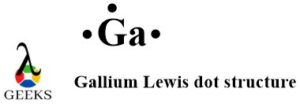Gallium (Ga), with an atomic number of 31, has three valence electrons. Its Lewis dot structure represents these electrons as three dots surrounding the symbol ‘Ga’. Gallium’s electron configuration is [Ar]3d¹⁰4s²4p¹, indicating its tendency to lose three electrons or share them in covalent bonds. The first ionization energy of gallium is 578.8 kJ/mol, reflecting its moderate reactivity. Gallium’s ability to form +3 oxidation state and covalent compounds, like GaAs in semiconductors, is crucial for its applications in electronics. Its bonding versatility and melting point near room temperature (29.76°C) are key to its unique properties.
Gallium Lewis dot structure is similar to many other metal Lewis dot structures. It belongs to group 13 (Aluminum family) of the periodic table. So it has 3 electrons in its valence shell. Being a monoatomic element gallium Lewis dot structure representation is simply the presence of 3 electrons around the gallium (Ga) symbol.
Discussing more gallium element than it is a soft silvery metal discovered by French chemist Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran. Its appearance is silvery blue and it is malleable and ductile. Too much pressure or force on gallium can lead to brittle fractures like pieces of glass. It has a low melting point and can tolerate high temperatures as well.
Gallium does not exist in its elemental form, but it can be obtained by smelting. In the earth’s crust, its presence is very nominal in the reserves of bauxite and zinc ores. The existence of these ores is even less than 1%. So mining and extraction from ores is the only way to obtain gallium.
Though the existence of Gallium is negligible, its applications are spread widely. The semiconductor industry is dominated by gallium metal. High purity gallium is usually used semiconductor industry. It is used to make and develop integrated circuits, ultra-high-speed logic chips, and low-noise microwave preamplifiers which are used in smartphone production. It also has uses in the optoelectronic industry contributing to the development of laser diodes and LEDs.
Though Gallium metal is not linked to the human body directly it has a role to play in the pharmaceutical and biomedical industry. Many salts of gallium have anti-cancer properties and can work similarly to ironworks for the human body. Its trace elements are also spotted in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans and have been used as a tracer for iron and aluminum reserves in the sea.
There are many properties associated with gallium that help in easy understanding and reliable structural development of gallium Lewis dot structure. The two important ones are:
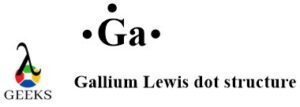
· Valence electrons of gallium Lewis dot structure
· Electronic configuration of gallium Lewis dot structure
Valence electrons of gallium Lewis dot structure
The electrons present in the outermost shell of any element are called valence electrons. These electrons participate in every kind of chemical reaction and chemical bond formation by gaining, losing, and sharing electrons. They are responsible for determining the gallium Lewis dot structure.
Elaborating on gallium Lewis dot structure, then the atomic number of gallium is 31 and it belongs to group 13 of the periodic table. For determining the valence electrons of the gallium Lewis dot structure, it is important to look for the number of protons and electrons present in it. The nucleus is the center of an atom and protons and neutrons are situated in it. The atomic number denotes the number of protons and protons are always equal to the number of electrons. This means that there are 31 electrons in the gallium Lewis dot structure.
Now we can look for the number of valence electrons by arranging the electrons in the shell according to Bohr’s principle. So in gallium Lewis dot structure
1st Shell (K) = 2
2nd Shell (L) = 8
3rd Shell (M) = 18
4th Shell (N) = 3
thereby clearly depicting that there are 3 electrons in the gallium Lewis dot structure.

Electronic configuration of gallium Lewis dot structure
Electronic configuration can be defined as the arrangement and distribution of electrons in their atomic orbital. It not only informs about the number of electrons present in the shell but also educates about the exact positioning of each electron.
Coming back to the gallium Lewis dot structure then its atomic number is 31 which implies the presence of 31 electrons. Its electronic configuration can be written according to orbital energy distribution as: 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p1.
Gallium Lewis dot structure can be formed with several other elements particularly non-metals which lead to the formation of stable compounds. Some of these are:
· Gallium Lewis dot structure with nitrogen (GaN)
· Gallium Lewis dot structure with oxygen (Ga2O3)
· Gallium Lewis dot structure with sulfur (Ga2S3)
Gallium Lewis dot structure with nitrogen (GaN)
Gallium (Atomic number = 31 and electronic configuration = 2,8,18,3) belongs to group 13 of the periodic table with 3 valence electrons. On the other hand nitrogen (Atomic number = 7 and electronic configuration = 2,5) belongs to group 15 of the periodic table with 5 valence electrons. So to acquire the octet stability gallium will lose 3 electrons which will be gained by nitrogen due to its high electronegativity. This leads to Ga3+ ion and N3- ion and the formation of the ionic compound GaN.

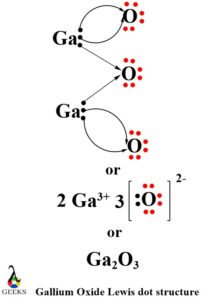
Gallium Lewis dot structure with oxygen (Ga2O3)
Gallium belongs to group 13 of the periodic table with 3 valence electrons. Oxygen (Atomic number = 8 and electronic configuration = 2,6) belongs to group 16 of the periodic table with 6 valence electrons. To achieve the octet stability criteria 2 gallium atoms will donate their 3 electrons each to 3 oxygen atoms. The 3 oxygen atoms due to their high electron attracting ability will accept those electrons resulting in Ga3+ cation and O2- anion. This results in the formation of the best-suited gallium Lewis dot structure with the oxygen atom.
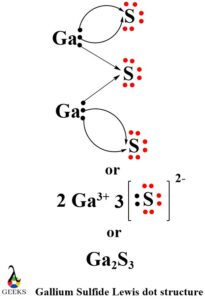
Gallium Lewis dot structure with sulfur (Ga2S3)
Gallium Lewis dot structure with sulfur is analogous to the gallium Lewis dot structure with oxygen. This is because sulfur belongs to the oxygen family. Sulfur (Atomic number = 16 and electronic configuration = 2,8,6) belongs to group 16 of the periodic table with 6 valence electrons. To fulfill the octet stability criteria 2 gallium atoms will donate their 3 electrons to 3 sulfur atoms. Being electronegative sulfur will gain those electrons thereby forming an ionic bond and ionic compound gallium sulfide.
Gallium Lewis dot structure (Related FAQs)
Why gallium was designated as eka-aluminum?
According to Mendeleev’s periodic table, every element is related to each other chemically. Due to this notion, there were empty spaces in the periodic table. The space with the number 31 was still empty but he knew that such an element exist but was not discovered yet. He even went ahead and predicted the properties of the not yet discovered element and called it eka-aluminum because its properties were similar to the metal. So that’s why gallium was earlier known as eka-aluminum.
How many isotopes of gallium are present in nature?
Gallium has many isotopes. It has as many as 25 isotopes. But out of those only two isotopes exist in stable form- Gallium 69 and Gallium 71. Radioactive isotopes of gallium also exist out of which Gallium 67 is the most famous one.