociated in water solution slightly due to its ionic nature. Its lattice energy is greater than hydration energy. It can not break its lattice motif to produce sufficient ions.
Is AlF3 acid or base?
An acid takes up electrons and a base donates electrons according to lewis acid base theory. Let us check if AlF3 is acid or base.
AlF3 is an acid. It is called a lewis acid due to its electron deficiency nature. It has incomplete octet that needs more electrons to fulfil the octet rule. This happens by taking up two electrons in its subshells, 3px and 3py. AlF3 has a tendency to pull electrons towards itself in the presence of any base.
Is AlF3 electrolyte?
An electrolyte is a substance that consists of cations and anions held together by interionic forces of attraction. Let us discuss in details.
AlF3 is an electrolyte as it is an ionic compound. The AlF3 molecules consists of Al3+ and F– as cations and anions. These ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction. The forces can be dipole dipole interactions. It can dissolve in a soluble solution to shows its electrolytic nature.
AlF3 is used particularly as an electrolyte for many electrolysis reaction to produce aluminum from crude ore.
Is AlF3 salt?
A salt is a chemical substance with the composition of cations and anions. Let us check if AlF3 is a salt or not.
AlF3 is a salt. Since it comprises of chemical composition of cations and anions due to its ionic nature, it is viewed as a molten salt. Al3+ and F– are cations and anions that are found in AlF3. Due to its more ionic nature and electron transferring process, it is regarded as a salt similar to an electrolyte.
Is AlF3 molecular compound?
A molecular compound is a molecule whose stoichiometric coefficients represents the total number of atoms present in that molecule.
AlF3 is not a molecular compound. This is because AlF3 is present in hydrated form which has x amounts of water molecules linked to the compound. Moreover, it exists in dimer form. Hence, its stoichiometric coefficients cannot be directly accounted for the total number of atoms present in it.
The x can vary from 1 to 3 or more. It is found more abundantly in trihydrated form with 3 water molecules attached to AlF3.
Conclusion
AlF3 is a nonpolar ionic molecule that is used as a molten salt or an electrolyte in electrolysis processes. It is present in dimer form in solid state.
Read more about following Lewis structure
Also Read:
- Ocn lewis structure
- Cno lewis structure
- Ch3nh2 lewis structure
- Sp2 lewis structure
- Al2s3 lewis structure
- Ccl2o lewis structure
- Carbonic acid lewis structure
- Hco2 lewis structure
- Sicl2br2 lewis structure
- Socl2 lewis structure

Hello…. I am Nandita Biswas. I have completed my master’s in Chemistry with a specialization in organic and physical chemistry. Also, I have done two projects in chemistry- One dealing with colorimetric estimation and determination of ions in solutions. Others in Solvatochromism study fluorophores and their uses in the field of chemistry alongside their stacking properties on emission. I am working as a Research Associate Trainee in Medicinal Department.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-https://www.linkedin.com/in/nandita-biswas-244b4b179