This article will study some intracellular enzyme examples and learn facts about them.
Intracellular enzymes, also known as endoenzymes, are present inside cells and perform their functions within the cell. In most circumstances, an intracellular enzyme or an endoenzyme is an enzyme that attaches to a bond within the body of a massive molecule, usually a polymer. Here are some intracellular enzyme examples:
What is an intracellular enzyme?
Intracellular enzymes, also known as endoenzymes, are present inside cells and perform their functions within the cell. In most circumstances, an intracellular enzyme or an endoenzyme is an enzyme that attaches to a bond within the body of a massive molecule, usually a polymer.
The majority of enzymes are intracellular enzymes that activate only within the cell. It plays a very important role in all crucial activities in the body cell. Intracellular enzymes are involved in various activities, including photosynthesis(found within the chloroplast), cellular respiration, intracellular digestion, DNA replication, and so on.
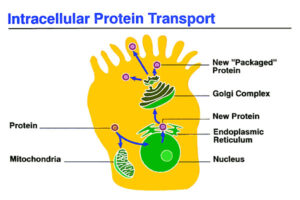
These can only be found in chloroplasts, cytoplasm, nuclei, mitochondria, and other cell components. Intracellular enzymes could be found in the cytoplasmic plasma or attached to cellular components. It also helps with glycolysis and the Krebs cycle process in the mitochondria.
Moreover, intracellular enzymes are amino acid-based protein molecules. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, these intracellular enzymes are present. Big polymers are broken down into specific smaller chains of monomers as their subunits by intracellular enzymes.
Intracellular Enzyme Structure
Intracellular enzymes are proteins made up of one or more polypeptide chains of amino acids joined collectively. Its primary structure refers to the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide chain. A polypeptide or protein results from this process of the primary structure. It influences the enzyme’s tri-dimensional structure and the active site’s form.
So, Intracellular enzymes are made up of amino acids joined together in a straight chain by amide or peptide binding. The DNA sequence of the relevant gene specifies the specific pattern of amino acids in the protein.
Intracellular enzymes are positioned, including protein, and bind with the corresponding enzymes in a linear line, depending on the structure of the enzymes. Some of the proteins are globular and organized in a tertiary structure. Secondary and quaternary structures also influence the arrangement of intracellular enzymes.
Intracellular Enzyme Examples
Here are some intracellular enzyme examples:
1. Aldolase
Aldolase is a cytoplasmic enzyme present inside the cell. It is essential in the metabolism of glucose and fructose. It involves the conversion of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate, which is a reversible process.

2. Hexokinase
Hexokinase is a cytoplasmic enzyme that serves in the process of glycolysis. Hexokinase enzymes are isoenzymes, which means they have the same function but have a distinct structure. Glucose is converted to glucose 6-phosphate by this enzyme. In glycolysis, hexokinase is a rate-limiting enzyme.
3. Phosphoglucose Isomerase
The cytosolic enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase catalyzes the reversible isomerization of Glucose-6-phosphate and F6P. Its approach is required for glycolysis and gluconeogenesis to occur. It also involves the pentose phosphate pathway and lipid, protein, and other molecule glycosylation.
4. Mutase
A mutase is an isomerase enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one point inside a molecule to the other. Coenzyme methylmalonyl Mutase is a cytoplasmic enzyme that converts R-methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in a reversible manner.
5. Pyruvate kinase
Pyruvate kinase is a cytoplasmic enzyme that regulates cell metabolism. It is by catalyzing the synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate and ADP to pyruvate and ATP during glycolysis.
6. Isomerase
Isomerase is a catalytic enzyme that converts its substrate into an isomeric form. It catalyzes the conversion of L-alanine to D-alanine, which is its isomeric form.
7. Enolase
Enolase is a glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the glycolytic process. ATP is made from the energy produced during glycolysis. As a result, it catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
8. Malate dehydrogenase
Gluconeogenesis is also facilitated by malate dehydrogenase. Pyruvate carboxylase reacts with pyruvate in the mitochondria to produce oxaloacetate, which is a citric acid cycle stage.
9. Glucose 6-phosphatase
The initial step in glucose metabolism is glucose-6 phosphate. It plays a crucial part in the liver’s metabolic activities. It serves as a metabolic crossroads for glycolysis. The final phase of the gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis processes is catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphatase.
10. PEP carboxykinase
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is a lyase enzyme involved in the gluconeogenesis metabolic pathway. Oxaloacetate is converted to carbon dioxide and phosphoenolpyruvate by this enzyme.
11. Glycogenin
Glycogenin serves as a primer, polymerizing the first few glucose molecules before taking over by other enzymes. To make an oligosaccharide primer, glycogenin is self-glucosylated.
12. ATPase
In cellular biology, the ATPase pump is essential. It catalyzes the formation of ADP from the hydrolysis of a phosphate bond in ATP.
13. RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase (enzymes that are responsible for the synthesis of RNA) is an enzyme that copies a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence during the transcription process.
14. DNA polymerase
DNA polymerase, or DNAP for short, is an enzyme that forms new copies of DNA in the form of nucleic acid molecules.
15. Ligase
Ligase is an enzyme that forms bonds with the help of ATP. It’s used to connect denatured restriction endonuclease segments in recombinant DNA cloning.
16. Arginase
Arginase catalyzes the hydrolysis of arginine to generate ornithine and urea in the mitochondria. It’s a crucial part of the urea cycle.
17. Glycosidase
Glycoside hydrolases are also known as glycosidases and glycosyl hydrolases in some instances. Glycosidases are enzymes that hydrolyze glycosidic bonds and are found both within and outside cells.
18. Aconitase
Aconitase is an intracellular enzyme that influences cellular metabolism by containing an iron-sulfur cluster susceptible to oxidation.
Also Read:
- Diffusion in cell
- Do animal cells have lysosomes
- Do prokaryotes have trna
- Cytoplasm structure
- Dna replication steps 2
- Do prokaryotic cells have a cell wall
- Do fungi have enzymes
- When does the cytoplasm divide
- Are bacteria decomposers
- Function of flagella
Hey! I’m Roshny Batu. I got a Bachelor of Science degree in Botany. In the domain of academic writing, I consider myself fortunate to be a part of the Lambdageeks family as an SME in Bio-Technology. Apart from that, I love designing interiors, painting, and mastering makeup artist skills.