Direct current is a current which flows in One Direction without changing its polarity with time.
This article will discuss Direct Current Examples such as DC generator, DC motor, battery, electronic circuits, electroplating, solar power supply, high-voltage direct current transmission, etc.
Some Direct Current Examples:
- DC generator
- DC motor
- Battery
- Electronic Circuits
- Electroplating
- Solar Power Supply
- High-voltage Direct Current Transmission
- Telecommunication
DC generator
We know that generators can be either AC or DC type of generator, the design of DC generators is very much simple, parallel operations are more straightforward, and the system is mostly stable.
DC generator is a type of generator that converts the mechanical form of energy into DC electricity, this kind of generator generates DC power supply.
And that DC power generated from DC generator is used for testing purposes in different laboratories, used for charging batteries, exciting the alternators, and can be used as a portable generator that supplies small power, can be used for driving motors, etc.
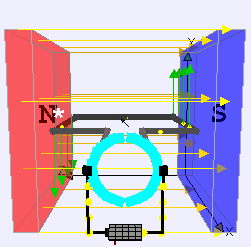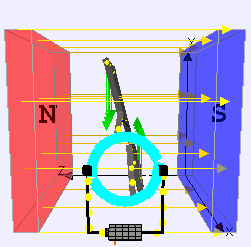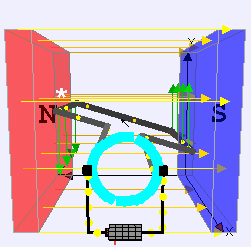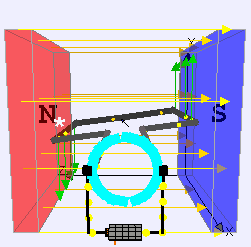
DC Motor
DC motor is an application of DC electric current which converts the direct electric current into mechanical energy creating a magnetic field.
The magnetic field generates the DC powers due to the attraction and repulsion in the magnetic field, and the rotor starts to rotate. DC Motors are used where high torque or accurate speed control over an extensive range is needed.
There are different types of DC Motors which have various applications, such as Elevators, conveyors, rolling mills, Trolleys, Cranes, heavy planers, steel mills, locomotives, excavators, drilling machines, etc.
Battery
Different types of batteries are available that can be recharged by using external power supply set as Nickel- metal hydride, Lithium-ion, Nickel-cadmium, lead-acid, lithium-ion polymer, and other alkaline rechargeable batteries.
While recharging any battery DC is required, DC power supply is used for recharging any battery, as with DC, the electron will flow in one constant direction back into the battery creating the potential difference needed when the battery is fully charged.
An Alternative Current (AC) cannot be used for recharging a battery because the positive half of the AC cycle will charge the battery, where the negative half of the AC cycle will discharge the battery. While recharging the battery, the specification of the battery must be taken into consideration and adjust the current to the proper levels.

Electronic Circuits
Electronic circuits are the concept of MOSFET, BJT, diodes, transistors, logic circuits, integrated circuits, etc.
As DC does not change its polarity with time, with constant and stable magnitude value, there is no power factor or the phase shift, so for proper biasing of the transistor, diode, or any other electronics element, constant DC is preferred.
As AC does not maintain any direction of current flow as it reverses direction periodically, the operation of any electronic components is not possible with an AC power supply.
For example, for proper operation of IC, any IC needs a ripple-free and pure DC power supply as input to generate the required output. Electronics are primarily digital devices that operate using either on or off or high or low signals. When AC is used as a power supply for electronic circuits as for the frequency of AC supply, every second generates lots of on or off signals, which is harmful to the electronic circuit operations.

The processor of the electronic circuit won’t be able to determine the difference in on or off signal in case of any e noise present in that AC signal. While using DC power supply to the electronic circuits, the biasing of any circuit element can be determined or controlled easily. DC is very stable, easy to manage, and accurate; using DC supply to electronic circuit makes it easy to handle or operate any electronics circuit.
Many electronics use an adaptor to convert AC to DC as generally power supply at home is AC power supply, so for proper operations, for example, flashlight charger, television adaptor, computer adaptor, electrical vehicle adaptor phone charger, etc.
Electroplating
For the electroplating procedure, a DC power supply is preferred over AC. Electroplating is a process in which a metal gets deposited over other metal plates in the presence of metal salt.
When DC supply is used in electroplating, one metal gets oxidized, and the ions from that metal get dissolved in the electrolytic solution and then get reduced at the other metal, which is known as electroplated metal while forming a cote on the electroplated metal of electroplating ions.
As for the principle of electroplating, each metal plate must be maintained at opposite polarity at constant during the continuous procedure, which is only possible by supplying a DC. If an AC supply is used, the polarity of both metal plates or electrodes will change continuously, and the ions will oscillate back and forth between electrodes or metal plates where electroplating is not possible. Even if pulsating DC can be used as the direction of the current is not changing with time.
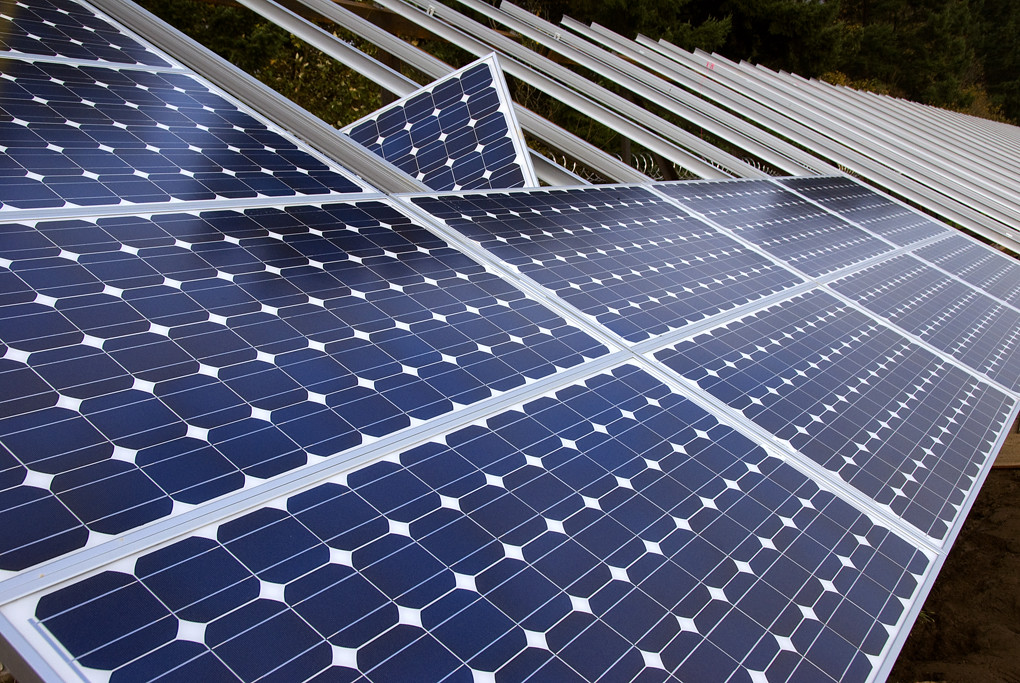
Solar Power Supply
Photovoltaic cell converts the light into a DC using photovoltaics effect, so the power generated from a solar panel is a DC power.
Photovoltaics system uses a solar panel that receives sunlight directly and then converts that light into electric power, while the electricity generated is DC, but can fluctuate with the intensity of sunlight, so before practical use, that DC voltage is required to convert into desired DC voltage or AC, by the use of filters or inverters.
Many photovoltaic power systems are connected to the grid for use on a larger scale, such as satellites, Lighthouse, batteries, etc. By using a grid-connected photovoltaic system, the capacity of any photovoltaic system can be maximized to 10 kilowatts for different requirements of the consumers.

High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission
HVAC stands for high voltage direct current, which is used for power transmission over enormous distances.
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) is preferred over High Voltage Alternating Current (HVAC) for transmitting power of more than 600 km. So transmitting power using HVDC through a long transmission line is way cheaper than that of HVAC For distance over break-even distance.

As for transmission lines, HVDC has only required two conductors where HVAC requires three or more than three conductors, HVDC has a uniform magnetic field with constant magnitude throughout the transmission, so HVDC has relatively lower losses than HVAC transmission. The power flow in HVAC lacks compatibility relative to HVDC, and intelligence between asynchronous systems for intelligent grids while using HVDC is relatively more straightforward than HVAC. In DC, there is no frequency or phase shifts.
Telecommunication
The telecommunication network uses a DC power supply, as negative 48 volt DC is found in the landline; the AC power supply is not in the used invoice line because the AC power supply will disturb and disrupt communication.
DC power supply is not restricted to any frequency vibration or landing power factor in telecom. DC power can be easily stored for backup in telecom buses. The battery is used, which provides a DC power supply without any power conversion loss.
I have graduated in Applied Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering. I’m a curious-minded person. I have an interest and expertise in subjects like Transducer, Industrial Instrumentation, Electronics, etc. I love to learn about scientific researches and inventions, and I believe that my knowledge in this field will contribute to my future endeavors.
