Saprophytic fungi rely on dead or decaying plants for their growth and reproduction. As a primary decomposer, a significant role in our ecosystem. Some are useful, while some can be harmful in our daily lives. Now we are going to know about them in this article.
Saprophyte fungi are unicellular and filamentous microorganisms with a lack of chlorophyll organelles. They cannot make food through photosynthesis, depending upon decaying organic matters for nutrients and water. These microbes are present in our food, medicines, and diseases.
Saprophytes came from two Greek words, “sapros”, which means putrid, and “phuton“, which means plants. It refers to those microorganisms that eat dead plants, especially fungi; they belong to this group, and they can break down complex organic matter like lignin, cellulose, and other organic plants matters. Some beneficial saprophytic fungi are mushrooms, yeast, Penicillium and mucor etc.
Some examples of saprophytic fungi
Many saprophytic fungi are utilized in many organic reactions, and colonies can be seen quickly by our naked eyes. Some saprophytic fungi are:
Mold
Mold is filamentous fungi which grow in a threat like structure called hyphae. They are responsible for the biodegradation of useless food or other organic material. They can also help in producing antibiotics, food and dairy products, alcohols, enzymes, medicines and pigmentation for the research purpose. Mucor and Penicillium are commonly known as mould fungi.

Yeast
Yeast has been used for centuries, but people didn’t acknowledge it as fungi. They are dimorphic fungi that can change their physical form depending on different temperatures and conditions. The process of fermentation, where carbon dioxide is released from carbohydrates that are used in the production of alcohol and backing cake. Examples: Saccharomyces, Taphrinomycotina.

Mushrooms
mushrooms are umbrella-like structures. Some, like button mushrooms (Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes), are tasty and nutritious, and some, like fly agaric (Amanita mucaria), are toxic. They are present in different colours and shapes. Raw brown mushroom is rich in protein, vitamin D and other minerals.

Rhizopus
Rhizopus is a well-known species of saprophytic fungi; found in the roots of plants, and some lived as parasites on humans. This species causes major diseases, mucormycosis. Some species are used in many food production industries for the fermentation process.
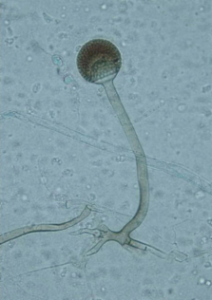
Penicillin
Penicillin is a revolutionary saprophytic fungus in medicine which usually found on moulds. It’s effective on many bacterial infections. Therefore, it is known as Antibiotics. Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming discovered antibiotics in 1928; later, he got the noble prize for his discovery. It saved many lives during World War II and is still widely used in pharma industries.
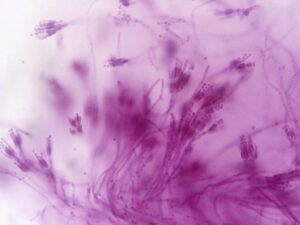
Mycelium
Mycelium is saprophytic fungi, primarily present in the breakdown of the decomposed organic compound. It is helpful to decrease pollution by degrading the complex carbon matters or chemicals such as Petroleum products and some pesticides. Mycelial mats are used in the filtration of soil and water. This species is also helpful in agriculture, woody plants and the production of unique kinds of leather.

Malassezia
Malassezia is saprophytic yeast; pityrosporum ovale and p. orbiculare live as parasites on human skin problem like dandruff. It causes pigmentations and allergies. These fungi depend on lipids that are present in the human body. It is hard to grow them in the laboratory for research purposes.

Frequently Asked Questions:
Are all fungi saprophytic in nature?
Most fungus species are saprophytes in nature and can decompose complex organic matter and convert it into the soil with rich nutrients. Saprophytic fungi release enzymes on decaying plants and transform them into inorganic molecules that can decompose by other microbes.
Where can we find saprophytic fungi? Their habitats.
Saprophytic fungi are present in the air we breathe, can grow in 5-35°C temperatures, and are found on dead plant matter such as wood, leaves and fruits. Their natural habitats are in terrestrial environments such as forests, grassland, and shady places. And for agriculture purposes, mushrooms yield in woody mulches and composite soil in the lawns.
How do saprophytic fungi increase nutritious value in soil?
Saprophytic fungi are the primary and active decomposers present in the soil. They are essential to our ecosystem, balancing nutrients through carbon, nitrogen and other cycles. Fungi work as decomposers to transform the energy from dead plants and animals or their unwanted organic matter and dissolve it in soil. Plants grow in the soil, then animals eat plants, and after their deaths, they decompose in the ground again; therefore, fungi play a crucial part in the ecosystem.
Is saprophytic fungus causing disease?
Some saprophytic fungi are beneficial like antibiotics, but on the other hand, some species can cause diseases, refers as mycosis. Conditions like Athlete’s foot, Ringworm, Jock itch, yeast infections, etc., can be caused by fungal infections that usually are harmful to our skin which can lead to problems like rashes or bumps.
What is a saprophytic fungal infection? And how to treat them?
Some harmful saprophyte fungi can invade the human body, and it might get challenging to kill them, as they survive even after the treatment. Many antifungal drugs are available on the market with a doctor’s consult; also, essential hygiene habits can help prevent fungal infections.
Example of some eatable saprophytic fungi and their nutritious value for a human being?
Agaricus, commonly known as mushrooms, consists of some edible species of mushrooms with over 300 varieties. It contains multiple nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals and water. They are rich in low-calorie source of fibre, protein, and antioxidant which helps in diseases like Alzheimer’s, heart problems, cancer and diabetes. Some yeast and moulds are helpful in fermentation for food production.
What will happen without saprophytic fungi?
The world without fungi will not be possible cause there are much plant matter piled up on the ground and no space left for plantation or any other vegetation. The professor of Cardiff University of bioscience, Lynne Boddy, said, “(fungi) are the garbage disposal agents of the natural world.”
Also Read:
- Are bacteria biotic or abiotic
- Pome fruit examples
- Eyelid anatomy
- Terrestrial biome examples
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum function 2
- Chest anatomy
- Do cytoplasm have mitochondria
- Example of prokaryotic cell
- Is protein receptor
- Chromosome structure

Hello, my name is Kriti Singh from Agra. I have completed a post-graduation degree in Biotechnology and a B.Ed. degree. Biology is my favorite subject since childhood and I never felt tired or bored with this particular subject. As I have an inquisitive personality, always been curious and fascinated to know more about life and nature.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn: