In this article, we are going to see what are the examples of ionic covalent bond types, facts and detailed insights.
- Sodium hydroxide NaOH
- Sodium nitrate NaNO3
- Ammonium chloride NH4Cl
- Calcium carbonate CaCO3
- Potassium cyanide KCN
- Potassium nitrite KNO2
- Potassium sulphate K2SO4
- Barium cyanide Ba(CN)2
Some compounds contain both ionic bonds and covalent bonds in their molecular structure. They are also termed polyatomic compounds. To attain stabilization some molecules form more than one type of bonding. Here we are going to see some molecules which are ionic covalent bond types examples .
Ionic Bond
An Ionic bond is defined as two different ions, cations and anions attract each other and form a bond. Electrovalent bond is another term used for ionic bonding. Ionic compounds show this type of bonding in their atomic structure. This type of bond is formed in Metal and Non-metals.
Characteristics
- An electrovalent bond is another term attributed to the ionic bond.
- A strong electrostatic force of attraction is used to combine anions and cations together.
- They have a high melting point.
- They are a good conductor of electricity in a molten state or dissolved in solvents, but in the solid state, they are a bad conductor of electricity.
- They can be dissolved in polar solvents and did not dissolve in non-polar solvents.
Read More On : 10 Ionic Bond Examples: Explanation And Detailed Facts
Covalent bond
The covalent bond is determined as two atoms sharing their equal valence electrons to gain a stable electronic configuration. Covalent compounds contain this kind of bonding in their molecular structures.
Characteristics
- The bond is formed between the same or different atoms.
- It is further classified based on the electronegativity of atoms as a polar and non-polar covalent bond.
- They have a property of low melting and boiling point.
- They are unable to conduct electricity.
- They are can be dissolved in solvents that are non-polar and do not dissolve in water which is a polar solvent.
Read More On : 4 Single Covalent Bond Examples : Detailed Insights And Facts
Ionic Covalent bond types Examples
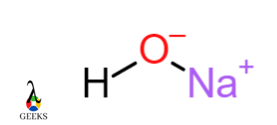
Sodium hydroxide NaOH
Sodium hydroxide, Oxygen atom and Hydrogen atom show the formation of a covalent bond by sharing electrons. Hydroxide ion has a negative charge and sodium ion has a positive charge. These two ions OH– and Na+ attract each other forms an ionic bond.
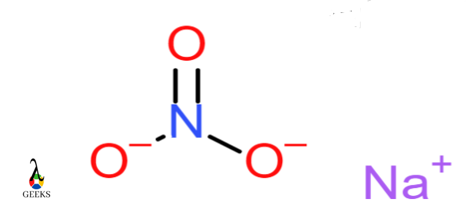
Sodium nitrate NaNO3
In Sodium nitrate, the Nitrogen atom forms a bond with three oxygen atoms. The bond formed between Nitrogen and oxygen is termed as a covalent bond. Nitrite ion NO3 has a negative charge while sodium ion Na has a positive charge. Na+ and NO3– ions form ionic bonds. Hence this is an example of a molecule having an ionic and covalent bond.
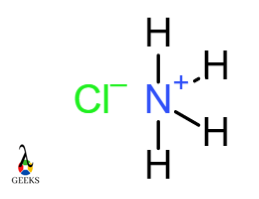
Ammonium chloride NH4Cl
In the Ammonium chloride molecule, the Nitrogen atom forms four covalent bonds with four different hydrogen atoms. NH4 acquires a positive charge. This ammonium ion combines with negatively charged chloride ion. NH4+ and Cl– ions form an ionic bond.
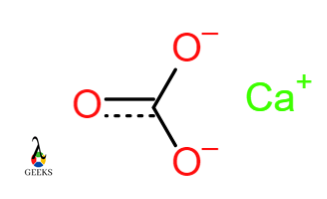
Calcium carbonate CaCO3
In Calcium carbonate, the covalent bonds form between the three Oxygen atoms and a Carbon atom. Carbonate ions acquire a negative charge and combine with positively charged Calcium metal ions. Ca+ and CO3– form an ionic bond.
Potassium cyanide KCN
In Potassium cyanide, the Carbon atom is combined with the Nitrogen atom covalently. The carbon atom and Nitrogen atom shares three electrons with each other. Cyanide CN is more electronegative than potassium. It acquires a negative charge. Potassium has a positive charge. K+ and CN– form an ionic bond.
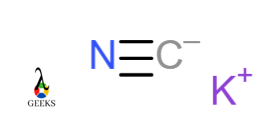
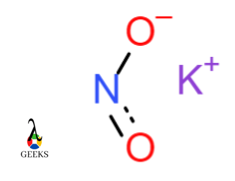
Potassium Nitrite KNO2
In the Potassium Nitrite molecule, the Nitrogen atom forms two covalent bonds with two different oxygen atoms. Positively charge potassium ion K+ and negatively charged nitrate ion NO2– forms an ionic bond. KNO2 has both ionic and covalent bonding.
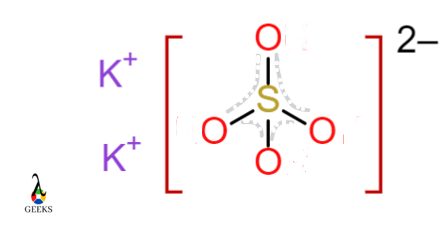
Potassium Sulphate K2SO4
In Potassium Sulphate, the Sulphur atom shares electrons with four Oxygen atoms. Sulphur forms an ionic bond with Potassium metal ions. Negatively charged SO4-2 ion and Positively charged K+2 ion forms bond.
Barium cyanide Ba(CN)2
In Barium cyanide, the Carbon atom and Nitrogen atom share three electrons with each other. Negatively charged cyanide ion forms an ionic bond with Positively charged Barium ion. CN– and Ba+2 form ionic bonds.
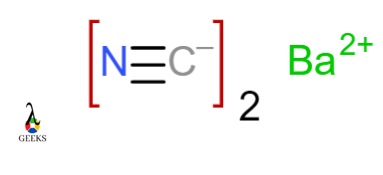
Read More On : 15 Coordinate Covalent Bond Examples: Detailed Insight And Facts
Facts
- Chemical bonding is consists of both ionic as well as covalent bonding.
- Both the bonds provide stability to the compounds.
- Some compounds are completely soluble in water and some of them are sparingly soluble in water.
- Most of these compounds are salts.
- They can conduct electricity in a molten state.
- In an aqueous solution, they separated to form cations and anions.
Frequently asked questions:
Question: How is KCN ionic and covalent?
Answer: KCN has both ionic and covalent bonds.
In Potassium cyanide, the Carbon atom is combined with the Nitrogen atom covalently. The carbon atom and Nitrogen atom shares three electrons with each other. Cyanide CN is more electronegative than potassium. It acquires a negative charge. Potassium has a positive charge. K+ and CN– form an ionic bond.
Question: NH4S has ionic and covalent bonds?
Answer: NH4S has both bonds.
In ammonium sulphide, nitrogen is combined with four hydrogen atoms covalently. The electronegativity difference leads to form an ionic bond between ammonium ion and sulphur. Hence NH4S not only have an ionic but also have covalent bonding.
Question: CaCO3 is ionic or covalent?
Answer: CaCO3 is considered an ionic compound.
In Calcium carbonate, the three oxygen atoms form three covalent bonds with a Carbon atom. Carbonate ions acquire a negative charge and combine with positively charged Calcium metal ions. Ca+ and CO3– form an ionic bond.
I am Smruti Bhosale. I am from Mumbai. I have Master’s degree in Inorganic chemistry from Guru Nanak Khalsa College, Mumbai. I always have a passion for writing and to inspire as many willing minds through my words. Chemistry is a subject that is used by everyone in their normal lives.
I want to explain the subject in the most understandable and simplest way possible. I am a creative, hard working person and passionate about learning new things. I like to read books.