The Lewis structure of IF4- (Iodine Tetrafluoride Ion) involves a central iodine atom bonded to four fluorine atoms with one lone pair, totaling 36 valence electrons (7 from iodine, 7 from each of the four fluorines, plus 1 additional for the negative charge). This results in a square pyramidal geometry. Each I-F bond is a single bond, with 2 shared electrons, fulfilling fluorine’s octet. The extra electron gives the ion a -1 charge, concentrated on the iodine.
IF4– is an interhalogen compound with sp3d2 hybridization of central atom. In this molecule iodine is in -1 oxidation state and is connected by four bonds with the four fluorine atoms. Actual structure of this molecule is square planar with a bond angle 900. Though the actual geometry of IF4– is octahedral.
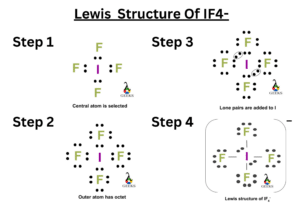
Let’s have a look on the following topics of the IF4– written below.
How to draw IF4– lewis structure?
Lewis structure, introduced by Gilbert. N. Lewis, is basically a very simplified structural representation in which valance shell electrons play a significant role.
- Finding out the valance electron: IF4– is consisting with two types of atoms, iodine and fluorine. Both are halogen compounds and both have same number of electrons (seven) in their respective valance shell.
- Determination of bonds and bonding electrons: Total four covalent bonds are present in IF4– molecule between one iodine atom and four fluorine compounds. Thus, total (4×2 =8) electrons are involved in bond formation.
- Finding out nonbonding electrons: In IF4–, both the atoms, iodine and fluorine have nonbonding electrons. Iodine has four nonbonding electrons or two lone pairs and fluorine has six nonbonding electrons or three pair of lone electrons.

IF4– lewis Structure Shape
Geometrical shape of any molecule can easily be determined from hybridization of central atom only if any lone pair and bond pair repulsion is absent. Shape of any molecular species is changed with the change of the hybridization of central atom.
| Hybridization of central atom | Structure |
| sp | Linear |
| sp2 | Trigonal planar |
| sp3 | Tetrahedral |
| sp3d | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| sp3d2 | Octahedral |
Otherwise, shape of the molecule is deviated from its actual geometrical structure. Thus, there are two structure determining parameter-
- Hybridization
- Repulsion
Basically, three types of repulsion are responsible in structure determination. They are-
- Lone pair- lone pair repulsion
- Lone pair-bond pair repulsion
- Bond pair-bond pair repulsion
The increasing order of the above repulsion is-
Lone pair -lone pair repulsion > Lone pair – bond pair repulsion > Bond pair- bond pair repulsion.
In IF4–, iodine has two lone pairs. But these lone pairs are not involved in lone pair -lone pair repulsion with each other. Not only that, these lone pairs are not also repelled by the bonding electrons of I-F covalent bond because of their position. These lone pair are the reason of deviation from its actual geometry.
In IF4–, central atom iodine is sp3d2 hybridized. Thus, the actual shape of the molecule should be octahedral. But due to the presence of the two lone pair of iodine, the observed shape of the molecule is square planar with two lone pair and four bond pair. Lone pairs are placed in the axial position to minimize the repulsion between them and bond pairs are planar with each other and placed in the equatorial position of the octahedral.
Due to planar structure, the bond angle of one I-F bond with another I-F bond is 900.

In the above image the actual geometry of IF4– is shown. For IF4–, the yellow circular area will be substituted by the lone pair of iodine and the white circular area will be replaced by four fluorine atoms.
IF4– Lewis Structure Formal Charge
Formal charge is mainly calculated in chemistry to identify the most stable lewis structure of the molecule. Formal charge calculation also helps to determine the overall charge of the molecule as well as the charge of the individual atom.
- Formal charge = Total number of valance electrons – number of electrons remain as nonbonded – (number of electrons involved in bond formation/2)
- Formal charge of iodine (I) = 7 – 4 – (8/2) = -1
- Formal charge of each of the fluorine atom (F) = 7 – 6 – (2/2) = 0
Valance shell electron configuration of iodine and fluorine are 5s2 5p5 and 2s2 2p5. Iodine is connected by 4 bonds with the four fluorine atoms. Thus, the bonding electrons of iodine is 8 (4×2 =8) and for fluorine 2 (1×2 =2)
From the calculation of formal charge, it is clear that iodine is negatively charged but fluorine atoms are neutral.
IF4– Lewis Structure Angle
Bond angle can also be determined from the hybridization of central atom. If repulsion (described in the point of shape of IF4–) are present then bond angle does not match with the hybridization.
In this molecule, central atom iodine is sp3d hybridized. Thus, the expected structure will be octahedral. But due to presence of lone pair, the actual shape of IF4– is square planar. All the I-F bonds are placed in one plane. So, IF4- attains a completely planar structure and the bond angle between (placed in the four corner of a square) two I-F bond is 900 and the angle between two lone pair (placed in two axial position) is 1800.

IF4– Lewis Structure Octet Rule
Octet rule is introduced in chemistry because it has a great significance. This rule states that any atom in a molecule should have the electron configuration in their respective which resembles the nearest noble gas valance shell configuration.
In general, iodine in IF4– dose not obey octet rule because after calculating the valance shell electrons and bonding electrons of iodine, the total number of electron becomes 12 (eight electrons from four covalent bonds and rest of the four electrons are from two lone pairs). This number of electrons does not match with the nearest noble gas electron configuration, Xenon (5s2 5p6).
But octet rule is satisfied in the case of fluorine. Each of the fluorine atom has seven electrons in its valance shell. After forming bond with iodine atom in IF4– each of the fluorine atom achieve eight electrons in their valance shell. This electron configuration matches with the nearest noble gas valance shell electron counting, which is Ne (2s2 2p5).
IF4– Lewis Structure Lone Pairs
There are two types of valance electrons an atom can have, bonding electrons and nonbonding electrons. Bonding electrons are involved in chemical bond formation. Nonbonding electrons cannot participate in chemical reaction.
- Nonbonded electron = Total number of valance electron – number of bonded electrons.
- Nonbonding electrons on Iodine (I) = 8 – 4 = 4 or 2 lone pair
- Nonbonding electrons on each of the fluorine atoms (F) = 7 – 1 = 6 or three lone pairs.
Total number of nonbonding electrons in IF4– = {4 + (6×4)} = 28 or 14 pair of lone electrons.
IF4– Valence Electrons
Valance electrons are none other than the electrons revolving in the valance shell or outer most shell in any atom. Any atom participates in different types of reaction due to this valance shell electron not the inner shell electrons because the nuclear attraction on the valance electrons is the least in any atom.
In IF4–, both the iodine and fluorine have seven electrons (ns2 np5). In IF4–, iodine is in -1 oxidation state.
Thus, total number of valance electrons in IF4– is {8 + (7×4)} = 36
IF4– Hybridization
Hybridization of central atom in any molecule is defined as the combining of two atomic orbitals and a new hybrid orbital is generated. These atomic orbitals must have almost similar energies, shapes and symmetry. Overlap between the orbitals will be very effective if these properties will be fulfilled.
In IF4–, iodine is sp3d2 hybridized with two lone pairs (on iodine) and four bond pairs (four I-F bonds). In this hybridization, one s orbital. Three p orbital and two d orbital take part. The s orbital and one p orbital contain the two lone pairs.

Iodine in this molecule is in -1 oxidation state thus valance electrons are shown is eight in IF4- hybridization. The hybridization predicts the structure of IF4– as octahedral but due to having two lone pairs in axial position, IF4– shows its actual structure, square planar.
Is IF4– Ionic or Covalent?
IF4– is definitely a covalent compound. Covalency is none other than the sharing of electron between two atoms. In this molecule four covalent bonds are present between iodine and fluorine atoms.
This are the following evidences behind its covalency-
- Sharing of valance electrons between iodine and fluorine. In ionic compounds, valance electrons are donated from less electronegative atoms
- Both iodine and fluorine are nonmetal atoms. To be an ionic compound atleast one atom must be metal
- Electronegativity difference between iodine and fluorine is not so high. This difference must be high to be an ionic compound.
In conclusion, it can be said that IF4– is a covalent compound.
Is IF4– stable?
IF4– is stable compound in which iodine exists as I–. It is an interhalogen compound having iodine and fluorine. Thus, it is less stable than any normal halogen compound like I2. The reason behind this less stability is the good overlap in I2 with respect to any inter halogen compound.
Please, click to know about SBr2 Lewis Structure and SbCl5 Lewis Structure.
Also Read:
- Cas lewis structure
- Ni3 lewis structure
- P2o5 lewis structure
- Xecl4 lewis structure
- Ph3 lewis structure
- Na3po4 lewis structure
- Co lewis structure
- Asf6 lewis structure
- N2h4 lewis structure
- Cos lewis structure

Hello,
I am Aditi Ray, a chemistry SME on this platform. I have completed graduation in Chemistry from the University of Calcutta and post graduation from Techno India University with a specialization in Inorganic Chemistry. I am very happy to be a part of the Lambdageeks family and I would like to explain the subject in a simplistic way.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-https://www.linkedin.com/in/aditi-ray-a7a946202