Covalent Oxides are binary compounds formed by the reaction of the oxygen with a non-metal which are held together by covalent-bonds. Some metalloids and transition metals also form covalent oxides. Here we will know about covalent oxide example
The examples covalent oxides formed by non-metals, transition metals, metalloids and alkaline earth metals are:
- Dinitrogen monoxide (N2O)
- Nitrogen monoxide (NO)
- Dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
- Dinitrogen tetraoxide (N2O4)
- Dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5)
- Nitrogen trioxide (NO3)
- Phosphorus(III) oxide (P4O6)
- Phosphorus(V) oxide (P4O10)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Carbon suboxide (C3O2)
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
- Chromium trioxide (CrO3)
- Manganese heptoxide (Mn2O)
- Silicon dioxide (SiO2)
- Diboron trioxide (B2O3)
- Arsenic pentoxide (As2O5)
- Antimony pentoxide (Sb2O5)
- Beryllium oxide (BeO)
1)Dinitrogen monoxide (N2O)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It is a colourless gas and has a pleasant odour. It is called as laughing gas .
2)Nitrogen monoxide (NO)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as colorless gas, colorless liquid and also as solid when pure. It is produced by oxidizing nitrogen
3)Dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It is a blue liquid. It exists only in liquid and solid state.
4)Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as a brown gas. The molecules of nitrogen dioxide are paramagnetic in nature.
5)Dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. It is diamagnetic in nature.
6)Dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as colorless solid.
7)Nitrogen trioxide (NO3)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as unstable radical. They are used in fertilizers.
8)Phosphorus(III) oxide (P4O6)
It is a covalent hexoxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as white crystalline solid or liquid and smells like garlic. Though the correct name is tetraphosphorus hexoxide but the name phosphorus trioxide is still used today.

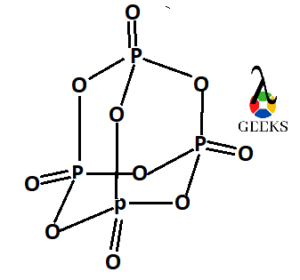
9)Phosphorus(V) oxide (P4O10)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It is a white flocculent powder. It is an acid anhydride of orthophosphoric acid.
10)Carbon monoxide (CO)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as a colorless, tasteless and odorless. It contains a triple bond between carbon and oxygen.
11)Carbon dioxide (CO2)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as colorless gas with no odor. It is a greenhouse gas.
12)Carbon suboxide (C3O2)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It is a colorless and foul smelling gas.This gas is produced by dehydrating malonic acid
13)Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a non-metal. It exists as gas at room temperature.It is a colorless gas. It has choking smell.
Read more about H2CO lewis structure
14)Chromium trioxide(CrO3)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a transition metal. It is a dark purple solid (when anhydrous) while bright orange (when wet).
15)Manganese heptoxide (Mn2O7)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a transition metal. It is a volatile liquid. It is a basic oxide and is highly reactive.
16)Silicon dioxide (SiO2)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a metalloid. It is also known as silica. It is a white or a colorless crystalline compound.
17)Diboron trioxide (B2O3)
It is a covalent oxide example formed by a metalloid. It is a colorless and a transparent solid. It is also known by the name Boric oxide.
18)Arsenic pentoxide (As2O5)
It is an example of a covalent oxide formed by a metalloid. It is a glassy, white solid. It is also known as Arsenic (V) oxide.
19)Antimony pentoxide (Sb2O5)
it is an example of a covalent oxide formed by a metalloid. It is a yellow powdered solid. It exists in the hydrated form.
20)Beryllium Oxide (BeO)
It is an example of covalent oxide formed by a alkaline earth metal. It is amphoteric in nature. It is the only element which forms a covalent oxide from group 2.
Conclusion:
Covalent oxides are formed by non-metals. Covalent oxides are acidic in nature. Covalent oxides react with base to form salt.When Covalent oxides react with water, they form acids.When covalent oxides react with bases, they form salts.

Hi…I am Sonali Jham. I have done my Post-Graduation in Chemistry and also completed B. Ed. I am a Teacher and a Dietician by profession.
My hobby is reading and painting.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn-