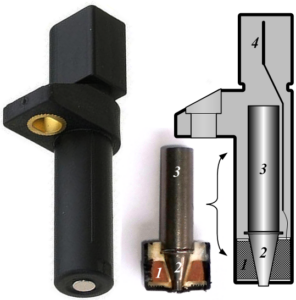
Crankshaft Position Sensor as the name indicates it is a type of sensing device. In this article we will discuss about Crankshaft Position Sensor Diagram.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Diagram has importance in both petrol and diesel engines because Crankshaft Position Sensor is an electronic device most widely used to detect ignition timing and engine RPM. This diagram helps in proper installation of the sensor.
To maintain the efficiency of a car’s engine it is necessary to maintain a suggested speed by all the internal parts. To make it possible the crankshaft position sensor must senses the precise position of the crankshaft. In automobile engineering Crankshaft Position Sensor is commonly abbreviated as CKP.
What is a Crankshaft Position Sensor?
The main function of a crankshaft position sensor is to investigate the position or rotational speed of the crankshaft in both petrol and diesel engines.
Crankshaft Position Sensors perform multiple activities, mainly it monitors the exact movement of the crankshaft and in turn we get other related important parameters like engine speed and ignition and fuel injection timing. Engine speed in RPM can also measured by using these sensors.
Depending on model, year of manufacturing and making the crankshaft position sensor wiring diagram are quite different from each other. Generally the manufacturer of these sensors decide the wiring diagram as per the requirement and demand in the market.
For different brands of Position Sensors the color of wires are different and color codes also vary as per the brands. Before wiring a specific make and model of sensor one has to check the car’s owner manual.

Crankshaft Position Sensor Working
CKP is placed very near to the reluctor ring so that the teeth attached to it rotates close to the sensor tip. There is a gap maintained in between the reluctor teeth to give the ECU a reference point to the crankshaft rotation or position.
With the rotation of the crankshaft, a pulsed voltage signal is produced by the sensor, each pulse is corresponding to the teeth of the reluctor ring.
Using these signals the engine control unit to determine the exact timing of fuel injection or spark ignition and in which cylinder. If anyone of the cylinders misfires, the signal from the cylinder also indicates it. Whenever the signal from the sensor is missing the control unit stops spark and fuel injector won’t operate.

2 Wire Crank Sensor Wiring Diagram
The two-wire crankshaft position sensor consists of a Signal Wire, a Ground Wire and an ECU.
In 2 wire crank sensor, the function of the signal wire to send the voltage from position sensor to the ECU(Electronic Control Unit). The ground wire is required to complete the electric circuit. Both of these wires are connected to ECU.
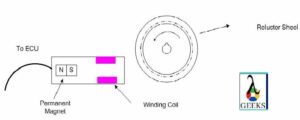
2 wire crank sensor is an inductive type sensor which consists of sensor magnet and winding coil and a toothed wheel. As the reluctor ring or the toothed wheel comes closer to the crank sensor, the magnetic field fluctuates as a result voltage is produced in the wiring coil. This voltage or signal is sent to the ECU which will calculate the position of the crankshaft.
Inductive type position sensors does not require any external voltage source wire to energize it. When any item comes near to it produces the voltage itself. The Crankshaft Position Sensor Diagram for 2Wire is given below:
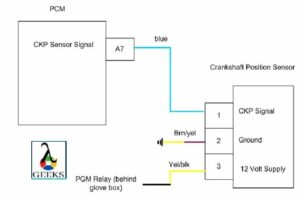
Crankshaft Position Sensor diagrams are different depending on the type and model of the sensors.
3 Wire Crank Sensor Wiring Diagram
3 wire crank sensor mainly consists of 3 wires, reference voltage, signal and ground wire. This type of sensors are classified as hall effect type sensor.
A 3 wire crank sensor has a magnet and a steel type material like germanium and a transistor. As soon as the toothed wheel comes near the sensor, the magnetic flux of the magnet in the sensor changes and as a result voltage is produced. This voltage is ampliphied by the transistor and sent to the car computer.
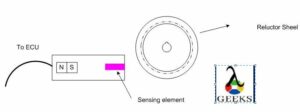
Additional external voltage is required in 3 wire crank sensor. This type of sensor has an integrated circuit and an outside power source is necessary to work which amplifies the voltage.
That’s why it has three wires, earth, voltage, and a signal wire. The Crankshaft Position Sensor Diagram for 3 Wire is given below:

Crankshaft Motion
A crankshaft plays an important role inside an IC Engine by transforming the reciprocating movement of the piston into rotary motion.
In a reciprocating engine, using a connecting rod piston and crankshaft are connected so that reciprocating motion of the piston can be delivered to the crankshaft. After receiving this reciprocating motion from piston via connecting rod, crankshaft changes it into rotary motion.
Crankshaft is essential to get rotary motion for the flywheel which ultimately responsible for moving the car wheels.