Nuclear energy has become an integral part of our modern world, providing a reliable and efficient source of power. At the heart of nuclear power generation are nuclear fuels, which play a crucial role in the production of electricity. These fuels undergo a process called nuclear fission, where the nucleus of an atom is split, releasing a tremendous amount of energy. The most commonly used nuclear fuel is uranium-235, which is found in nature and can be mined. Other examples of nuclear fuels include plutonium-239, thorium-232, and uranium-233. Each of these fuels has its own unique properties and advantages, making them suitable for different types of nuclear reactors. In this article, we will explore these nuclear fuels in more detail, highlighting their characteristics and applications. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of nuclear fuels and discover how they power our world.
Key Takeaways
- Nuclear fuels are materials that can sustain a nuclear chain reaction and release a significant amount of energy.
- The most commonly used nuclear fuel is uranium-235, which undergoes fission reactions in nuclear reactors.
- Other examples of nuclear fuels include plutonium-239, thorium-232, and uranium-233.
- Nuclear fuels provide a reliable and efficient source of energy, but their use raises concerns about safety, waste disposal, and the potential for nuclear weapons proliferation.
Main Nuclear Fuels
Uranium-based Fuels

Uranium-based fuels are widely used in nuclear reactors due to their high probability of fission and energy release. Let’s take a closer look at their description, properties, and use in various reactor types.
Uranium-based fuels, such as Uranium-235 (U-235) and Uranium-238 (U-238), are the most common nuclear fuels used in power generation. These fuels are composed of uranium isotopes, which undergo fission when bombarded with neutrons.
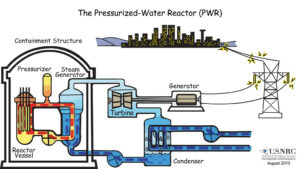
Uranium-235 is the most widely used nuclear fuel due to its higher probability of fission compared to Uranium-238. It is the primary fuel in light water reactors (LWRs) and pressurized water reactors (PWRs), which are commonly used for power generation.
In these reactors, the uranium fuel is enriched to increase the concentration of Uranium-235. The enriched uranium is then formed into cylindrical rods, which are bundled together to form fuel assemblies. The fuel assemblies are placed in the reactor core, where a chain reaction occurs, releasing a tremendous amount of energy through fission.
Apart from power generation, uranium-based fuels have also been used in nuclear armaments. The highly enriched uranium is used in the production of nuclear weapons due to its ability to sustain a self-sustaining chain reaction.
Other Types of Nuclear Fuels
In addition to uranium-based fuels, there are several other types of nuclear fuels that offer unique advantages and applications. Let’s explore some of these fuels and their uses in different reactor types.
-
Plutonium-Uranium Combination: This fuel combines plutonium with natural or depleted uranium. It serves as an alternative to low enriched uranium fuel and is used in light water reactors (LWRs) for power generation. It offers advantages over oxide fuels, such as better thermal conductivity and higher resistance to oxidation.
-
Uranium-Chromium Alloy and Uranium-Iron Alloy: These alloys are commonly used in small research reactors like Advanced High-Temperature Reactors (AHRs). They have high resistance to oxidation, corrosion, and high temperatures, making them ideal for research and isotope production.
-
Tri-Structural Isotropic Particle Fuel (TRISO): TRISO fuel consists of a TRISO particle surrounded by a burnable poison layer. It is used in gas-cooled fast reactors and offers enhanced safety and performance under accident conditions.
-
Mixed Oxide Fuel (MOX): MOX fuel is a mixture of uranium, plutonium, fission products, and transplutonium metals. It is used in both power reactors and research reactors. MOX fuel helps in the reduction of radiation hazard through radioactive decay.
-
Sodium-Bonded Fuel: This fuel consists of sodium between the cladding and the pellet. It helps in temperature reduction and is used in sodium-cooled liquid metal fast reactors (SFRs).
These are just a few examples of the different types of nuclear fuels and their applications. Each fuel has its own unique properties and advantages, making them suitable for specific reactor types and purposes. The continuous research and development in nuclear fuel technology aim to improve fuel performance, enhance safety, and maximize energy generation in nuclear power plants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nuclear fuels play a crucial role in the generation of nuclear power. They are used to produce heat through nuclear fission, which is then converted into electricity. The most commonly used nuclear fuel is uranium-235, which is found in nature and can be enriched to increase its concentration. Other examples of nuclear fuels include plutonium-239, thorium-232, and even certain isotopes of hydrogen. Each of these fuels has its own advantages and disadvantages, and their use depends on various factors such as availability, efficiency, and safety. Despite the controversies surrounding nuclear power, it remains an important source of clean and reliable energy, and the development of advanced nuclear fuels continues to be an area of active research and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do nuclear fuels work?
Nuclear fuels work by undergoing a process called nuclear fission, where the nucleus of an atom is split into two smaller nuclei. This releases a large amount of energy in the form of heat.
What is the definition of nuclear fuels?
Nuclear fuels are substances that can undergo nuclear fission and release energy. They are typically used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
How is nuclear energy used?
Nuclear energy is used to generate electricity in nuclear power plants. It is also used in some countries for other purposes such as desalination of water or powering submarines.
What are the main nuclear fuels?
The main nuclear fuels used in nuclear power plants are uranium-235 and plutonium-239. These fuels are capable of sustaining a nuclear chain reaction.
How is nuclear fuel used to generate electricity?
Nuclear fuel, such as uranium-235, is used in a nuclear reactor. The fuel rods containing the nuclear fuel are placed in the reactor, where the fission process occurs, generating heat. This heat is then used to produce steam, which drives a turbine to generate electricity.
Can you provide a sentence example of nuclear fuel?
Sure! “Uranium-235 is a commonly used nuclear fuel in nuclear power plants due to its ability to sustain a chain reaction.”
What are two examples of nuclear fuels?
Two examples of nuclear fuels are uranium-235 and plutonium-239. These fuels are commonly used in nuclear reactors.
Can you provide a list of nuclear fuels?
Certainly! Some examples of nuclear fuels include uranium-235, plutonium-239, thorium-232, and neptunium-237.
What are some examples of nuclear fuel?
Examples of nuclear fuels include uranium-235, plutonium-239, and thorium-232. These fuels are used in nuclear reactors to generate energy.
What are nuclear fuels used for?
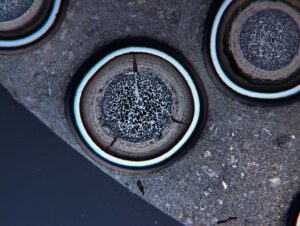

Nuclear fuels are primarily used for generating electricity in nuclear power plants. They are also used in some research reactors and in the production of nuclear weapons.
Also Read:
- Nuclear fusion in stars
- Is nuclear fusion renewable
- Nuclear fission examples
- Is nuclear fusion possible
- Nuclear fusion process
- Nuclear reactions examples
- Nuclear fusion examples
- When does nuclear fusion begin
- Nuclear fusion in the sun
- Nuclear fusion waste
Hello, I am Deeksha Dinesh, currently pursuing post-graduation in Physics with a specialization in the field of Astrophysics. I like to deliver concepts in a simpler way for the readers.