Nucleotides in RNA structure are the basic structural and functional monomers, better to say building blocks of nucleic acid. Let’s compare all nucleiotides in RNA structure and discuss each aspects regarding them.
RNA or Ribonucleic acid is a single polynucleotide chain made up of nucleiotides. There are four different nucleotides found in RNA structure, such as –
- Adenosine Monophosphate Or AMP
- Guanosine Monophosphate or GMP
- Cytidine Monophosphate or CMP
- Uridine Monophosphate or UMP
Adenosine Monophosphate or AMP
Adenosine Monophosphate is one of the four nucleobases, made up of a ribose pentose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase Adenine. The adenine of AMP is a Purine base and forms hydrogenous double bonds with Uracil of UM which increases stability.
The adenine of AMP makes the poly A tail of RNA means the RNA contains multiple Adenine residue at the end. The AMP can be converted into ADP or ATP as the energy source of a cell. As Cyclic AMP, it also controls hormone regulation in cells.
Guanosine Monophosphate or GMP
Guanosine monophosphate is one of the four nucleotides in RNA structure, typically comprising a five- carbon ribose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase Guanine in it. Guanine is a purine base and makes hydrogenous triple bonds with Cytosine of CMP molecules.
It is an important monomer in RNA structure. In the 5-prime end of RNA modified GMP or Guanine sequence makes the 5-prime cap which is important to protect the nucleic acid and helps RNA processing and translation process. The GMP also plays a significant role in signal transduction and hormone regulation process.
Cytidine Monophosphate or CMP
Cytidine Monophosphate is also a basic monomeric unit of RNA. It has three components, such as a ribose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase cytosine. Cytosine is a pyrimidine base , pairs with the Guanine of GMP by forming hydrogenous triple bonds. In signal transduction the role of CMP is immense.
Uridine Monophosphate or UMP
Uridine Monophosphate is a monomer nucleotide in RNA structure. It is a Nucleotide which is only found in RNA, absent in DNA structure. It is composed of three subunits, such as a ribose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase Uracil. The Uracil is a derivative of Thymine, which makes hydrogenous double bonds with adenine. UMP also plays a crucial role in glycogen synthesis.
These four nucleotides in RNA structure bind with each other, decoding specific sequences making the whole nucleic acid.As there are different kinds of RNA molecules present to perform different cellular activities, the nucleotides are arranged in them according to their type and support their specific functions.

Nucleotides in RNA Structure from Wikimedia Commons
Comparative analysis between all Nucleotides in RNA structure
All the four nucleotides in RNA structure have some similarities and differences between them. Let’s compare all of the nucleotides in RNA structure regarding every possible aspects between them.
| Characteristics | Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP) | Guanosine Monophosphate (GMP) | Cytidine Monophosphate (CMP) | Uridine Monophosphate (UMP) |
| Definition | Adenosine monophosphate is a nucleotide made up of an Adenosine nucleoside and one phosphate group. It is a structural unit of RNA, also used as the energy currency of a cell. | Guanosine Monophosphate is a nucleotide made up of a Guanosine nucleoside and a phosphate group. It is a structural unit of RNA which performs a crucial role in RNA capping. | Cytidine Monophosphate is a nucleotide having a Cytidine Nucleoside and a phosphate group in its structure. It serves as one of the building blocks of RNA and stimulates signal transduction procedures. | Uridine Monophosphate is a Nucleotide which is only found in RNA structure, typically composed of a Uridine nucleoside and a phosphate group. UMP is mostly used in the RNA synthesis process. |
| Base type | Purine | Purine | Pyrimidine | Pyrimidine |
| Complementary base | Uracil | Cytosine | Guanine | Adenine |
| Structure | It has an Adenine base , a ribose sugar and one phosphate group in its structure. | It has a Guanine base, a ribose sugar and one phosphate group in its structure. | It has a Cytidine base, a ribose pentose sugar and one phosphate group in its structure. | It contains a Uracil base, a ribose pentose sugar and one phosphate unit in it . |
| Derivatives | ATP | GTP | CTP | UTP |
| Formula | C10H14N5O7P | C10H14N5O8P | C9H14N3O8P | C9H13N2O9P |
| Mass | 347.22 g/mol | 363.223 g·mol-1 | 323.198 g·mol-1 | 324.182 g·mol-1 |
| Functions | It acts as a structural unit of RNA, decodes genetic information by making codons, and also makes a poly A tail of RNA. | Used as a monomeric unit in RNA construction, serving as second messenger in cellular activities also helps in RNA capping. | Used as monomer Nucleotides in RNA structure, stimulates signal transduction pathways of cells. | Used as an important monomer in RNA structure. By forming base pairs bring stability and enhances efficiency of RNA molecules. |
| Number of making hydrogen bonds | Double bonds | Triple bonds | Double bonds | Triple bonds |
| Synonyms | Adenylic acid, Adenosine 5′-monophosphate, 5′-Adenylic acid, etc. | 5′-Guanidylic acid,5′-Guanylic acid, Guanosine 5′-monophosphate, etc. | Cytidylic acid, Cytidine 5′-monophosphate,Cytidylate, Cytidine 5′-phosphate; | Uridylic acid; Uridine 5′-monophosphate; 5′-Uridylic acid; Uridine 5′-phosphate; Uridine phosphate; 5′-UMP; Uridine 5′-phosphoric acid, etc. |
After the comparison between all Nucleotides in RNA structure, we found some similarities and differences between them. The analytical information is given below-
Definition
- AMP: AMP is one of the Structural monomeric units of RNA. It is an ester of Adenosine nucleoside and phosphoric acid, mostly serving as energy currency of cells.
- GMP: GMP is one of the Structural monomeric units of RNA. It is an ester of Guanosine nucleoside and phosphoric acid, mostly used as the second messenger of cells.
- CMP: CMP is one of the Structural monomeric units of RNA. It is an ester of Cytidine nucleoside and phosphoric acid, which helps in signal transduction.
- UMP: UMP is one of the Structural monomeric units of RNA. UMP is only found in RNA structure.
Base type
- AMP: It is a purine base.
- GMP: It is a purine base.
- CMP: It is a pyrimidine base.
- UMP: It is a pyrimidine base.
Complementary base
- AMP: It makes a complementary base pair with uracil.
- GMP: It makes a complementary base pair with Cytosine.
- CMP : It makes a complementary base pair with Guanine.
- UMP: It makes a complementary base pair with Adenine.
Structure
- AMP: It is made up of three units, such as a five-carbon ribose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase Adenine.
- GMP: It is made up of three units, such as a five-carbon ribose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase Guanine.
- CMP : It is made up of three units, such as a five-carbon ribose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase Cytosine.
- UMP: It is made up of three units, such as a five-carbon ribose sugar, a phosphate group and nucleobase Uracil.
Derivatives
- AMP: Adenosine monophosphate is a derivative of Adenosine triphosphate.
- GMP: Guanosine monophosphate is a derivative of Guanosine triphosphate.
- CMP : Cytidine monophosphate is a derivative of Cytidine triphosphate.
- UMP: Uridine monophosphate is a derivative of Uridine triphosphate.
Formula
- AMP: The chemical formula of AMP is C10H14N5O7P.
- GMP: The chemical formula of GMP is C10H14N5O8P.
- CMP: The chemical formula of CMP is C9H14N3O8P.
- UMP: The chemical formula of UMP is C9H13N2O9P.
Mass
- AMP: The molar mass or AMP is 347.22 g/mol.
- GMP: The molar mass or GMP is 363.223 g·mol-1.
- CMP:The molar mass or CMP is 323.198 g·mol-1.
- UMP: The molar mass or UMP is 324.182 g·mol-1.
Functions
- AMP: AMP is one of the four monomeric units of RNA. Along with other Nucleotides by making Codons it encodes genetic informations, stimulates protein synthesis. It makes the poly A tail of RNA to prevent shortening of RNA. It is also an energy source of cells.
- GMP: GMP is one of the four monomeric units of RNA. By forming codons they carry genetic information. By RNA capping it prevents breakage.
- CMP : CMP is one of the four nucleotides used in the RNA synthesis process. As codons carry genetic information, it stimulates signal transduction.
- UMP: UMP is a Nucleotide used in the RNA synthesis process. Carry genetic information in it. Helps in the translation process.
Number of making hydrogen bonds
- AMP: AMP makes hydrogenous double bonds with Uracil.
- GMP: It makes hydrogenous triple bonds with Cytosine.
- CMP: CMP forms hydrogen triple bonds with Guanine of GMP.
- UMP: It makes hydrogenous double bonds with adenine.
Synonyms
- AMP: Some well known synonyms of Adenosine monophosphate are Adenylic acid, Adenosine 5′-monophosphate, 5′-Adenylic acid, etc.
- GMP: Some commonly known synonyms of Guanosine monophosphate are 5′-Guanidylic acid, 5′-Guanylic acid, Guanosine 5′-monophosphate, etc.
- CMP: Some common synonyms of Cytidine Monophosphate are Cytidylic acid, Cytidine 5′-monophosphate,Cytidylate, Cytidine 5′-phosphate, etc.
- UMP: UMP is also known as Uridylic acid; Uridine 5′-monophosphate; 5′-Uridylic acid; Uridine 5′-phosphate; Uridine phosphate; 5′-UMP; Uridine 5′-phosphoric acid, etc.
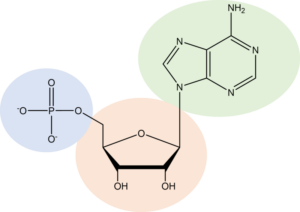
Basic nucleotide structure from Wikimedia Commons
Where are nucleotides found in RNA?
The nucleotides are the building blocks which associate in a specific manner, constructing the whole polynucleotide RNA strand.
The phosphate of one nucleotide binds with other sugar, making the sugar phosphate backbone of nucleic acid. Though the RNA is a single stranded structure, some complementary bases eventually come in close contact and pairs construct a hairpin loop. These structural properties including base pairing, brings stability and enhances efficiency of RNA molecules.
To know more about nucleotides read our article on Nucleotide Examples:Detailed Insights
What nucleotides are used in RNA?
There are four nucleotides used in RNA, such as Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP), Guanosine Monophosphate (GMP), Cytidine Monophosphate (CMP) and Uridine monophosphate (UMP).
What nucleotide is found in RNA and not DNA?
DNA and RNA both nucleic acids are made up of predominantly the same nucleotide units, except one.
The nucleotide Uridine monophosphate or UMP is present in RNA, not in DNA. Because the nucleobase Uracil is only present in RNA, in DNA it is present in its methylated version that is called Thymine. The nucleotide made up of Thymine is called Thymidine Monophosphate.
To know more read our article on Adenine vs Thymine: Comparative Analysis
What is the Role of Nucleotides in Protein Synthesis?
Nucleotides play a crucial role in the protein synthesis process. During translation, ribosomes read mRNA molecules, composed of nucleotides, to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Nucleotides also serve as the building blocks of DNA and RNA, storing and transmitting genetic information necessary for proper protein synthesis.
How are the nucleotides arranged in RNA?
The nucleotides in RNA structure are arranged in a specific manner.
Nucleotides which decodes genetic information for protein synthesis by forming codons, are present in the middle of the strand. At the 5′ end, Guanines are arranged, making the 5′ cap that gives protection. At the 3′ end or tail position several Adenosine Monophosphates are attached, making the poly A tail of RNA to protect shortening.
Composition of nucleotides in RNA?
Nucleotides are generally an ester between nucleosides and phosphoric acids.
Every nucleotide has a five carbon ribose sugar moiety, a phosphate group and one of the four nucleobases in its structure. The four nucleobases are Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C) and Uracil (U).
The Adenine and Guanine are purine bases. Cytosine and Uracil are pyrimidine bases.
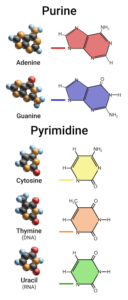
Purine and pyrimidine Nucleotides in RNA structure from Wikimedia Commons
As a whole we can say the role of nucleotides in RNA structure are immense. After comparative analysis between all of them we state some similarities and differences regarding them. Hope this article regarding Nucleotides in RNA structure will be helpful to you.
Also Read:
- Indigenous species examples
- Are algae multicellular
- Nucleic acid examples
- Are proteins inherited
- Osmosis example
- Is lipase an enzyme
- Does nucleus have double membrane
- Endoplasmic reticulum in cytoplasm
- Crab examples
- Barnacle characteristics

Hello, I am Piyali Das, pursuing my Post Graduation in Zoology from Calcutta University. I am very passionate on Academic Article writing. My aim is to explain complex things in simple way through my writings for the readers.