Bioindicators are the organisms used to biomonitoring and assess Earth’s living system changes by anthropogenic activities. It may be microbial biomass, fungi, actinomycetes, lichens, and the population of earthworms, nematodes, termites, and ants.
Let us see some bioindicator examples:
- Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- Euglena gracilaris
- Chlorella vulgaris
- Vogesella indigofera
- Hyloconium splendens
- Paramoecium Aurelia
- Lobaria pulmonaria
- Wolfia globosa
- Cyclops
- Benthos/Macroinvertebrate
- Fungi
- Frog and Toads
- Earthworm
- Nematodes
- Salmon
- Ants
- Pteridophyta
Bioindicators are of four types depending upon the indication of behavioural and functional changes in their surroundings by their activity, growth and behaviour.
- Pollution bioindicators
- Ecological bioindicators
- Biodiversity bioindicator
- Environmental bioindicator
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
This is prokaryotic, unicellular green algae. They show aquatic contamination of heavy metals. As they offer the metal toxicity of cadmium and copper. They cannot grow above 0.3µM. They inhibit the function of nitrate reductase (NR), nitrite reductase (NiR) and glutamate synthase required for the cycling of nitrate and sulphate ions.
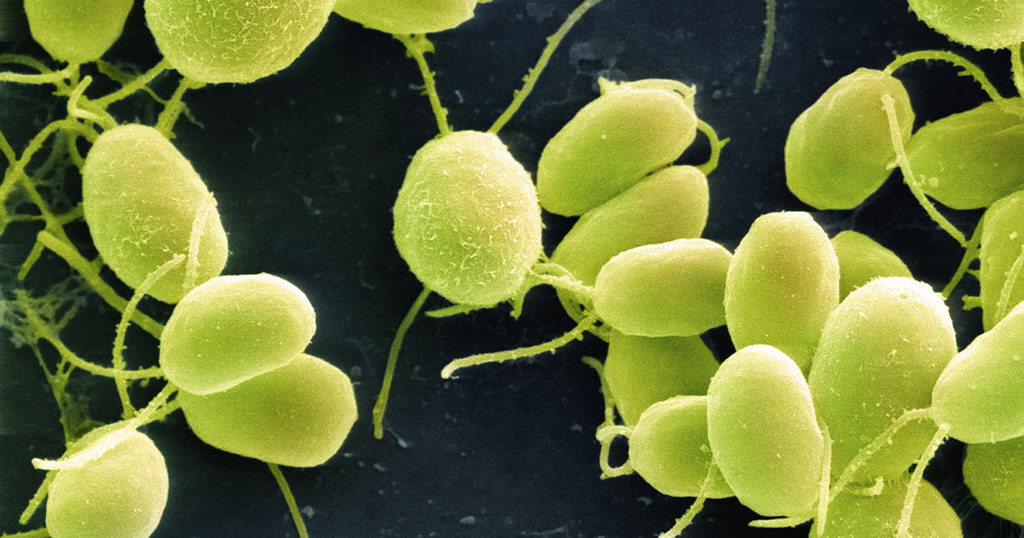
Image credit: Flickr
Vogesella indigofera
It is strictly aerobic, non-pathogenic, gram-negative, bioluminescent bacteria found in fresh water. As they release a blue pigment which shows the toxic level of some specific metallic ions.
Pigmentation is blocked due to the toxicity of hexavalent chromium ions, as it gets reduced by almost 50%. The Cr6 + threshold concentration of inhibition of pigment production was 200-300 μg ml-1.
Euglena gracilaris
They show heavy metal contamination in water as they revealed the genotoxic effect of organic pollutants in Taihu lake of China,2008. They affect the activities of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase and peroxidase by bond breakage in DNA and manipulating the synthesis of proteins.
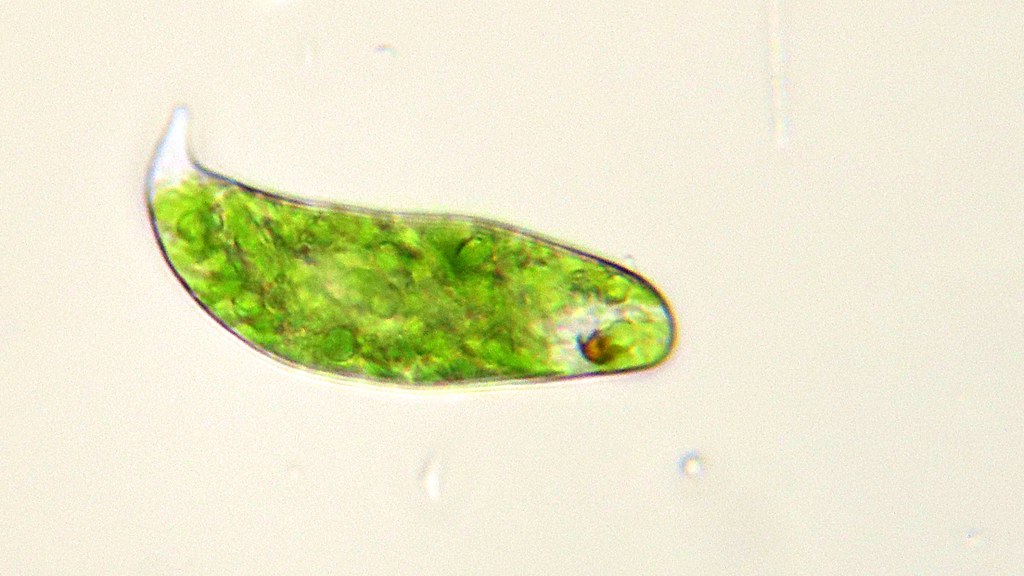
Image credit: Flickr
Chlorella vulgaris
It is also one of the bioindicator examples most intensively studied microalgae used for waste treatment. They start releasing stress proteins encounters with contamination of two pesticides in water bodies i.e. 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and Atrazine.

Image credit: Wikimedia commons
Hyloconium splendens
They show the toxicity of metal pollutants in the terrestrial ecosystem. As they are bryophytes and have no true root system for absorption of nutrients so they depend on the composition of elements present in the air.
They show some physiological changes above a few heavy metals like lead, manganese, copper, zinc, nickel etc. Unit varies for different metals.
Paramoecium aurelia
They show a great effect on respiratory metabolism and oxidative stress by cellular disruption and apoptosis by increasing the level of benzene and organic-phosphorous compounds in an aquatic ecosystem.

Image credit: Flickr
Lobaria pulmonaria
As this is the lichen present in tree trunks and access the air pollutant in the surrounding. They are very sensitive to sulphur dioxide and sulphur-containing organic compounds. They are also known as lung-lichen as they cannot live in heavy pollutants.
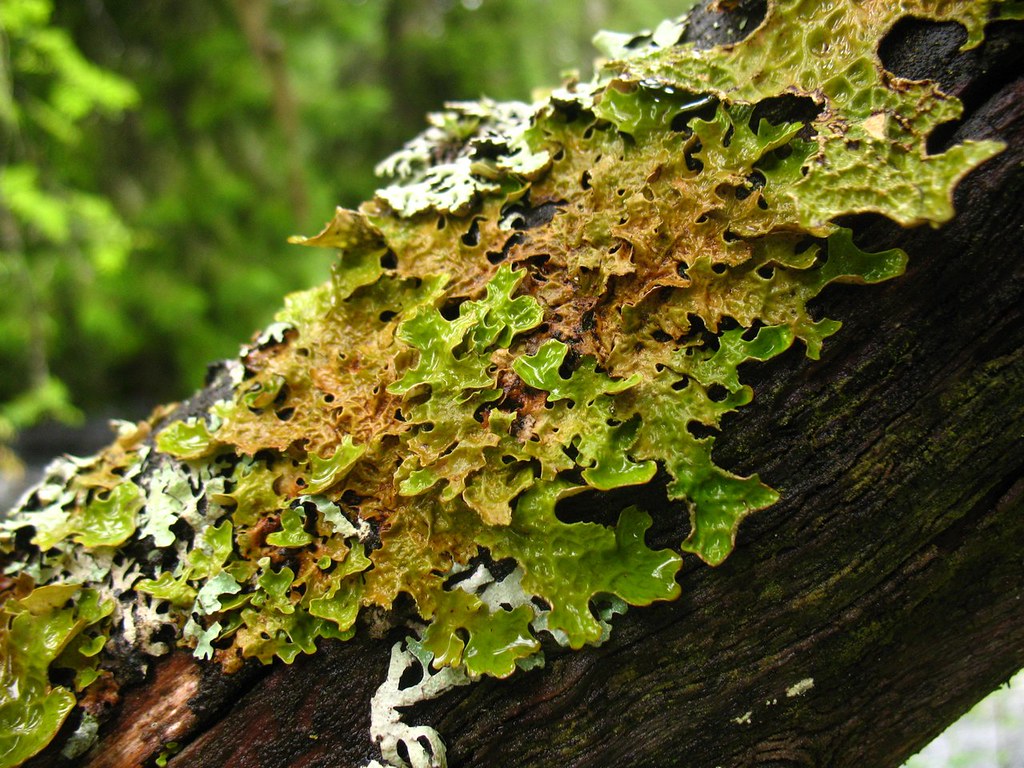

Image credit: Flickr
Wolfia globosa
This is the smallest angiospermic plant. They show the phytotoxicity of cadmium and chromium ions. This decreases biomass productivity and chlorophyll content.
Cyclops
These organisms are indicating water quality or eutrophication in a river basin. They show some behavioural changes due to the accumulation of cadmium in their cells, as they react towards the excess amount of cadmium in water.
Benthos
Macroinvertebrates of the benthic zone include some crustaceans, Crayfish, a few echinoderms and molluscs. The heavy metals Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn affect the growth and life cycle of members of the benthic zone.

Image credit: Flickr
Fungi
Ecto-mycorrhizae are the highly sensitive fungal bioindicators of air pollution. They show the heavy metal toxicity present in soil and also influence the soil biota. Heavy metals are nickel, cadmium, manganese is sometimes responsible for phytotoxicity.
Frogs and Toads
They are most sensitive to some pollutants like fungicides, herbicides, and pesticides. As they show reactivity against nitrate, sulphate, calcium, zinc etc. These may alter the function of some enzymes like cholinesterases, glutathione-S-transferases and their respective proteins.
Earthworms
This organism acts as an ecological indicator as it helps to recognise the metal pollution monitoring in the soil ecosystem. The number of individuals present resembles the soil health and accumulation of chemicals in a particular area. The concentration of Zn, Fe, Pb and Mn affects the growth of earthworms.

Image credit: Pixabay
Nematodes
They indicate the heavy metal toxication in soil ecology. Abundance in soil shows the good quality of the soil. Increased chromium concentration in sediments was found to increase the prevalence of four nematode species. They get their nutrient from the detrimental organism.
Salmon
Chinook salmon is an aquatic species that shows the contamination of water or eutrophication due to the accumulation of chemicals in their cells and indicates by some behavioural changes. Fishes also act as a bioindicator for aquatic pollution.
Ants
They are everywhere, great variety of insects that dominate many ecosystems with numbers and biomass. Reflecting the loss of diversity, changes in species composition, and changes in interspecific and intraspecific interactions. They are involved in soil decomposition, nutrient cycling, seed dispersal etc.

Image credit: Wikimedia commons
Pteridophytes
Pteridophytes are a positive indicator of forest integrity because they show a typical plant response to the harmful environmental conditions of the city. They reflect climate change and the global biodiversity crisis are often overlooked due to the relatively small size and lack of vibrant colours of these species.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the bioindicator from different classes of organisms like some algae, plants, zooplankton, phytoplankton and fishes etc. The purpose of their existence is to indicate the contamination and pollution in the different ecosystems and contribute to the conservation of respective biota.
Also Read:
- Inhibitor enzyme example
- Protein synthesis in endoplasmic reticulum
- Insectivorous plant example
- Prism
- Gamete
- Anticodon example
- Purine fundamental structure
- Competitive inhibition examples
- Examples of dicot
- Do bacteria have enzymes

Hi….I am Anushree Verma, I have completed my Master’s in Biotechnology. I am a very confident, dedicated and enthusiastic author from the biotechnology field. I have a good understanding of life sciences and great command over communication skills. I thrive to learn new things every day. I would like to thank this esteemed organization for giving me such a great opportunity.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/in/anushree-verma-066ba7153