This article contains about SCl6 lewis structure, its hybridization, shape, and many more important facts in detail.
SCl6 is a hexacoordinated halogenated molecule of sulfur. But it has octahedral geometry. The bond angle of the SCl6 lewis structure is 900. All the bond angles and S-Cl bond lengths are equal. It is sp3d2 hybridized. Involving the d orbital in the hybridization causes more energizes the system.
Central S is surrounded by six Cl atoms at its six sites in an octahedral geometry. S has no lone pairs in this molecule all the valence electrons are involved in the bond formation, and only Cl atoms have the lone pairs.
Some detailed facts about SCl6
Actually, in reality, SCl6 does not exist but SF6 can. The reason behind this is F is a more electronegative atom and due to its electronegativity, the energy of the d orbital of S decreases and can be involved in the bond formation via sp3d2 hybridization.
But Cl is less electronegative than f and it cannot lower the energy of the d orbital of S and due to the large size of Cl, there is steric repulsion between six Cl atoms.
If we thought of SCl6 theoretically then we can find its bond angle, hybridization, and shape also. But it cannot be synthesized in the laboratory. So, we cannot get the physical date of the SCl6 lewis structure.
How to draw the SCl6 lewis structure?
Lewis structure is often known as the lewis dot structure, and it is very important to draw the lewis structure of any molecule to predict the basic property of this molecule. There are a few steps we should follow to draw the SCl6 lewis structure.

To draw the SCl6 lewis structure, we need the total number of valence electrons present in this molecule. We count the valence electrons for S and Cl and then adding together. Now it’s time for identifying the central atom based on less electronegativity. S is less electronegative than Cl so, so S is the central atom here and six Cl are present in six corners of the S atom.
The valence electrons involved in the SCl6 lewis structure are 6+(7*6) =48 electrons and the electrons required according to the lewis dot formula are 7*8 =56 electrons, so bonding electrons will be 56-48 = 8 electrons, and the required bond 8/2 = 4 bonds. But here we need 6 bonds so it is an example of the violation of the octet rule. The extra two electrons from two bonds are from the d orbital of S.
Now add all the atoms via single bonds and the number of single bonds is six. No need to add any multiple bonds.
SCl6 lewis structure shape
The total valence electrons in the SCL6 lewis structure involved in bond formation will be 6 for S and 6 Cl atoms each contributing 1 electron, so the total electrons participating in bond formation in the SCl6 lewis structure will be 6+ (6*1) = 12, and according to VSEPR theory if the valence electron count for a molecule is 12 then the structure of the molecule is octahedral.

In the SCl6 lewis structure, S is present at the central position whereas all six Cl atoms are present at the six corners of the octahedral moiety. For this arrangement all the S-Cl bond length is equal and all the bond angle is equal to 900. The molecule adopts a symmetrical shape.
SCl6 valence electrons
From the SCl6 lewis structure, we can calculate the number of valence electrons for the SCl6 molecule. Valence electrons are called those electrons which are present at the outermost orbitals of an atom, they can form a bond with another atom.
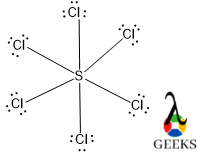
In the SCl6 lewis structure, two types of atoms are present S and Cl, so we need to find out the valence electrons for S and Cl atoms. S belongs to group 16th element from the O family, so it has the same electronic configuration as O so, it has also six electrons in its valence shell like O.
Again, Cl is from the halogen family, and all the halogens belong to group 17th which means it has seven electrons in its valence shell, so Cl has also seven electrons in its valence electrons. There are six Cl atoms are present in the SCl6 lewis structure. So, the total valence electrons for six Cl atoms are 7*6 = 42 electrons.
Now for the SCl6 lewis structure, the total number of valence electrons will be 6+ 42 =48 electrons.
SCl6 lewis structure formal charges
For any neutral molecule, it is important to find out its formal charge by accounting same electronegativity of every atom in this molecule. In the SCl6 lewis structure, find out the formal charge for S and Cl separately.
The formula we can use to calculate the formal charge, F.C. = Nv – Nl.p. -1/2 Nb.p.
Nv = number of electrons in the outermost orbital
Nl.p. = number of electrons in the lone pairs of subsequent atoms
Nl.p. = number of electrons are involved in the direct bond formation
In this molecule, all the six Cl atoms are equivalent so we need to calculate the formal charge for only one Cl atom and the central S atom.
The formal charge over the S atom is, 6-0-(12/2) = 0
The formal charge over the Cl atom is, 7-6-(2/2) = 0
So, the formal of either S or Cl is zero and this is also reflected in the result that the SCl6 molecule is neutral.
SCl6 lewis structure lone pairs
In the SCL6 lewis structure, only Cl atoms contain lone pairs in their valence shell which are not participating in the bond formation. S is a lack of lone pairs.

S is from the O family so it has six electrons in its valence shell and the SCl6 lewis structure, there are six bonds of S with six Cl atoms. So, S has no electron in its valence shell after bond formation and it is lack lone pairs.
Cl is a halogen and belongs to group 17th and for this reason, it has only seven electrons in its outer shell. Every Cl atoms make a sigma bond with S, so they share only one electron with S. except for that one electron the rest of the six electrons are present in the outermost orbital of Cl. Those six electrons appear as three pairs of lone pairs.
SCl6 lewis structure octet rule
According to the octet rule, every atom in a molecule tries to fulfill its valence shell by accepting a suitable number of electrons or via sharing electrons in bond formation and also gaining the same electronic configuration of their nearest noble gas. In the SCl6 lewis structure, S and Cl both try to complete the octet.
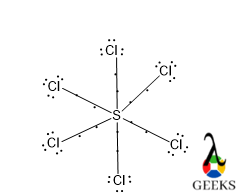
In the SCl6 lewis structure, Cl has three pairs of lone pairs and shares one electron with S in a single bond, to complete its octet via gaining eight electrons in its valence electrons.
But in the case of S, there are six electrons in its valence shell and all the electrons are shared with electrons of six Cl atoms. So, there are twelve electrons for S which is a violation of the octet rule and that’s another reason for the not exitance of SCl6.
SCl6 lewis structure bond angle
According to VSEPR (Valence Shell Electrons Pair Repulsion) theory, a molecule that has 12 electron counts generally adopts octahedral geometry and the bond angle in the octahedral is equally distributed and is 900 which is equivalent for all the atoms. All the bond angles will equal the SCl6 lewis structure.
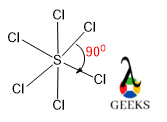
In the lewis structure, the Cl-S-Cl bond angle will be 900. All the equatorial and axial bond angles will be the same. It adopts octahedral geometry with central atom S and all six Cl atoms are the six corners with bond angle 900. According to bent’s rule, the bond angle can be calculated and it is 900. In the hybridization, we can discuss its detail.
SCl6 lewis structure resonance
SCl6 lewis structure does not exist in reality so it does not have any resonating structure from the delocalization of electrons clouds in different skeleton forms.
Actually, in the SCl6 lewis structure, there is an electronegativity difference between central S and surroundings Cl atoms is very lower, so the electrons delocalization process does not occur there. Again, there are no extra electron clouds that can be delocalized, so in the SCl6 lewis structure, there is no resonance.
SCl6 hybridization
In the SCl6 lewis structure, both S and Cl atoms undergo sp3d2 hybridization involving the d orbital to form a new hybrid orbital. There will be differences in the energy of different orbitals so they undergo hybridization to form equivalent hybrid orbitals.
There will be a specific formula to calculate the hybridization of a molecule and that is,
H = 0.5(V+M-C+A),
where H= hybridization value, V is the number of valence electrons in the central atom, M = monovalent atoms surrounded, C=no. of cation, A=no. of the anion.
In the SCl6 lewis structure, the number of valence electrons for S is 6 which are directly involved in the bond formation. There are 6 Cl atoms are present in the octahedral geometry.
So, the hybridization of the SCl6 molecule is, ½(6+6+0+0)= 6 (sp3d2)
| Structure | Hybridization value | State of hybridization of central atom | Bond angle |
| Linear | 2 | sp /sd / pd | 1800 |
| Planner trigonal | 3 | sp2 | 1200 |
| Tetrahedral | 4 | sd3/ sp3 | 109.50 |
| Trigonal bipyramidal | 5 | sp3d/dsp3 | 900 (axial), 1200(equatorial) |
| Octahedral | 6 | sp3d2/ d2sp3 | 900 |
| Pentagonal bipyramidal | 7 | sp3d3/d3sp3 | 900,720 |
From the above table we can say that if the number of orbitals contributed in hybridization is equal to six then the molecule will be sp3d2 hybridized.

From the box diagram of S in the SCl6 lewis structure, we can see that there is a total of six orbitals are involved in the hybridization. All the six orbitals of S undergo hybridization to form an sp3d2 hybrid orbital of equivalent energy.
S has a vacant d orbital in its electronic configuration. Due to the presence of six electronegative atoms Cl the energy of the d orbital somewhat decreases and accessible for hybridization.
S has six electrons in its ground state and is it also confirmed by its electronic configuration. In the ground state, two electrons are paired in s orbitals and 4 electrons are in the p orbital. When the system will be energized the electrons are no longer stable in their position and one electron from the s orbital and one electron from the p orbital are promoted to the vacant d orbital. Now S has six unpaired electrons (one in s, three in p, and two in d orbitals). These six unpaired electrons can easily form six single bonds with six Cl atoms undergoing mixing of the three orbitals.
Here one s, three p, and two d orbitals are get mixed to form a new hybrid orbital and the hybridization will be sp3d2.
For the consequences of sp3d2 hybridization, the SCl6 lewis structure is octahedral geometry and the bond angle will be 900.
According to the Bent’s rule, we can predict the bond angle via hybridization using the formula,
COSθ =s/s-1, where s is the % of s character in hybridization and θ is the bond angle.
In the SCl6 lewis structure, the hybridization is sp3d2, so the % of s character is 1/6th.
So, applying the bent’s rule we get θ = 900.
Again, from VSEPR theory if the molecule is AX6 type of molecule having no lone pairs over central atom always adopt octahedral geometry, and bond angle will be 900.
So, we can comment that if a molecule is sp3d2 hybridized then the geometry will be octahedral and the bond angle will be 900 or vice versa.
So, from the hybridization, we can predict the geometry as well as the bond angle of the molecule.
SF6 is exist but SCl6 is not. Why?
In the SF6 there are six F atoms around the S atom. To form a hexacoordinated molecule the central atom should undergo sp3d2 hybridization. S has an energetically unaccessible d orbital. But in the presence of the six most electronegative F atoms the energy of the d orbital decreases and it can undergo sp3d2 hybridization and form a stable molecule.
But when F atoms are replaced with Cl atoms, they are less electronegative and the energy of d orbitals remains high so it cannot form proper hybridization.
Again, the size of F is very small so six f can adjust in octahedral geometry but the size of Cl is large and there will be steric repulsion in the octahedral moiety.
Conclusion
SCl6 lewis structure cannot be synthesized in the laboratory or it cannot exist in reality due to the above reasons. So, all the data is given in this article based on theory. Hexacoordinated S compound is not going typical type of hybridization rather it can be described as the 3C-4e model.
Also Read:
- Cli3 lewis structure
- Cao lewis structure
- O2 lewis structure
- Ca3n2 lewis structure
- Bao lewis structure
- Agno3 lewis structure
- So3 lewis structure
- Hco3 lewis structure
- Scl4 lewis structure
- Brf2 lewis structure 2

Hi……I am Biswarup Chandra Dey, I have completed my Master’s in Chemistry from the Central University of Punjab. My area of specialization is Inorganic Chemistry. Chemistry is not all about reading line by line and memorizing, it is a concept to understand in an easy way and here I am sharing with you the concept about chemistry which I learn because knowledge is worth to share it.