In this article, we are going to see what is combustion reaction, combustion examples in detail.
- Reaction of Methane and Oxygen
- Reaction of Ethane and Oxygen
- Reaction of Propane and Oxygen
- Reaction of Butane and Oxygen
- Reaction of Methyl alcohol and Oxygen
- Reaction of Naphthalene and Oxygen
Combustion reaction
The combustion reaction is defined as an exothermic chemical reaction that occurs between hydrocarbons (compounds having carbon and hydrogen) and atmospheric oxygen and results in the formation of carbon dioxide and a water molecule. It is also known as burning. General reaction:
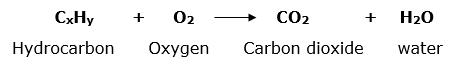
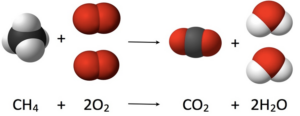
Image Credits : wikipedia
Also Read On : Is O2 a triple bond: Why, How, Characteristics and Detailed Facts
Combustion examples :
Reaction of Methane and Oxygen
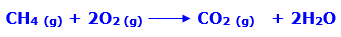
Methane is a most simple form of alkane that is hydrocarbons. it is found in natural gas. It has a burning property hence used as fuel. Methane burns in a blue flame in presence of air. When methane reacts with oxygen it results in the formation of carbon dioxide and water. As shown in above figure.
Reaction of Ethane and Oxygen
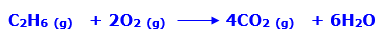
Ethane is a simple form of alkane containing two carbon atoms and six hydrogens that are hydrocarbons. It has a burning property hence used as a gaseous fuel. Ethane burns in a blue flame in presence of air. When ethane reacts with oxygen it results in the formation of four molecules carbon dioxide and six water molecules.
Reaction of Propane and Oxygen
Propane is a simple form of alkane containing three carbon atoms and seven hydrogens that are hydrocarbons. It has a burning property hence used as a gaseous fuel. It is used in fireplaces, some types of cookstoves and gas grills. Propane burns in a blue flame in presence of air. When propane reacts with oxygen it results in the formation of six molecules of carbon dioxide and seven water molecules.

Reaction of Butane and Oxygen
Butane is a simple form of alkane containing four carbon atoms and ten hydrogens that are hydrocarbons. It has a burning property hence used as fuel. It is usually found in a lighter. Butane burns in a blue flame in presence of air. When butane reacts with oxygen it results in the formation of eight molecules of carbon dioxide and ten water molecules.

Reaction of Methyl alcohol and Oxygen
Methyl alcohol also termed as wood alcohol, is a simple form of alcohol-containing one carbon atom, one oxygen and four hydrogens that are hydrocarbons. Methyl alcohol burns in a pale blue flame in presence of air. When methyl alcohol reacts with oxygen it results in the formation of two molecules of carbon dioxide and four water molecules.

Reaction of Naphthalene and Oxygen
Naphthalene, is a simple form of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, containing ten carbon atoms, eight hydrogens that are hydrocarbons. Naphthalene burns in a yellow flame in presence of air. When naphthalene reacts with oxygen it results in the formation of ten molecules of carbon dioxide and four water molecules.

Also Read On: N2 polar or nonpolar: Why, How, Characteristics, And Detailed Facts
Frequently Asked Questions:
Question : Why oxygen is needed in combustion?
Answer : The oxygen is required for the combustion because,
Oxygen reacts with substances (fuel or combustible materials) by releasing a high amount of energy. This energy is in the form of light and heat or fire. In the combustion reaction oxygen acts as a reactant and supports burning. Hence oxygen is required for the combustion reaction.
Question : What is the difference between complete and incomplete combustion?
Answer : The difference between complete and incomplete combustion are,
| Complete combustion | Incomplete combustion |
| The hydrocarbons burns in presence of oxygen or air produce only carbon dioxide and water. | The hydrocarbons burns in presence of oxygen or air produce not only carbon dioxide and water. |
| This does not form carbon mono oxide, soot or carbon. | This results in the formation of carbon mono oxide, soot or carbon with carbon dioxide. |
| Also known as Clean combustion. | Also known as Dirty combustion. |
| For example, the burning of wax in a candle | For example, the burning of coal. |
Question : What are the types of combustion?
Answer : Combustion reactions are classified as,
Complete combustion – The hydrocarbons burned in presence of oxygen or air produce only carbon dioxide and water.
Incomplete combustion – The hydrocarbons burns in presence of oxygen or air produce not only carbon dioxide and water.
Smoldering reaction – It is a type of incomplete reaction, flame-less and slow.
Spontaneous reaction- It is shown by self-heating substances.
Rapid reaction- It is the fast reaction with the evolution of a large amount of light and heat energy.
Turbulent reaction – It shows a turbulent flame.
Micro combustion- Occur in a very small amount.
Question : What is a combustion reaction?
Answer : The combustion reaction is,
The combustion reaction is defined as an exothermic chemical reaction that occurs between hydrocarbons (compounds having carbon and hydrogen) and atmospheric oxygen and results in the formation of carbon dioxide and a water molecule. It is also known as burning.
Also Read On : CH2CL2 Lewis Structure Why,How,When And Detailed Facts
I am Smruti Bhosale. I am from Mumbai. I have Master’s degree in Inorganic chemistry from Guru Nanak Khalsa College, Mumbai. I always have a passion for writing and to inspire as many willing minds through my words. Chemistry is a subject that is used by everyone in their normal lives.
I want to explain the subject in the most understandable and simplest way possible. I am a creative, hard working person and passionate about learning new things. I like to read books.