In this article we are going to see what is a coordinate covalent bond, its characteristics are facts along with some coordinate covalent bond examples in detail.
During the bond formation sharing of electron pair takes place by only one atom, it is called a coordinate covalent bond. Only one atom in a molecule shares both the electrons to form a bond. This type of bonding is seen in following examples.
- Ammonium boron trifluoride NH3→BF3
- Ammonium ion NH4+
- Formation of Hydronium ion H3O+
- Tetrafluroboron BF4–
- Formation of Aluminium chloride AlCl6
- Sulphur dioxide SO2
- Sulphur trioxide SO3
- Sulphuric acid H2SO4
- Nitrogen pentaoxide N2O5
- Nitromethane
- Hexammine cobalt(lll) chloride
- Hexaaquo cobalt (ll) chloride Co(H2O)6
- Tetracarbonyl nickel Ni(Co)4
- Hexaaquo Aluminium (lll)
- Ozone
The coordinate covalent bonds are also entitled as a dipolar bond or dative bond. In a coordinate covalent bonding, both electrons are shared by an individual atom, another one is the electron acceptor. Denoted by arrow ‘→’, pointing towards atom who accepts electrons.
A → B A gives electron pair or two electrons, termed as Donor atom
B accepts electron pair or electrons, termed as Acceptor atom.
The coordinate covalent bond differs from a covalent bond only in the way it is formed, once formed it is exactly like a covalent bond. The coordinate covalent bond may form when one of the combining atoms has an unused lone pair of electrons besides its completed octet.
Characteristics
- Electron pair or both the electrons of a bond given by only one atom.
- Also called dipolar bond or dative bond.
- Coordinate covalent bonds are shown as ‘→‘.
- Compounds containing this type of bonding are called coordinate covalent compounds.
- Sharing of electrons leads to the stabilization of all the atoms.
- The donor atom acquires a slight positive charge and a slight negative charge acquired by the acceptor atom.
Coordinate Covalent Bond Examples
Formation of Ammonium boron trifluoride NH3→BF3
In the NH3 molecule, Nitrogen has 5 electrons in its valence shell. N has a complete octet by the formation of three bonds with three hydrogen atoms. But it is still left with a pair of unused electrons. This lone pair of electrons may be donated to the B atom in BF3, which is electron-deficient forming a coordinate covalent bond. Due to this Boron atom also completes its octet.
Image credits : Wikipedia
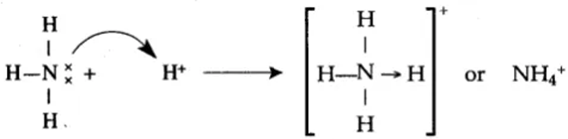
Formation of Ammonium ion NH4+
In the NH3 molecule, the Nitrogen atom has lone pair of electrons after completing its octet. This lone pair of electrons share with the H+ ion of HCl. The coordinate covalent bond formed between N and H, which leads to the formation of Ammonium ion NH4+.
Image Credits: Staticflickr
Formation of Hydronium ion H3O+
During the formation of hydronium ions, water molecules act as donor atoms. The oxygen atom present in H2O has lone pair of electrons which is used to form a coordinate covalent bond with the hydrogen atom present in HCl.
Image Credits: Brainkart
Formation of tetrafluroboron BF4–
Fluorine atoms share lone pair of electrons with Boron. Fluorine act as a donor atom and boron act as an acceptor. The formation of tetrafluroboron takes place by a coordinate covalent bond.

Image Credits: Redchemistry
Formation of Aluminium chloride AlCl6
Aluminium has three electrons in its valence shell, hence it forms three bonds with Chlorine. Chlorine has 7 electrons from which one is used for bond formation rest act as lone pair. Chlorine share one lone pair of electrons with another aluminium atom forming a coordinate covalent bond.

Image Credits: Redchemistry
Sulphur dioxide SO2
In sulphur dioxide molecule sulphur has 6 valence electrons hence act as donor atom and oxygen acts as an acceptor. Sulphur form a double bond with one of the oxygen and shares one lone pair with other oxygen.
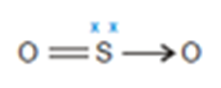
Image Credits: Redchemistry
Sulphur trioxide SO3
After the formation of a double bond with oxygen, Sulphur shares two lone pairs of electrons with two oxygen atoms by a coordinate covalent bond.
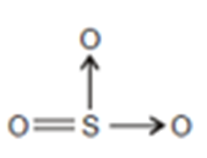
Image Credits: Redchemistry
Sulphuric acid H2SO4
Sulphur present in sulphuric acid forms two coordinate covalent bonds with two different oxygen atoms. Sulphur has two lone pairs.

Image Credits: gstatic.com
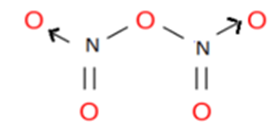
Nitrogen pentaoxide N2O5
Nitrogen has 5 electrons in its valence shell, out of which three electrons are used to form one single and one double bond with oxygen. The remaining electrons act as lone pairs. This lone pair was utilized to form a coordinate covalent bond with the oxygen atom.
Image Credits: encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com
Nitromethane
In nitromethane, Nitrogen atoms form coordinate covalent bonds with oxygen atoms. Nitrogen forms a double bond with one oxygen and a single bond with a carbon atom of the methyl group and completes its octet.
Image Credits: Brainkart
Hexammine Cobalt (lll) chloride Co(NH3)6Cl3
In Hexammine Cobalt (lll) chloride complex, Six Nitrogen atoms of the ligand, Ammonia NH3 shares lone pair of electrons with central metal Cobalt.
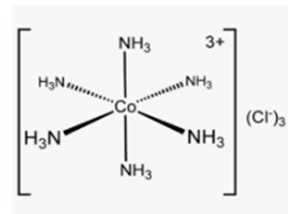
Image Credits: Wikipedia
Hexaaquo cobalt (ll) chloride Co(H2O)6Cl2
In Hexaaquo cobalt (ll) chloride, Six water H2O molecules are the ligands, act as donor atoms. Central metal atom Cobalt act as an acceptor atom. The oxygen atom of H2O has lone pair of electrons that share with Cobalt forming a coordinate covalent bond.

Image Credits: encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com
Tetracarbonyl Nickel Ni(CO)4
In Tetracarbonyl Nickel, Ni acts as acceptor, and CO acts as a donor atom. Four oxygen atoms of ligand share lone pair with Nickel forming a coordinate covalent bond.

Image Credits: Wikimedia
Hexaaquo Aluminium (lll)
In this complex, the oxygen atoms of H2O shares lone pair with the central metal atom Aluminium.
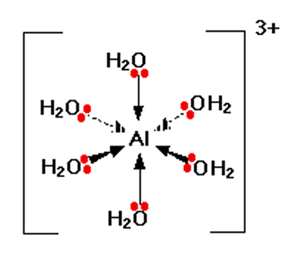
Image Credits: Chemguide
Ozone
The oxygen atom has 6 electrons in its valence shell. Two electrons are utilized to form a double bond with one oxygen and one lone pair is used to form a coordinate covalent bond with another oxygen.

Image Credits: Redchemistry
Read on :SN2 Examples: Detailed Insights And Facts
Frequently asked questions:
1)Question: What is meant by a dative bond?
Answer: Dative bond is defined as
During the bond formation sharing of electron pair takes place by only one atom, it is called a coordinate covalent bond. Also called dipolar bond or dative bond.
2)Question: What are the differences between coordinate and covalent bonds?
Answer: Difference between a coordinate and covalent bond
| Coordinate bond | Covalent bond |
| Only one atom in a molecule shares both the electrons to form a bond. | Both the atoms of the molecule share electrons to form a bond. |
| A minimum of one lone pair of electrons is required. | It does not require any lone pair of electrons. |
| Should not have unpair electrons | Should have unpair electrons |
| Empty orbital should be present in the acceptor atom. | Empty orbital does not require. |
| It is a polar bond. | It may be polar or non-polar depending on atoms forming a bond. |
| Represented by arrow → | Represented by a dash – |
3) Question: Is the coordinate bond directional?
Answer: Coordinate bond is directional,
The coordinate bond form when both the electrons are shared by only one atom, the donor atom hence coordinate bond is directional. Also represented by an arrow → pointing towards the acceptor atom.
Also Read:
- Monomer examples
- Displacement reaction examples
- Ecosyetm examples
- Purple sulphur bacteria examples
- Sn1 examples detailed insights and facts
- Kinetic friction examples
- Neutralization reaction examples
- Interference of sound examples
- Chemical change examples
- Physical change examples
I am Smruti Bhosale. I am from Mumbai. I have Master’s degree in Inorganic chemistry from Guru Nanak Khalsa College, Mumbai. I always have a passion for writing and to inspire as many willing minds through my words. Chemistry is a subject that is used by everyone in their normal lives.
I want to explain the subject in the most understandable and simplest way possible. I am a creative, hard working person and passionate about learning new things. I like to read books.