The polymers of carbohydrates refer to the long and complex chains of simple sugars that we normally consume in our diet.
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy in most living organisms. Breaking down glucose to make ATP is the chief source of energy. Glucose is the most common monomer of most carbohydrates, and some other monomers are converted to glucose by chemical changes.
The equation as mentioned above is the simplest chemical reaction to show how glucose is broken down in living organisms to produce the energy required for all bodily functions. This energy is also required to make sure the heart, lungs, brain, and other organs can work nonstop.
Carbohydrates :
Large molecules of sugar are simply called carbohydrates or carbs. Sugars do not always refer to the white sweet table sugar that we eat every day. Carbs are called sugars are mostly broken down to form glucose which is the simplest sugar or its isomers. Since glucose is sweet people usually associate carbs with anything that tastes sweet. Below are listed what are the polymers of carbohydrates that we commonly see and use.
Examples of the commonly used Polymers of Carbohydrates :
Natural complex carbohydrate polymers can be found in both plants and animals. They can be composed of the same type of monomer(homopolysaccharide) or the monomer itself may be complex( heteropolysaccharides). In the latter case, the monomers may be made up of 2 or more different monosaccharides and their derivatives.

These include starch, cellulose, inulin, glycogen xanthan and many more. Here we have discussed a few of them. However, there are a few more basic polymers or disaccharides (made of only 2 monomers). We will discuss them as well.
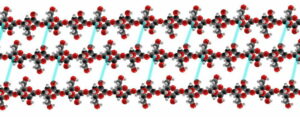
Image: Wikipedia
Examples of simple carbohydrate polymers:
- SUCROSE: Sucrose commonly referred to as table sugar or cane sugar is a disaccharide made of two glucose molecules. This is the most commercially used and available sugar and because of its small and simple structure, it is considered a major cause for weight gain. As a result, in recent years, consumers have begun to replace sugar with healthy alternatives such as stevia and honey. It requires an enzyme called sucrase present in most animals while plaque and cavity-causing bacteria can convert it into a dextran-based compound that they can use.
- LACTOSE: Due to the presence of the disaccharide lactose, milk is inherently sweet. Composed of two monomers -glucose and galactose and requires an enzyme called lactase to hydrolyze. This enzyme is absent in a large population of individuals leading to what is called lactose intolerance. People suffering from this condition are unable to digest any dairy or dairy-based products.
- MALTOSE: Maltose or malt sugar is another disaccharide formed of two glucose molecules. It is found in the majority of grains and pulses and often major components of commercial health drinks.
Examples of Larger polysaccharides:
- STARCH: The reason we wash potatoes and pasta is to get rid of a white powdery substance present in them. This starch is a polysaccharide found in plants that they use to store food by attaching glucose molecules via α(1→4) and α(1→6) glycosidic linkages. This reduces the molecular structure and makes it easier to store. Starch is made of 2 parts amylose (glucose molecules attached via α(1→4) glycosidic bonds) and amylopectin (glucose molecules attached via α(1→6) glycosidic bonds).
- CELLULOSE: Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide made up of hundreds of glucose molecules and is the major component of plant cell walls. They are joined by β(1→4) glycosidic linkages. Herbivores have gut bacteria that can break down cellulose, unlike carnivores and omnivores. Hence in our case, leafy green vegetables act as roughage for good intestinal health.
- GLYCOGEN: Another storage polysaccharide occurring in animals, fungi and bacteria, glycogen is the first source of saved glucose that is hydrolysed in case of unavailability of food. Reserved in the muscles and liver cells and human cells of humans glycogen is structurally glucose units linked together linearly by α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. Branches are connected to the chains from which they branch off by α(1→6) glycosidic bonds between the new branch’s initial glucose and the glucose on the stem chain below.
- CHITIN: Also a large polysaccharide occurring naturally. It forms a major structural component of exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans, cell walls of fungi and invertebrates and fish. Unlike the former polymers, chitin is made up of numerous N-acetylglucosamine(a substituted form of glucose).
- INULIN: Not as commonly heard of, inulin is a storage polysaccharide present in the majority of plants like banana, onions, wheat and garlic. But industrially it is extracted from chicory that is often added to coffee. It’s a fructose polysaccharide made up of many repeating disaccharide units. Inulin producing plants do not store their food reserves as starch anymore.
Dietary sources of carbohydrate polymers:
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy in our diet and most cases comprise the major portion of it too. Across the globe, people obtain their daily carbohydrate needs through different cereals, grains or preparations made of these pulses and grains- rice, bread, pasta or starchy vegetables like potatoes and yams.

Image: Wikipedia
But carbs can also be obtained from sweet and unhealthy foods like cakes, chips, soft drinks, chocolates and biscuits.
Good and bad carbohydrates:
The concept of bad and good and carbs rose into question after a majority of the global population was found to have obesity issues due to excessive consumption of fried and junk food items.
Carbohydrates are found naturally in fruits, vegetables, pulses, grains, and cereals called complex carbs. They are long-chain carbohydrate polymers that take a long time to be broken down by the body, allowing the monomers to be absorbed and assimilated optimally.This means it can keep us feeling full for longer.
On the other hand, those in cakes, sweets and fried food consist of carbs made of simple sugars. They are easily broken down and instead of being used up, they get reserved as fat due to its quick assimilation. This makes us feel full at the immediate moments but gives rise to consistent cravings after a short period. These are the carbs that are the actual cause of unhealthy weight gain and issues related t it.
Also Read:
- Do animal have enzymes
- Hydrolase enzyme examples
- Nucleotides in dna structure
- Trilobite characteristics
- Cytoskeleton structure
- Are bacteria herbivores
- Do plant cells have lysosomes
- Polygenic inheritance example
- Is fatty acid polar
- Millipedes examples

I am Trisha Dey, a postgraduate in Bioinformatics. I pursued my graduate degree in Biochemistry. I love reading .I also have a passion for learning new languages.
Let’s connect through linked in: