In this article, “addition reaction example”, different types of examples on addition reaction are discussed briefly.
The examples are-
- Halogenation Reaction
- Hydration Reaction
- Hydrogenation Reaction
- Polymerization Reaction
- Hydrohalogenation Reaction
- Addition of Hydrogen Cyanide to Carbonyl Compound
- Addition of Grignard Reagent to Carbonyl Compound
- Oxymercuration Reaction
- Hydroboration Oxidation Reaction
- Prins Reaction
- Epoxidation Reaction
- Ozonolysis Reaction
What is an Addition Reaction?
In Organic Chemistry, addition reaction is defined as one type of reaction in which two or more than two compounds are combined with each other to form a larger compound.
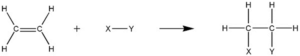
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Addition reaction can be classified into two types. They are-
- Electrophilic Addition Reaction
- Nucleophilic Addition Reaction
In electrophilic addition reaction, substrate is generally electron rich (having multiple bonds in substrate structure) species and it is attacked by an active electrophile. In nucleophilic addition reaction, electron deficient substrate is getting attacked by a nucleophile, an electron rich species.
Halogenation Reaction
Halogenation reaction is that type of chemical reaction in which any halogen molecule (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) is added with a compound eliminating hydrogen or any other atom.

Image Credit: Flickr.com
Halogenation reaction is classified into three types. They are-
- Halogenation reaction to a saturated hydrocarbon through formation of free radical
- Addition of halogen to an unsaturated species
- Halogenation to any aromatic compound (electrophilic substitution)
Hydration Reaction
Hydration reaction takes place when any chemical compound reacts with water molecule. Water is added any molecular species having multiple bond (alkene or alkyne, ketone, ketene) and compound having O-H group is obtained as product.
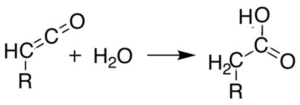
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
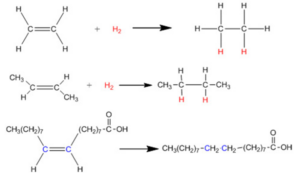
Hydrogenation Reaction
Hydrogenation is one type of reduction in which molecular hydrogen is added with any molecular species having unsaturation in presence of nickel palladium or platinum catalyst. Pressure and temperature play an important role in hydrogenation reaction.
To know more please check: Peptide Bond vs Disulfide Bond: Comparative Analysis and Facts
Polymerization Reaction
Polymerization is one type of addition reaction in which monomer molecules reacts with each other to form strong three dimensional macromolecular structure, known as polymer. Three steps are involved in polymerization reaction. They are-
- Addition of free radical known as initiation step.
- Propagation
- Termination

Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Hydrohalogenation Reaction
Hydrohalogenation is one type of addition reaction (electrophilic addition) between alkene or alkyne with hydrohalic acid (HCl, HBr, HF, HI). This addition reaction proceeds through Markovnikov rule. For an unsymmetrical alkene, halogen will be added to that side of double bond having lesser number of hydrogen atoms and hydrogen will be added to that side having greater number of hydrogen atoms.

Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Addition of Hydrogen Cyanide to Carbonyl Compound
Reaction between hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and carbonyl compound (aldehyde/ketone) in presence of acid is one type of nucleophilic addition reaction. Cyanide ion (CN-1) acts as nucleophile and attacks at the carbonyl carbon (electrophilic centre) and form an addition product, hydroxynitrile commonly known as cyanohydrins.

Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
To know more please follow: 4 Single Covalent Bond Examples : Detailed Insights And Facts
Addition of Carbonyl Compound to Grignard Reagent
Grignard reagent is one type of chemical species denoted by RMgX where R and X is alkyl or aryl group and halogen molecule respectively. It reacts with aldehyde and ketone to form different types of alcohol (primary, secondary, tertiary).
R– in Grignard reagent attacks the carbonyl centre and MgX adds with the O–. Addition proceeds with two pathways. One is 1,4 addition and another one is 1,2 addition.
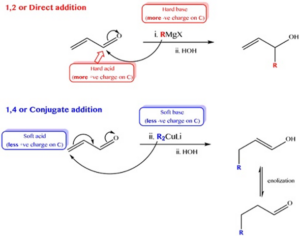
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Oxymercuration Reaction
Oxymercuration ix one type of electrophilic addition reaction by which an alkene is converted into a neutral alcohol. The reverse reaction of oxymercuration is demercuration that converts alcohols into carbonyls.
In oxymercuration, alkene reacts with Hg(OAc)2 (mercuric acetate) and acetoxymercury is obtained as the addition product and one hydroxy group (OH–) on the double bond. This reaction is also proceed using Markovnikov’s rule like the hydrohalogenation reaction.
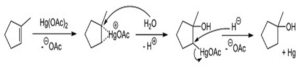
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Hydroboration-Oxidation Reaction
An alkene is converted into its corresponding alcohol through this hydration process like the oxymercuration process, but following different pathway. It is an example of anti Markovnikov rule followed by two step mechanism. In this addition reaction, electronegative hydroxyl part is attached with that side of C=C double bond having greater number of hydrogens.
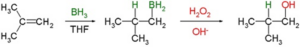
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
To know more please go through: N2 polar or nonpolar: Why, How, Characteristics, And Detailed Facts
Prins Reaction
Prins reaction is an electrophilic addition reaction between a carbonyl compound (aldehyde/ketone) with an alkene or alkyne and in presence of acid (used as catalyst) H+ ion is eliminated in the time of propagation of the reaction.
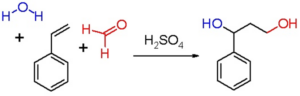
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Epoxidation Reaction
Carbon- carbon double bond is converted to epoxides or oxiranes through this epoxidation reaction. Different types of reagents like air oxidation, hypochlorous acid, peroxide can be used to form epoxides, a cyclic ether containing three membered ring.
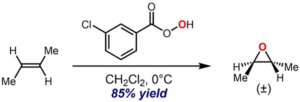
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Ozonolysis Reaction
The initial step of this ozonolysis is taken place through an electrophilic addition of ozone with the alkene and an intermediate named as molozonide is formed. The solution, used in this reaction is methanol or dichloromethane. Carbonyl compound is obtained as the final product of this ozonolysis reaction.
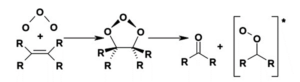
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
To know more please follow: SN1 mechanism: Detailed Insights And Facts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is meant by photo halogenation reaction?
Answer: When halogenation reaction is followed by using photochemical energy i.e sunlight is defined as photo halogenation reaction. It is also an addition reaction.
When addition reaction occurs?
Answer: Addition reaction occurs for combining any molecular species with an unsaturated compound (alkene or alkyne).
Also Read:
- Exothermic reaction
- Photochemical reaction
- How to balance redox reaction
- Light dependent reaction
- Is oxidation a redox reaction
- Redox reactions
- Exothermic reaction 3
- Synthesis reaction example
- Metathesis reaction
- Neutralization reaction

Hello,
I am Aditi Ray, a chemistry SME on this platform. I have completed graduation in Chemistry from the University of Calcutta and post graduation from Techno India University with a specialization in Inorganic Chemistry. I am very happy to be a part of the Lambdageeks family and I would like to explain the subject in a simplistic way.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-https://www.linkedin.com/in/aditi-ray-a7a946202